Ideological politics shapes policy decisions and social movements by grounding them in a set of core beliefs or values. Understanding these underlying ideologies helps clarify the motivations behind political actions and the divisions within society. Explore the rest of the article to see how ideological politics influence governance and public opinion in your community.
Table of Comparison
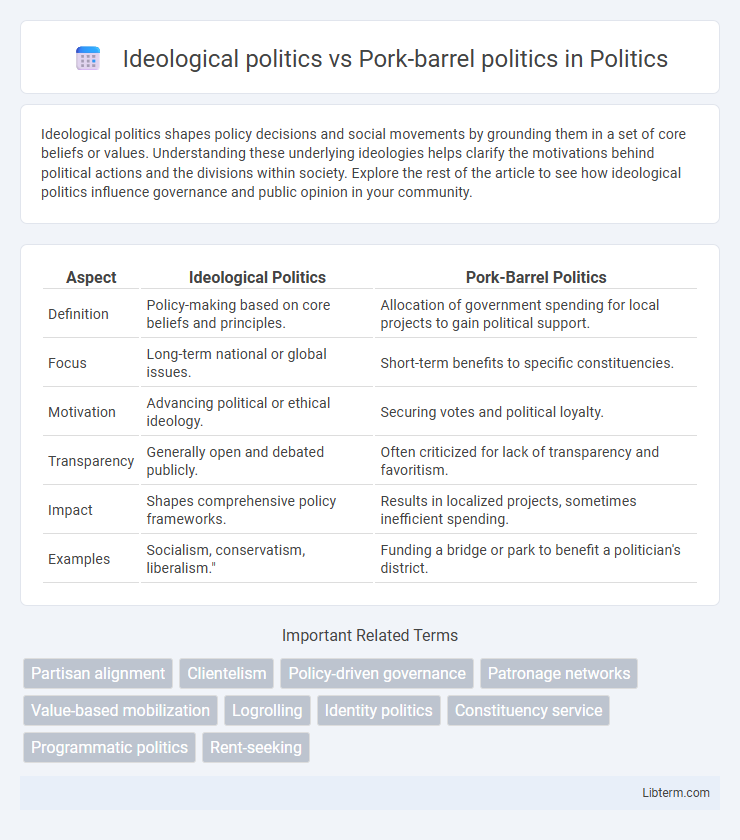
| Aspect | Ideological Politics | Pork-Barrel Politics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy-making based on core beliefs and principles. | Allocation of government spending for local projects to gain political support. |
| Focus | Long-term national or global issues. | Short-term benefits to specific constituencies. |
| Motivation | Advancing political or ethical ideology. | Securing votes and political loyalty. |
| Transparency | Generally open and debated publicly. | Often criticized for lack of transparency and favoritism. |
| Impact | Shapes comprehensive policy frameworks. | Results in localized projects, sometimes inefficient spending. |
| Examples | Socialism, conservatism, liberalism." | Funding a bridge or park to benefit a politician's district. |
Understanding Ideological Politics
Ideological politics centers on the adherence to a set of beliefs or values that guide policy decisions and political behavior, often reflecting a broader vision for society's structure and governance. This approach emphasizes consistency and principles in legislative agendas, contrasting with pork-barrel politics, which targets localized, often short-term gains through government spending for political advantage. Understanding ideological politics requires analyzing how political parties and leaders prioritize long-term goals and ideological coherence over immediate constituent benefits.
Defining Pork-Barrel Politics
Pork-barrel politics refers to government spending that is directed toward localized projects secured primarily to benefit a legislator's constituents, often to gain political support or favor. This practice involves the allocation of funds for public works or programs in specific districts in exchange for political allegiance rather than based on overall policy merit or ideological principles. Unlike ideological politics, which centers on advancing consistent policy agendas based on political beliefs, pork-barrel politics prioritizes tangible, short-term benefits for voters to secure electoral advantage.
Origins and Historical Context of Both Approaches
Ideological politics originated from the Enlightenment era and the rise of political philosophies emphasizing values, principles, and visions for society's organization, shaping parties around coherent beliefs like liberalism or conservatism. Pork-barrel politics emerged in the 19th century United States as legislators sought to secure federal funds for local projects to gain voter support, reflecting pragmatic and transactional governance over ideological purity. Both approaches reflect distinct political strategies where ideological politics prioritizes doctrinal alignment, and pork-barrel politics centers on tangible benefits and voter appeasement.
Core Principles of Ideological Politics
Core principles of ideological politics emphasize adherence to a consistent set of beliefs and values that guide policy decisions and political behavior. This approach prioritizes long-term goals based on ideology, promoting coherence and predictability in governance. Ideological politics contrasts sharply with pork-barrel politics, which focuses on short-term, localized benefits often driven by electoral incentives rather than overarching principles.
Mechanisms and Strategies in Pork-Barrel Politics
Pork-barrel politics operates through the strategic allocation of government funds to local projects that benefit specific constituencies, securing political support and votes in return. Mechanisms include targeted budget appropriations, earmarks, and grant distributions designed to deliver tangible benefits to legislators' districts. This approach contrasts with ideological politics by prioritizing practical incentives and localized gains over broad policy principles or ideological coherence.
Influence on Policy Development and Legislation
Ideological politics drives policy development through consistent adherence to a set of principles, shaping legislation that reflects long-term societal goals and values. Pork-barrel politics influences legislation by prioritizing local interests and securing funds for specific projects, often resulting in targeted benefits rather than broad policy reforms. The tension between these approaches impacts legislative agendas, with ideological politics favoring comprehensive policy frameworks and pork-barrel politics promoting localized, incremental changes.
Impacts on Voter Behavior and Public Trust
Ideological politics shapes voter behavior by aligning electoral choices with core values and policy preferences, fostering stronger political identity and engagement. Pork-barrel politics influences voter behavior through targeted resource allocation, often securing localized support but risking perceptions of favoritism and inefficiency. Public trust is generally higher in systems emphasizing ideological consistency, whereas pork-barrel practices can erode trust by promoting corruption and undermining transparent governance.
Case Studies: Global Instances of Ideological vs Pork-Barrel Politics
In the United States, ideological politics is exemplified by the polarization between Democrats and Republicans on issues like healthcare reform, contrasting with pork-barrel politics seen in congressional earmarks funding local infrastructure projects to secure votes. In India, the dominance of ideological politics is evident in the BJP's emphasis on Hindu nationalism, whereas pork-barrel politics manifests through targeted allocation of development funds in swing states to benefit particular constituencies. Brazil showcases ideological politics through the Workers' Party's focus on social inequality, while pork-barrel politics appears in municipal-level spending aimed at winning electoral support during presidential campaigns.
Pros and Cons: A Comparative Analysis
Ideological politics fosters policy consistency and voter alignment by promoting clear values and long-term goals, but it can lead to polarization and hinder bipartisan cooperation. Pork-barrel politics facilitates localized government funding and tangible community benefits, yet it risks encouraging inefficiency, corruption, and favoritism at the expense of broader national interests. Balancing ideological commitment with pragmatic resource allocation remains a key challenge in effective governance.
Future Trends and Implications for Democratic Systems
Ideological politics is expected to intensify as voters increasingly demand policies aligned with core values, while pork-barrel politics may face diminishing returns due to growing transparency and accountability measures in democratic systems. Advances in digital governance and social media amplify ideological polarization, but they also promote citizen engagement, challenging traditional patronage-based resource allocation. The evolving balance will influence democratic legitimacy, policymaking efficiency, and potentially reshape electoral dynamics with greater emphasis on issue-based campaigns.
Ideological politics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com