Proportional representation ensures that political parties gain seats in proportion to the number of votes they receive, promoting fairer and more inclusive governance. This electoral system prevents dominance by a single party and better reflects the diverse views of the electorate. Explore the details in the rest of the article to understand how proportional representation can impact your democratic participation.
Table of Comparison
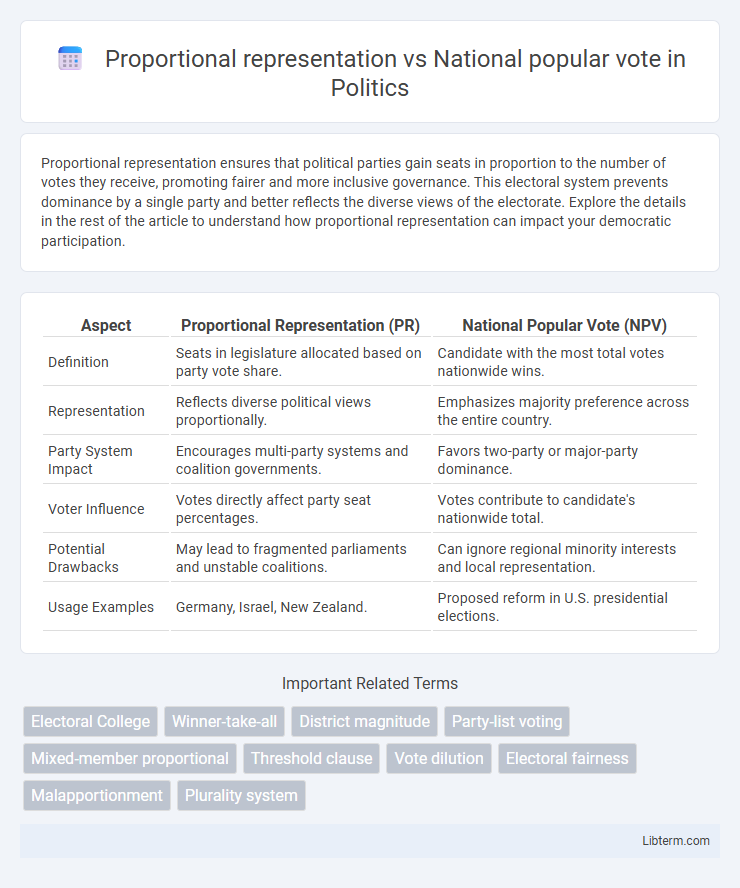
| Aspect | Proportional Representation (PR) | National Popular Vote (NPV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seats in legislature allocated based on party vote share. | Candidate with the most total votes nationwide wins. |
| Representation | Reflects diverse political views proportionally. | Emphasizes majority preference across the entire country. |
| Party System Impact | Encourages multi-party systems and coalition governments. | Favors two-party or major-party dominance. |
| Voter Influence | Votes directly affect party seat percentages. | Votes contribute to candidate's nationwide total. |
| Potential Drawbacks | May lead to fragmented parliaments and unstable coalitions. | Can ignore regional minority interests and local representation. |
| Usage Examples | Germany, Israel, New Zealand. | Proposed reform in U.S. presidential elections. |
Introduction to Electoral Systems
Proportional representation allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring diverse political views are represented fairly in government. The national popular vote system determines election outcomes by totaling all individual votes across the country, emphasizing direct voter influence on executive positions. These electoral systems shape democratic processes by balancing representational accuracy and majority rule in political decision-making.
What is Proportional Representation?
Proportional representation is an electoral system designed to allocate seats in a legislature in proportion to the votes each party receives, ensuring broader representation of political views. Unlike winner-takes-all systems, it enables smaller parties to gain parliamentary presence reflective of their actual support among voters. This system enhances democratic fairness by translating the national popular vote more accurately into legislative seats.
Understanding the National Popular Vote
National Popular Vote (NPV) ensures that the U.S. presidential election outcome reflects the total popular vote across all states, circumventing the Electoral College's state-by-state system. Under NPV, electoral votes are awarded to the candidate with the most nationwide votes, promoting equal voter influence regardless of state population size. This method addresses disparities inherent in Proportional Representation, where votes may be divided within states, often diluting the impact of the overall national vote.
Key Differences Between PR and NPV
Proportional representation (PR) allocates legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences across multi-member districts. In contrast, the national popular vote (NPV) tallies individual votes nationwide to determine the winner, often used in presidential elections but can ignore regional representation. PR promotes diverse party inclusion and coalition governments, while NPV emphasizes a direct, nationwide consensus but may overlook minority regional interests.
Advantages of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation ensures that political parties receive seats in the legislature corresponding directly to their share of the national vote, fostering a more accurate reflection of voter preferences. This system enhances minority representation and promotes political diversity by allowing smaller parties to gain legislative influence. Greater electoral fairness and increased voter turnout are common advantages tied to proportional representation.
Benefits of the National Popular Vote
The National Popular Vote ensures that every vote across the country has equal weight, promoting fairer representation in presidential elections and enhancing voter turnout by making all votes count equally. This system reduces the disproportionate influence of swing states and incentivizes candidates to campaign nationwide, addressing the interests of a broader electorate. By reflecting the true will of the majority, the National Popular Vote fosters greater democratic legitimacy and trust in election outcomes.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each System
Proportional representation faces challenges such as fragmented party systems and coalition instability, which can lead to legislative gridlock and difficulty in forming majority governments. National popular vote systems often encounter criticisms regarding the diminished influence of smaller states and the potential neglect of regional interests, potentially undermining federal balance. Both systems raise concerns over voter representation equity: proportional representation may dilute individual district accountability, while national popular vote can marginalize localized concerns.
Impact on Political Parties and Representation
Proportional representation encourages multiparty systems by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, enhancing diverse political representation and reducing the dominance of major parties. In contrast, a national popular vote system often sustains a two-party structure by awarding victory to the candidate with the most votes nationwide, potentially marginalizing smaller parties and minority interests. This difference significantly influences party strategies, voter engagement, and the inclusiveness of legislative bodies.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Proportional representation systems in countries like Germany and New Zealand allocate legislative seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring diverse and equitable political representation. In contrast, the United States utilizes the National Popular Vote in presidential elections only as a proposed alternative to the Electoral College, aiming to reflect the popular will more accurately without guaranteeing proportional legislative representation. Case studies from Iceland demonstrate that proportional representation can lead to coalition governments that better mirror voter preferences, whereas debates over the National Popular Vote highlight challenges in balancing state interests with national vote totals.
Future Prospects and Reforms in Electoral Systems
Proportional representation systems are gaining momentum globally as they enhance electoral fairness by better reflecting the diversity of voter preferences, with countries like New Zealand and Germany exemplifying successful implementations. Future reforms may involve hybrid models combining proportional representation with national popular vote elements to balance local representation and overall vote fairness. Advancements in technology and increased emphasis on voter equity are driving innovative electoral reforms aimed at improving democratic legitimacy and reducing partisan gerrymandering.
Proportional representation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com