A legislative coup occurs when a government body unlawfully seizes power by bypassing constitutional processes, undermining democratic principles and the rule of law. Such actions often lead to political instability and erosion of public trust in institutions. Discover how legislative coups impact governance and what signs to watch for in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
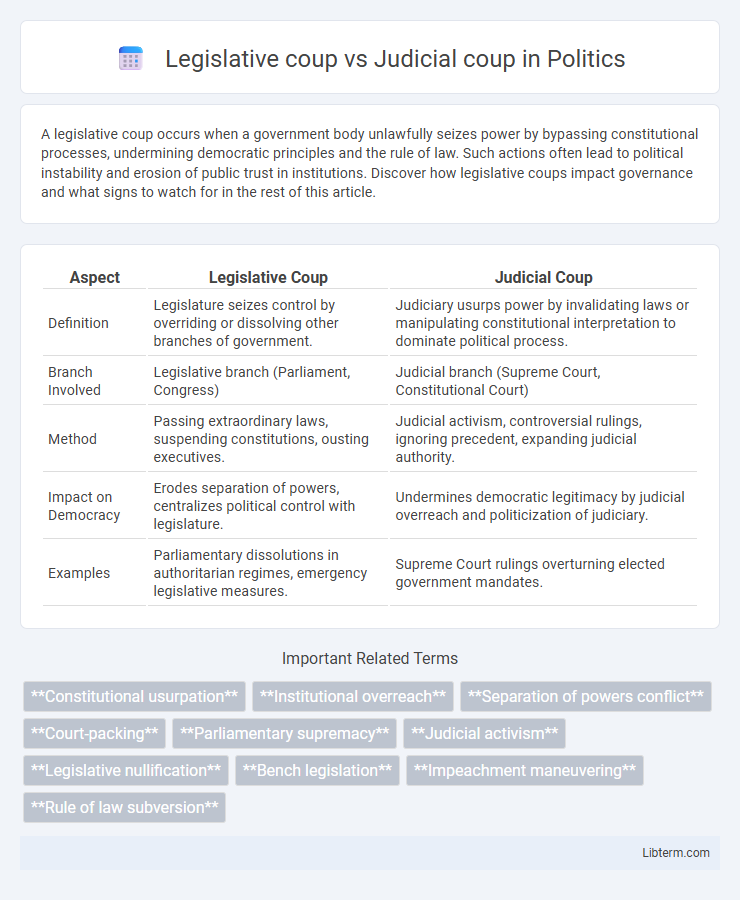
| Aspect | Legislative Coup | Judicial Coup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legislature seizes control by overriding or dissolving other branches of government. | Judiciary usurps power by invalidating laws or manipulating constitutional interpretation to dominate political process. |
| Branch Involved | Legislative branch (Parliament, Congress) | Judicial branch (Supreme Court, Constitutional Court) |
| Method | Passing extraordinary laws, suspending constitutions, ousting executives. | Judicial activism, controversial rulings, ignoring precedent, expanding judicial authority. |
| Impact on Democracy | Erodes separation of powers, centralizes political control with legislature. | Undermines democratic legitimacy by judicial overreach and politicization of judiciary. |
| Examples | Parliamentary dissolutions in authoritarian regimes, emergency legislative measures. | Supreme Court rulings overturning elected government mandates. |
Defining Legislative Coup and Judicial Coup
A legislative coup occurs when a legislature unlawfully seizes power by bypassing constitutional procedures, often dissolving other branches of government or altering the legal framework to entrench its authority. In contrast, a judicial coup involves a judiciary branch usurping control, typically by invalidating elected governments' actions or extending its influence beyond constitutional mandates to reshape political power. Both coups undermine democratic principles by disrupting the balance of powers, but the key distinction lies in whether the legislature or the judiciary orchestrates the illegitimate takeover.
Historical Context: Notable Examples Worldwide
The 1973 Chilean military coup led by General Pinochet illustrates a legislative coup where the existing legislature was dissolved, signaling a direct overthrow of constitutional order. In contrast, the 2017 Turkish constitutional changes exemplify a judicial coup, where the judiciary was leveraged to undermine checks and balances, consolidating executive power. Globally, these coups highlight distinct methods of subverting democratic institutions, with legislative coups often involving overt seizure of legislative authority, while judicial coups use legal mechanisms to delegitimize opposition.
