Parliamentary debate sharpens your critical thinking and public speaking skills by simulating real-world legislative discussions. It encourages quick reasoning and effective argumentation within a structured format. Discover how engaging in parliamentary debate can transform your communication abilities by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
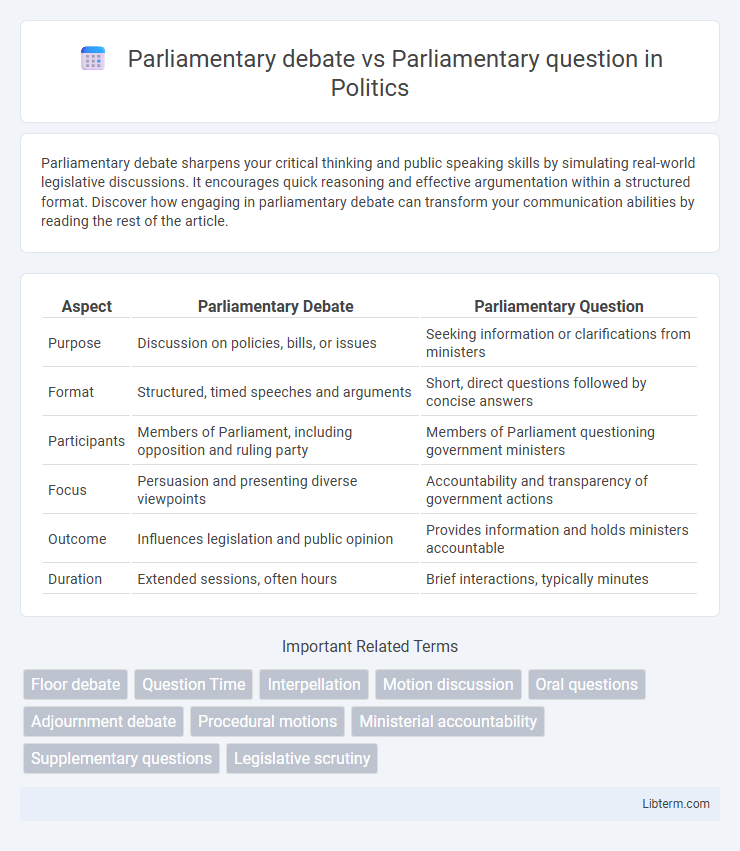
| Aspect | Parliamentary Debate | Parliamentary Question |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discussion on policies, bills, or issues | Seeking information or clarifications from ministers |
| Format | Structured, timed speeches and arguments | Short, direct questions followed by concise answers |
| Participants | Members of Parliament, including opposition and ruling party | Members of Parliament questioning government ministers |
| Focus | Persuasion and presenting diverse viewpoints | Accountability and transparency of government actions |
| Outcome | Influences legislation and public opinion | Provides information and holds ministers accountable |
| Duration | Extended sessions, often hours | Brief interactions, typically minutes |
Introduction to Parliamentary Procedures
Parliamentary debate involves structured arguments presented by members to discuss and resolve motions within a formal assembly, emphasizing clear reasoning and adherence to established rules. Parliamentary questions serve as procedural tools allowing members to seek specific information or clarifications from government officials or assembly leaders during sessions. Both practices are fundamental components of parliamentary procedures, facilitating transparent decision-making and accountability in legislative bodies.
Defining Parliamentary Debate
Parliamentary debate is a structured form of discussion where participants argue opposing viewpoints on a specific motion, emphasizing rhetoric, logic, and public speaking skills. It follows formal rules and procedures similar to those used in legislative assemblies, focusing on persuasion and critical analysis. Parliamentary questions, in contrast, are concise inquiries posed during sessions to obtain information or hold officials accountable, rather than extended argumentative exchanges.
Understanding Parliamentary Questions
Parliamentary questions serve as a fundamental tool for holding the government accountable by seeking detailed information on policies, decisions, and administrative actions. Unlike parliamentary debates that involve structured argumentation and discussion on bills or motions, parliamentary questions require precise, clear, and concise queries directed at ministers or government officials. Mastering the art of framing parliamentary questions enhances transparency, facilitates informed decision-making, and promotes effective governance.
Key Objectives: Debate vs. Question
Parliamentary debate focuses on presenting structured arguments to persuade or refute motions, aiming to clarify policy positions and influence legislative decisions. Parliamentary questions prioritize seeking precise information, holding the government accountable, and promoting transparency through targeted inquiries. Both serve the key objective of enhancing democratic governance but differ in approach: debate drives decision-making through discourse, while questions ensure oversight and clarity.
Structure and Format Comparison
Parliamentary debate typically follows a structured format with designated speaking times for proponents and opponents, emphasizing argumentation, rebuttal, and summary speeches, often organized into opening, constructive, and closing stages. Parliamentary questions, by contrast, involve a formalized procedure where members pose concise, pointed inquiries to the government or ministers, adhering to strict rules on timing, relevance, and response limits. The debate centers on extended discourse and persuasion, while questions focus on clarity, accountability, and precise information exchange within a regulated parliamentary framework.
Role of Members in Debates and Questions
Members in parliamentary debates actively present arguments, scrutinize bills, and influence policy decisions through structured speeches. In contrast, during parliamentary questions, members play a crucial role in holding the government accountable by seeking information, clarifications, and explanations from ministers. Debates emphasize persuasion and public discourse, while questions prioritize transparency and immediate government response.
Impact on Policy and Legislation
Parliamentary debates play a critical role in shaping policy and legislation by allowing detailed discussion, scrutiny, and public airing of different viewpoints on proposed laws. Parliamentary questions serve as a key tool for holding the government accountable, prompting clarification, and exposing issues that may influence legislative priorities and amendments. Together, debates and questions ensure transparency and responsiveness in the policymaking process, directly impacting the quality and direction of legislation.
Time Allocation and Procedural Differences
Parliamentary debates typically involve extended speeches with strict time limits allocated to each member, ensuring thorough discussion of legislation, whereas parliamentary questions require brief, timed inquiries and answers, promoting efficient information exchange. Procedurally, debates follow a formal order with speeches and amendments, while question sessions prioritize direct questioning by members and immediate government responses. Time allocation in debates ranges from several minutes per speaker, contrasting with the concise format of questions, which often last under a minute each.
Public Transparency and Accountability
Parliamentary debate facilitates public transparency by openly discussing proposed policies, allowing citizens to observe lawmakers' reasoning and stance on key issues. Parliamentary questions enhance accountability by enabling members to directly query government officials, ensuring timely and precise responses on public administration. Together, they create a dynamic system that promotes scrutiny, encourages government responsiveness, and strengthens democratic oversight.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool
Parliamentary debate and parliamentary question serve distinct purposes within legislative processes, with debate fostering in-depth discussion and parliamentary questions emphasizing accountability and information gathering. Selecting the appropriate tool depends on the objective: debates are ideal for exploring complex policy issues, while questions effectively scrutinize government actions and decisions. Understanding these differences ensures legislators maximize their impact in shaping policy and governance.
Parliamentary debate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com