Progressive approaches enhance adaptability and innovation in various fields, driving consistent improvement and future readiness. Embracing progressive methods allows you to stay ahead of trends and implement effective solutions. Discover how adopting progressive strategies can transform your outcomes by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
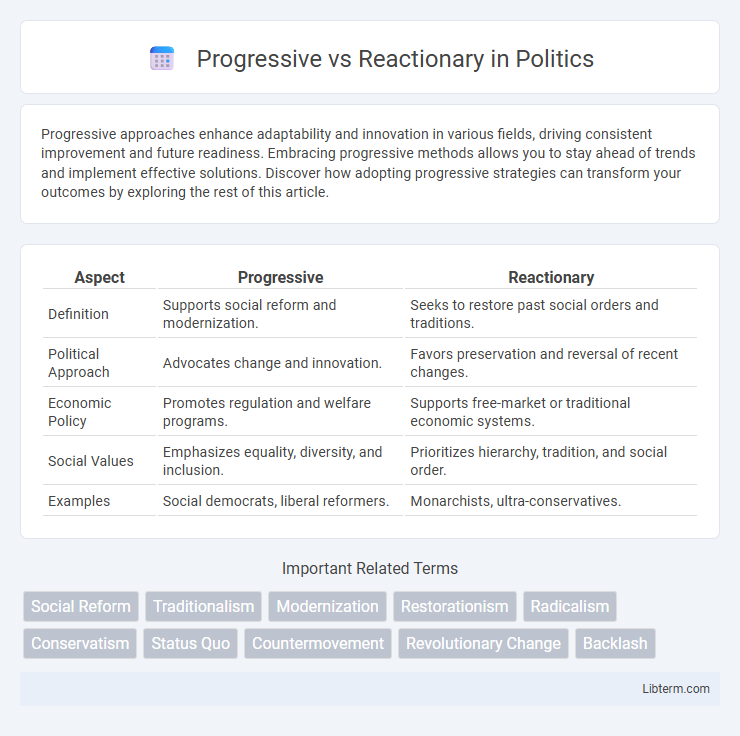
| Aspect | Progressive | Reactionary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supports social reform and modernization. | Seeks to restore past social orders and traditions. |
| Political Approach | Advocates change and innovation. | Favors preservation and reversal of recent changes. |
| Economic Policy | Promotes regulation and welfare programs. | Supports free-market or traditional economic systems. |
| Social Values | Emphasizes equality, diversity, and inclusion. | Prioritizes hierarchy, tradition, and social order. |
| Examples | Social democrats, liberal reformers. | Monarchists, ultra-conservatives. |
Defining “Progressive” and “Reactionary”
Progressive ideology advocates for social reform, innovation, and policies that seek to address inequality and promote inclusivity, often emphasizing forward-thinking governance and expanded rights. Reactionary beliefs resist change, aiming to preserve traditional social orders and institutions, often advocating a return to previous political or cultural conditions. Understanding these terms requires recognizing progressivism's alignment with change and reform, contrasted with reactionism's preference for preservation and restoration.
Historical Origins of Both Ideologies
Progressive ideology traces its roots to the Enlightenment and 19th-century movements advocating social reform, emphasizing reason, equality, and forward-thinking change. Reactionary thought emerged during periods of societal upheaval, notably in post-French Revolution Europe, aiming to restore traditional hierarchies and resist rapid transformation. Both ideologies reflect contrasting responses to modernization, with progressives championing innovation and reactionaries upholding established norms.
Core Values: Progress vs. Preservation
Progressive ideology centers on embracing change, innovation, and social justice to advance society, emphasizing equality and reform. Reactionary beliefs prioritize preserving traditional values, institutions, and cultural heritage, resisting rapid change to maintain social stability. The core conflict lies in the desire for progress versus the need for preservation, shaping political and social debates worldwide.
Policy Approaches: Innovation vs. Tradition
Progressive policy approaches emphasize innovation by advocating for forward-thinking reforms, such as renewable energy investments and expanding social welfare programs, to address contemporary challenges. Reactionary policies prioritize tradition, seeking to preserve established institutions and revert to previous governance models to maintain social order and cultural norms. This fundamental divide influences legislative agendas, with progressives promoting change and modernization while reactionaries resist shifts that disrupt historical frameworks.
Social and Cultural Perspectives
Progressive movements advocate for social equality, cultural diversity, and reforms that challenge traditional norms to promote inclusivity and human rights. Reactionary perspectives emphasize preserving established cultural values, social hierarchies, and institutions, resisting changes perceived as threats to societal stability. The tension between these views shapes debates on issues such as gender roles, racial justice, and freedom of expression within society.
Economic Policies and Priorities
Progressive economic policies prioritize social equity through wealth redistribution, increased minimum wages, and expanded public services to reduce income inequality and support vulnerable populations. Reactionary economic approaches emphasize preserving traditional market structures, reducing government intervention, and fostering free-market capitalism to maintain existing wealth hierarchies and promote individual economic freedom. These opposing priorities shape debates on taxation, welfare programs, and regulatory measures impacting economic growth and social stability.
Political Strategies and Methods
Progressive political strategies emphasize reform through inclusive policies, social justice initiatives, and expanding civil rights, often leveraging grassroots activism and legislative changes to address systemic inequalities. Reactionary methods prioritize preserving traditional social orders by resisting rapid changes, often utilizing conservative rhetoric, strict law enforcement, and mobilizing established institutions to maintain existing power structures. Both approaches employ media campaigns and political lobbying but differ fundamentally in their goals--progressives seek transformation, while reactionaries aim to restore or maintain prior conditions.
Influence on Modern Political Movements
Progressive ideologies have significantly shaped modern political movements by promoting social equality, environmental sustainability, and expanded civil rights, influencing policies such as universal healthcare and climate action. Reactionary movements often rally against rapid social changes, emphasizing a return to traditional values, hierarchical societal structures, and nationalistic rhetoric, impacting conservative and populist agendas worldwide. The ongoing tension between these forces drives contemporary political discourse, affecting electoral strategies and legislative priorities across diverse democratic societies.
Common Misconceptions and Stereotypes
Progressive individuals are often stereotyped as radical changemakers disregarding tradition, while reactionaries are mistakenly viewed solely as anti-development conservatives resistant to any form of social evolution. Common misconceptions obscure the nuanced motivations behind both ideologies, with progressives advocating for systematic reform addressing inequality, and reactionaries emphasizing the preservation of established social orders to maintain stability. Recognizing these complexities helps clarify that progressive and reactionary stances encompass a broad spectrum of beliefs beyond simplistic labels.
Bridging the Divide: Pathways to Dialogue
Bridging the divide between progressive and reactionary viewpoints requires fostering open dialogue rooted in mutual respect and empathy. Creating platforms for inclusive conversations enables both sides to find common ground by focusing on shared values and practical solutions rather than ideological extremes. Emphasizing active listening and critical thinking cultivates understanding, helping to transform polarization into collaborative progress.
Progressive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com