Constitutional Foundations and Violations
Legislative coups undermine constitutional foundations by bypassing or manipulating legislative procedures to concentrate power unlawfully within the legislature, often violating principles like separation of powers and checks and balances. Judicial coups occur when courts overstep their constitutional role by invalidating laws or overriding executive actions without proper legal grounds, thereby infringing on judicial impartiality and undermining the rule of law. Both forms of coups disrupt constitutional governance, with legislative coups subverting democratic mandates and judicial coups compromising judicial legitimacy.
Key Motivations Behind Each Coup Type
Legislative coups are primarily motivated by the desire of lawmakers to consolidate power and override executive authority through legal manipulation or constitutional amendments, often driven by political dominance or partisan advantage. Judicial coups seek to achieve similar power shifts by leveraging court rulings to invalidate or undermine legislative and executive actions, frequently motivated by ideological goals or the intent to reshape the balance of power within a government. Both coup types exploit institutional mechanisms but differ in their strategic focus--legislative coups emphasize statutory control, while judicial coups focus on judicial interpretation and constitutional review.
Comparative Impact on Democratic Institutions
Legislative coups undermine democratic institutions by allowing elected lawmakers to concentrate power through unconstitutional amendments or bypassing checks and balances, weakening separation of powers and eroding parliamentary accountability. Judicial coups affect democracy by enabling courts or judges to override legislative decisions or constitutional norms, potentially destabilizing the rule of law and judiciary impartiality. Both coups disrupt the balance of power, but legislative coups often erode democratic representation more directly, while judicial coups challenge legal legitimacy and institutional trust.
Roles of Political Actors and Stakeholders
Legislative coups occur when elected lawmakers manipulate or bypass constitutional norms to concentrate power, often supported by ruling party elites and political factions aiming to undermine checks and balances. Judicial coups involve judges or courts exceeding their constitutional authority, sometimes prompted by judicial activists or politically influenced magistrates seeking to alter political outcomes or policies. Key stakeholders in legislative coups include parliamentarians and political parties, while in judicial coups, the judiciary, legal institutions, and sometimes executive branches play pivotal roles in contesting or enforcing power shifts.
Public Response and Civil Society Reactions
Public response to a legislative coup often involves mass protests and widespread demands for the restoration of democratic norms, as citizens perceive the legislative body's takeover as a direct assault on electoral legitimacy. Judicial coups provoke significant concern among civil society organizations due to perceived breaches of judicial independence, leading to calls for legal reforms and efforts to protect the rule of law. Both scenarios typically result in heightened activism, with NGOs and grassroots movements mobilizing to defend democratic institutions and promote accountability.
International Perspectives and Legal Implications
Legislative coups involve the seizure or manipulation of legislative bodies to undermine democratic governance, often bypassing constitutional norms, while judicial coups pertain to courts or judicial authorities overruling elected officials or constitutional mandates to reshape political power. International perspectives on these actions vary, with legislative coups frequently condemned for eroding representative democracy and judicial coups scrutinized for overstepping judicial impartiality and separation of powers. Legal implications include challenges to the rule of law, violations of constitutional order, potential sanctions by international bodies, and debates over sovereignty versus external intervention.
Prevention Mechanisms and Safeguards
Prevention mechanisms against legislative coups include constitutional checks and balances, bicameralism, and federalism to disperse power and ensure legislative decisions face scrutiny from multiple institutions. Judicial coups are countered by safeguarding judicial independence through life tenure for judges, transparent appointment processes, and robust judicial review frameworks that prevent illegal or unconstitutional usurpation of powers. Both scenarios benefit from strong civil society oversight, free press, and enforcement of separation of powers to maintain democratic norms and prevent authoritarian overreach.
Lessons Learned: Ensuring Democratic Resilience
Legislative coups involve the unlawful seizure of power by elected representatives subverting constitutional norms, whereas judicial coups occur when courts overreach their authority to undermine democratic processes. Lessons learned highlight the necessity of strong institutional checks and balances, transparency, and civic engagement to guard against authoritarian encroachments. Reinforcing democratic resilience requires clear legal frameworks that prevent abuses within legislative agendas and judicial rulings while promoting accountability across government branches.
Legislative coup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com