A session refers to a designated period during which a user interacts with a system, website, or application, enabling activities like browsing, data entry, or transactions. Understanding how sessions work is crucial for optimizing user experience and maintaining security, especially in managing timeouts and preserving user data. Explore the rest of the article to discover how session management impacts your digital interactions.
Table of Comparison
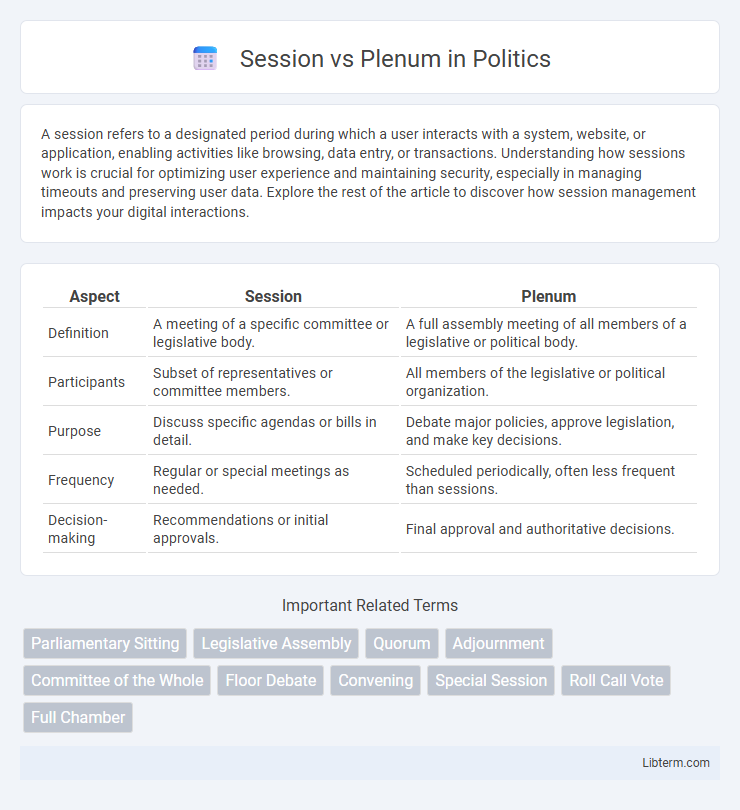
| Aspect | Session | Plenum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A meeting of a specific committee or legislative body. | A full assembly meeting of all members of a legislative or political body. |
| Participants | Subset of representatives or committee members. | All members of the legislative or political organization. |
| Purpose | Discuss specific agendas or bills in detail. | Debate major policies, approve legislation, and make key decisions. |
| Frequency | Regular or special meetings as needed. | Scheduled periodically, often less frequent than sessions. |
| Decision-making | Recommendations or initial approvals. | Final approval and authoritative decisions. |
Understanding Session and Plenum: Key Definitions
A session refers to a scheduled period during which a legislative or deliberative body meets to conduct its business, such as passing laws or debating issues. A plenum is a specific type of session where all members of the body are present, ensuring maximum participation and comprehensive decision-making. Understanding the difference between session and plenum is crucial for grasping legislative processes and the scope of participation in governance.
Historical Origins of Sessions and Plenums
Sessions originated from early parliamentary assemblies where periodic meetings were held to deliberate and make decisions, often linked to legislative or judicial functions. Plenums trace back to Roman and medieval councils, where all members of a governing body or party convened to discuss comprehensive policies or strategic directions. Both concepts evolved to structure governance and decision-making, with sessions emphasizing procedural order and plenums highlighting full membership participation.
Structural Differences: Session vs Plenum
A session refers to a meeting or series of meetings of a legislative or deliberative body for conducting its business, typically defined by a fixed period or agenda. A plenum denotes a full assembly where all members of a legislative or organizational body are present, emphasizing maximum participation for decision-making or discussions. Structurally, sessions may include various subsets or committees meeting separately, while plenums require the physical or virtual presence of the entire membership to ensure comprehensive representation.
Purpose and Functionality of a Session
A session serves as a formal period during which a legislative body convenes to discuss, debate, and pass laws, providing a structured timeline for decision-making and governance. Sessions enable focused legislative activity, fostering accountability and the orderly progression of government functions within designated timeframes. The plenum represents a full assembly of all members for comprehensive discussion or voting, while sessions organize these meetings into specific intervals with defined agendas.
Purpose and Functionality of a Plenum
A plenum serves as a chamber designed to distribute air uniformly within HVAC systems, ensuring optimized airflow and pressure regulation. Its primary functionality is to act as a central hub where conditioned air is collected or supplied, facilitating efficient air mixing and minimizing turbulence. Unlike sessions, which refer to structured meetings or gatherings, plenums focus on the integral role of air distribution in ventilation engineering and environmental control.
Decision-Making in Session vs Plenum
Decision-making in a session typically involves a smaller, specialized group focused on detailed deliberations, enabling faster and more targeted resolutions. In contrast, a plenum includes all members of a legislative or organizational body, facilitating broader consensus but often resulting in longer decision-making processes due to the larger number of participants. The session's streamlined approach enhances efficiency, while the plenum ensures comprehensive representation and legitimacy in final decisions.
Participants: Who Attends Sessions and Plenums?
Sessions typically involve a specific group of participants, such as committee members, delegates, or representatives focused on detailed discussions and decision-making within a particular domain. Plenums convene all members of a larger assembly or organization, bringing together every delegate or representative to address broader issues and make collective decisions. Participants in plenums engage in comprehensive debates and votes that affect the entire body, while session attendees participate in specialized tasks or preparatory work.
Frequency and Duration: Comparing Sessions and Plenums
Sessions typically occur with higher frequency, often meeting weekly or monthly to address ongoing legislative or organizational business, while plenums convene less frequently, sometimes only a few times per year, to discuss broader or more critical issues. Sessions tend to have shorter durations, ranging from a few hours to several days, allowing for focused debate and decision-making, whereas plenums usually last longer, providing extended time for comprehensive discussions and consensus-building among all members. The frequency and duration differences reflect the distinct purposes of sessions and plenums in governance and organizational frameworks.
Importance in Parliamentary and Organizational Contexts
Sessions and plenums are critical components in parliamentary and organizational contexts, serving distinct but complementary functions. A session refers to a series of meetings where legislative work or organizational decisions are conducted over a set period, ensuring systematic progress and continuity. Plenums, comprising full membership assemblies, provide a platform for comprehensive debate and final decision-making, reinforcing democratic participation and legitimacy.
Session vs Plenum: Pros, Cons, and When to Use Each
Sessions offer focused, time-limited discussions ideal for in-depth exploration of specific topics, promoting active participation in smaller groups. Plenums bring together all participants, fostering broad consensus and comprehensive information dissemination but may limit individual engagement due to larger audience size. Use sessions for specialized brainstorming or training, whereas plenums suit general updates, decision-making, or keynote presentations requiring full attendance.
Session Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com