The Transparency Act mandates organizations to disclose detailed information about their operations, promoting openness and accountability. Compliance with this legislation enhances trust among stakeholders and ensures ethical business practices. Discover more about how the Transparency Act impacts your responsibilities and corporate governance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
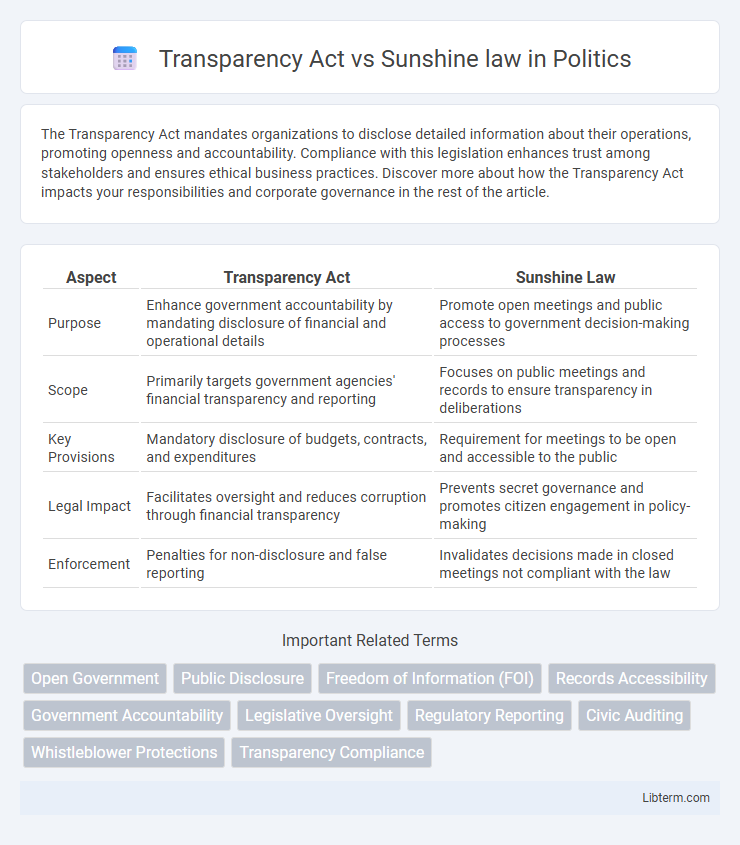
| Aspect | Transparency Act | Sunshine Law |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance government accountability by mandating disclosure of financial and operational details | Promote open meetings and public access to government decision-making processes |
| Scope | Primarily targets government agencies' financial transparency and reporting | Focuses on public meetings and records to ensure transparency in deliberations |
| Key Provisions | Mandatory disclosure of budgets, contracts, and expenditures | Requirement for meetings to be open and accessible to the public |
| Legal Impact | Facilitates oversight and reduces corruption through financial transparency | Prevents secret governance and promotes citizen engagement in policy-making |
| Enforcement | Penalties for non-disclosure and false reporting | Invalidates decisions made in closed meetings not compliant with the law |
Introduction: Understanding the Transparency Act and Sunshine Law
The Transparency Act mandates increased openness in government operations by requiring detailed public disclosures of financial transactions and decision-making processes. Sunshine Laws focus specifically on guaranteeing public access to government meetings and records to promote accountability. Both legislations aim to enhance governmental transparency but operate through distinct mechanisms targeting information accessibility and public oversight.
Historical Background of Transparency Legislations
The Transparency Act and Sunshine Laws both emerge from the mid-20th century push for open government, with Sunshine Laws first introduced in the 1950s to mandate public access to government meetings. The Transparency Act, enacted later, builds on this foundation by expanding disclosure requirements to include detailed financial and operational data of public agencies. These legislations reflect evolving demands for accountability and citizen empowerment in democratic governance.
Key Definitions: Transparency Act vs Sunshine Law
The Transparency Act mandates comprehensive disclosure requirements for government contractors and entities receiving federal funds, focusing on preventing corruption and ensuring accountability through detailed reporting. Sunshine Law refers to legislation ensuring that governmental meetings, decisions, and records are open and accessible to the public, promoting openness and citizen participation. Both laws aim to enhance openness but target different aspects: the Transparency Act emphasizes financial transparency and conflict-of-interest disclosures, while Sunshine Law prioritizes access to government meetings and records.
Core Objectives and Principles
Transparency Act mandates comprehensive disclosure of government spending and activities to promote accountability and prevent corruption, emphasizing proactive data publication and public access. Sunshine Law requires meetings and official proceedings of government bodies to be open to the public, ensuring real-time observation to promote openness and citizen participation. Both laws prioritize government transparency but differ in scope, with the Transparency Act focusing on information disclosure and the Sunshine Law on public access to decision-making processes.
Scope of Coverage: Who Is Affected?
The Transparency Act primarily targets federal agencies, large corporations, and lobbyists, mandating detailed disclosures of financial activities and lobbying efforts. Sunshine laws focus on government meetings at local, state, and federal levels, requiring that public officials conduct business openly to ensure citizen access to information. Both laws impact public accountability but differ by the specific entities and activities they regulate.
Disclosure Requirements Compared
The Transparency Act mandates comprehensive disclosure of financial transactions and ownership structures, aiming to prevent hidden conflicts of interest across corporate and governmental sectors. Sunshine laws generally require real-time public access to meetings and records of government agencies to ensure accountability and openness in public administration. While both emphasize transparency, the Transparency Act focuses on detailed financial and ownership reporting, whereas Sunshine laws prioritize accessibility of governmental proceedings and documentation.
Exceptions and Limitations
The Transparency Act primarily mandates disclosure of government contracts and financial dealings but includes exceptions for national security, proprietary business information, and ongoing investigations. Sunshine laws emphasize open meetings and public access to government decision-making processes but often exempt closed sessions involving personnel matters, legal consultations, and sensitive negotiations. Both laws balance transparency with confidentiality to protect privacy, security, and competitive interests while promoting accountability.
Enforcement Mechanisms and Penalties
The Transparency Act enforces compliance through rigorous audits and requires organizations to submit detailed reports, with penalties including substantial fines and potential suspension of licenses. The Sunshine Law mandates public access to government records and meetings, with enforcement primarily via court orders and sanctions against officials who unlawfully withhold information. Both laws emphasize accountability but differ in their enforcement frameworks: the Transparency Act employs proactive monitoring, whereas the Sunshine Law relies on judicial intervention to ensure transparency.
Impact on Public Access and Accountability
The Transparency Act mandates government agencies to proactively publish detailed records and financial disclosures, significantly enhancing public access to information. The Sunshine Law requires meetings of public bodies to be open and accessible, promoting real-time accountability through direct observation of decision-making processes. Together, these laws improve transparency by ensuring both comprehensive documentation and open dialogue, fostering stronger public trust in governmental operations.
Conclusion: Comparing Effectiveness and Future Trends
The Transparency Act mandates comprehensive disclosure requirements for corporations, enhancing accountability through detailed reporting of financial activities and lobbying efforts. Sunshine Laws focus primarily on government transparency by ensuring public access to meetings, records, and decision-making processes, promoting civic engagement and reducing corruption risks. Future trends indicate growing integration of digital platforms to increase real-time access and enforce stricter compliance measures across both legal frameworks, maximizing their effectiveness in fostering transparency and public trust.
Transparency Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com