Abstention plays a crucial role in democratic processes, reflecting a voter's decision to refrain from choosing any candidate or option. Understanding the causes and effects of abstention can provide deep insights into political engagement and voter behavior in your community. Explore the rest of the article to learn how abstention influences election outcomes and what it reveals about society.
Table of Comparison
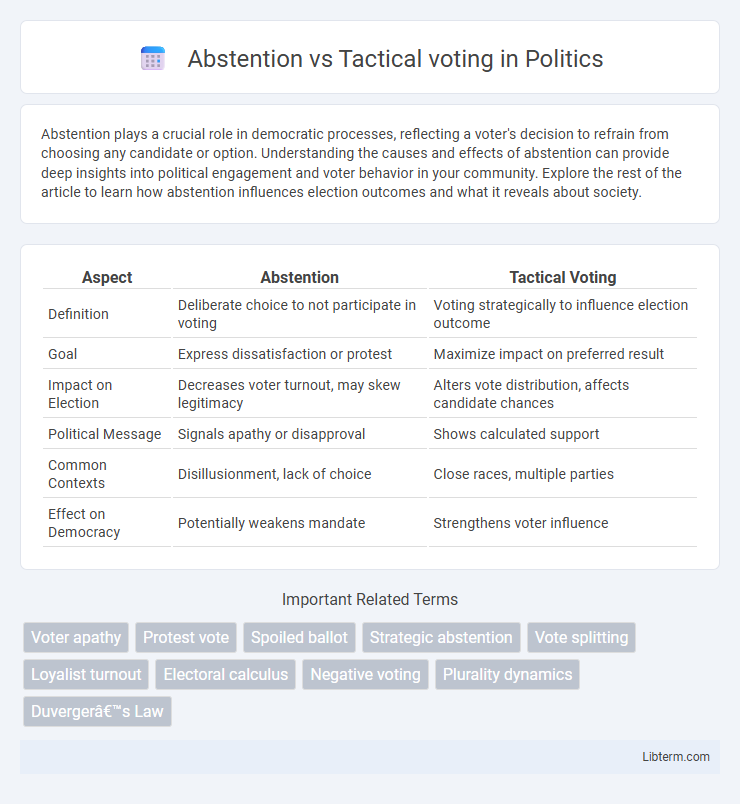
| Aspect | Abstention | Tactical Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate choice to not participate in voting | Voting strategically to influence election outcome |
| Goal | Express dissatisfaction or protest | Maximize impact on preferred result |
| Impact on Election | Decreases voter turnout, may skew legitimacy | Alters vote distribution, affects candidate chances |
| Political Message | Signals apathy or disapproval | Shows calculated support |
| Common Contexts | Disillusionment, lack of choice | Close races, multiple parties |
| Effect on Democracy | Potentially weakens mandate | Strengthens voter influence |
Understanding Abstention: Definition and Motivations
Abstention refers to the deliberate choice of eligible voters to refrain from casting a ballot in an election, motivated by factors such as political disillusionment, dissatisfaction with candidates, or a sense of inefficacy in the voting process. Motivations behind abstention include protest against the political system, lack of appealing options, or strategic non-participation to signal disengagement. Understanding abstention is crucial for analyzing electoral dynamics, as it affects voter turnout and the legitimacy of electoral outcomes.
What is Tactical Voting? Key Principles Explained
Tactical voting involves casting a ballot not for a preferred candidate, but for one with a better chance to defeat an opponent considered less desirable, often in plurality or first-past-the-post electoral systems. Its key principles include maximizing the impact of a vote by supporting a candidate aligned with the voter's strategic goal, preventing vote splitting among similar candidates, and influencing the election outcome by prioritizing electability over pure preference. This contrasts with abstention, where voters choose not to participate, forgoing any influence on the election result.
Historical Overview: Abstention and Tactical Voting Trends
Historical trends reveal fluctuating patterns of abstention and tactical voting influenced by electoral systems and socio-political contexts. In major democracies, higher abstention rates often correlate with voter dissatisfaction or apathy, while tactical voting surges in closely contested elections under plurality voting systems. Studies from the 20th century onward indicate strategic voting behaviors intensify in polarized political climates, whereas abstention peaks during periods of political disenchantment or restricted enfranchisement.
Reasons Voters Choose Abstention
Voters often choose abstention due to feelings of political alienation, dissatisfaction with available candidates, or a belief that their vote will not impact the election outcome. Perceptions of systemic corruption, lack of trust in government institutions, and barriers like complicated registration processes also contribute to low voter turnout. Abstention can reflect a protest against the political system or apathy stemming from socioeconomic factors such as low education and income levels.
Why Voters Opt for Tactical Voting
Voters opt for tactical voting to maximize the impact of their vote by supporting candidates with a realistic chance of winning instead of their preferred choice, thereby influencing election outcomes more effectively. This strategy often emerges in electoral systems like first-past-the-post, where splitting votes among similar candidates could unintentionally lead to an undesired winner. Tactical voting reflects a calculated compromise, prioritizing practical results over pure preferences to prevent less favored candidates from gaining power.
Impact on Election Outcomes: Abstention vs Tactical Voting
Abstention decreases voter turnout, which can skew election outcomes by amplifying the influence of highly motivated voter groups. Tactical voting, where voters select a less preferred but more viable candidate, can alter the distribution of votes to prevent undesirable candidates from winning, often affecting the final result more directly than abstention. Both behaviors significantly shape election dynamics, with abstention potentially lowering legitimacy and tactical voting strategically influencing winner selection.
Sociopolitical Factors Influencing Voting Strategies
Sociopolitical factors such as political alienation, perceived efficacy, and social norms heavily influence abstention and tactical voting behaviors. Voters disillusioned with mainstream parties often abstain, while strategic voters engage in tactical voting to prevent undesirable outcomes by supporting more viable candidates. Economic inequality and media framing further shape these strategies by affecting voter access to information and perceived stakes in elections.
Ethical Implications of Abstaining vs Tactical Voting
Abstaining from voting raises ethical questions about civic responsibility and the impact on democratic legitimacy, as non-participation can undermine representative governance and diminish accountability. Tactical voting involves ethical considerations regarding voter honesty and manipulation of electoral outcomes, potentially compromising the true reflection of voter preferences and distorting political mandates. Both choices carry significant moral implications influencing the fairness and integrity of democratic processes.
Case Studies: Famous Instances of Abstention and Tactical Voting
In the 2000 U.S. presidential election, Florida's narrow margin highlighted tactical voting where voters supported a less-preferred candidate to prevent the opposition's win. The 2019 UK General Election saw significant abstention in Scotland due to voter dissatisfaction with major parties, impacting overall turnout and seat distribution. India's 2014 general election presented tactical voting in regions where voters backed regional parties to counter dominant national parties, influencing coalition outcomes.
Future Prospects: The Evolving Role of Voter Strategy
Future prospects in voter strategy highlight a shift towards more sophisticated decision-making, where abstention may signal protest or dissatisfaction, influencing political parties to address voter concerns more directly. Tactical voting remains a critical tool for maximizing electoral impact, especially as data analytics and social media enable voters to coordinate more effectively. Emerging technologies and increasing political polarization suggest that both abstention and tactical voting will adapt, reshaping electoral dynamics and party strategies in upcoming elections.
Abstention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com