Coalition durability depends on factors such as shared goals, trust among members, and effective communication. Long-lasting coalitions often exhibit adaptability and strong conflict resolution mechanisms to maintain unity. Discover how these elements impact your coalition's success in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
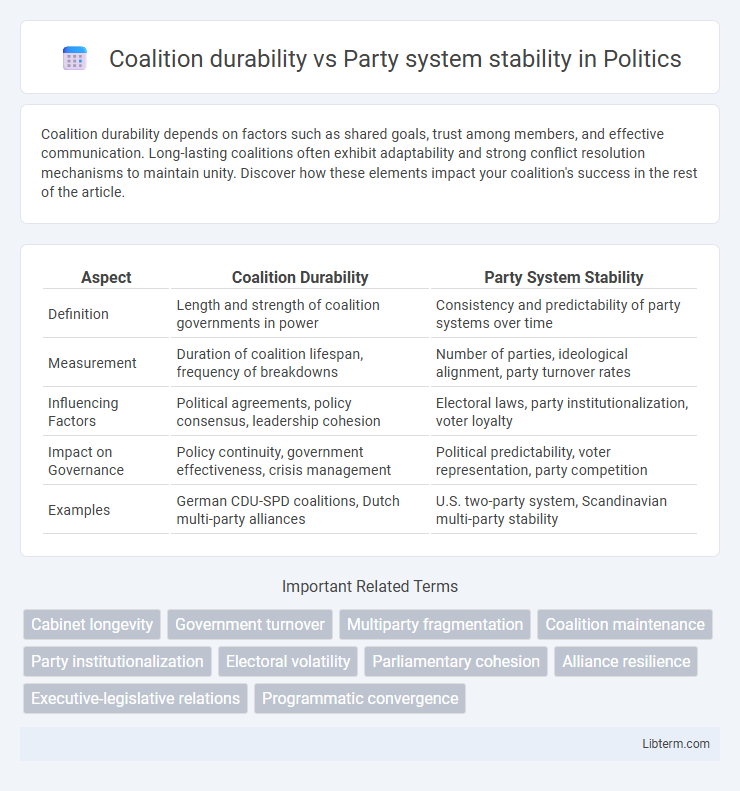
| Aspect | Coalition Durability | Party System Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Length and strength of coalition governments in power | Consistency and predictability of party systems over time |
| Measurement | Duration of coalition lifespan, frequency of breakdowns | Number of parties, ideological alignment, party turnover rates |
| Influencing Factors | Political agreements, policy consensus, leadership cohesion | Electoral laws, party institutionalization, voter loyalty |
| Impact on Governance | Policy continuity, government effectiveness, crisis management | Political predictability, voter representation, party competition |
| Examples | German CDU-SPD coalitions, Dutch multi-party alliances | U.S. two-party system, Scandinavian multi-party stability |
Understanding Coalition Durability: Key Concepts
Coalition durability refers to the longevity and resilience of alliances formed between political parties to govern, influenced by factors such as ideological compatibility, institutional frameworks, and power-sharing arrangements. Party system stability, on the other hand, measures the consistency and persistence of party competition patterns over time, often shaped by voter loyalty, electoral rules, and party organization strength. Understanding coalition durability requires analyzing how coalition agreements, trust among partners, and external pressures impact the ability of coalitions to withstand political shocks and maintain effective governance.
Party System Stability: Definition and Dimensions
Party system stability refers to the persistence and predictability of political parties within a democratic framework, encompassing dimensions such as electoral consistency, party institutionalization, and voter alignment. Stable party systems exhibit limited volatility in party competition, clear ideological distinctions, and enduring organizational structures that facilitate effective governance and voter loyalty. Evaluating these dimensions helps measure how parties sustain influence and maintain coherent collective identities over time, essential for democratic consolidation.
Historical Evolution of Party Systems and Coalitions
The historical evolution of party systems reveals that coalition durability often depends on the adaptability and ideological proximity of participating parties within multi-party frameworks. Stable party systems typically emerge in contexts where clear voter alignments and institutional mechanisms encourage enduring alliances, reducing the frequency of coalition breakdowns. Empirical studies demonstrate that shifts in electoral rules and political realignments significantly influence both the longevity of coalitions and the overall stability of party systems over time.
Factors Influencing Coalition Durability
Coalition durability is influenced by factors such as ideological compatibility among member parties, institutional frameworks including electoral systems and government structures, and the distribution of power within the coalition. Strong party discipline, effective conflict resolution mechanisms, and mutual policy goals enhance coalition stability compared to fragmented or highly competitive party systems. Economic conditions and external pressures also play a critical role in determining the longevity and effectiveness of governing coalitions.
Determinants of Party System Stability
Party system stability depends heavily on the durability of coalition arrangements, which are influenced by factors such as ideological cohesion, electoral incentives, and institutional frameworks. Stable coalitions often emerge in systems with clear ideological alignments and proportional electoral rules that encourage cooperation and reduce fragmentation. Institutional determinants, including the electoral threshold and the design of legislative bodies, further strengthen party system stability by promoting predictable alliance patterns and minimizing volatility.
Coalition Dynamics in Fragmented Party Systems
Coalition durability in fragmented party systems depends heavily on strategic negotiations and policy concessions among diverse parties to maintain government stability. Frequent ideological differences and shifting alliances increase the risk of coalition breakdowns, challenging consistent governance. Effective coalition management requires balancing party interests while adapting to evolving political landscapes to ensure sustained collaboration and minimize instability.
Impact of Electoral Systems on Coalition Durability
Proportional representation systems tend to enhance coalition durability by encouraging multi-party cooperation and reducing the likelihood of single-party majorities, thereby fostering stable and inclusive governance. In contrast, majoritarian electoral systems often produce stronger party system stability through dominant parties but can undermine coalition durability due to less frequent power-sharing incentives. The degree of electoral threshold and district magnitude significantly influences the formation and longevity of coalitions, with lower thresholds and larger districts promoting broader alliances and more stable coalitions.
Relationship Between Coalition Durability and Party System Stability
Coalition durability is closely linked to party system stability, as fragmented or highly volatile party systems often lead to short-lived coalitions. Stable party systems with clearly defined ideological divisions facilitate enduring coalitions through predictable alliances and trust among parties. Empirical studies show that countries with moderate multiparty systems tend to experience greater coalition durability compared to highly fragmented or two-party dominant systems.
Case Studies: Successful and Fragile Coalitions
Successful coalitions like Germany's CDU-CSU-SPD illustrate high coalition durability through institutionalized agreements and ideological overlap, ensuring sustained governance despite political shifts. In contrast, fragile coalitions such as Italy's frequent government turnovers reveal party system instability triggered by fragmented multiparty landscapes and weak party discipline. Comparative case studies highlight that coalition durability depends significantly on the underlying party system stability, where cohesive party frameworks foster enduring alliances.
Future Trends: Strengthening Stability in Multi-Party Systems
Future trends in coalition durability emphasize institutional reforms that foster transparent negotiation processes and enforce policy agreements, thereby strengthening party system stability. Enhanced voter alignment with ideological platforms reduces fragmentation, contributing to sustained coalition governance in multi-party systems. Digital tools for voter engagement and predictive analytics also optimize coalition formation, promoting long-term political stability.
Coalition durability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com