Ballot stuffing is a fraudulent practice where multiple votes are cast illegally to manipulate the outcome of an election, undermining the democratic process. It threatens the integrity of electoral systems by inflating vote counts and distorting true voter intent. Discover how ballot stuffing occurs and the measures in place to prevent it in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
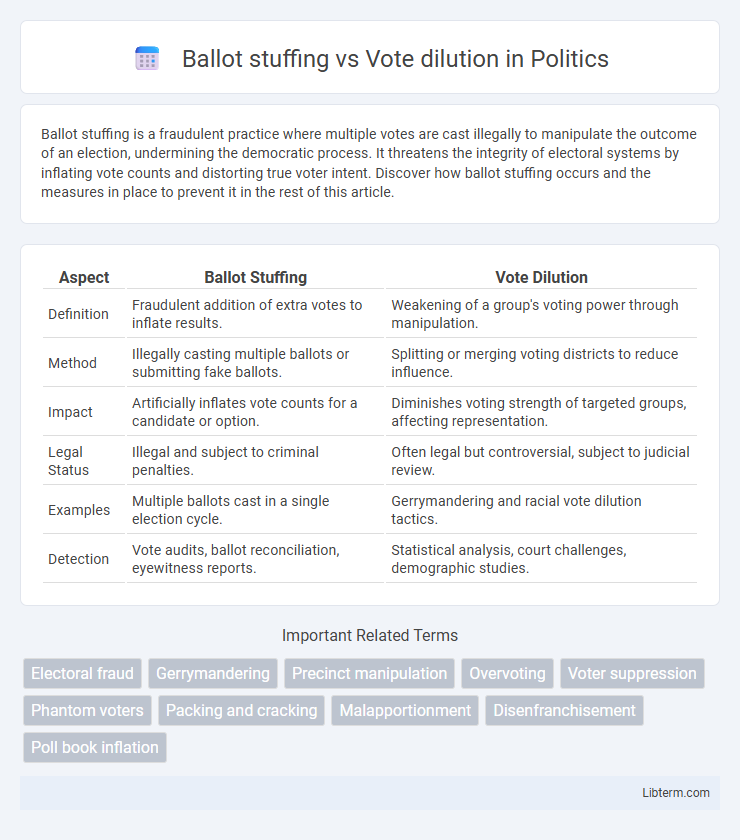
| Aspect | Ballot Stuffing | Vote Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraudulent addition of extra votes to inflate results. | Weakening of a group's voting power through manipulation. |
| Method | Illegally casting multiple ballots or submitting fake ballots. | Splitting or merging voting districts to reduce influence. |
| Impact | Artificially inflates vote counts for a candidate or option. | Diminishes voting strength of targeted groups, affecting representation. |
| Legal Status | Illegal and subject to criminal penalties. | Often legal but controversial, subject to judicial review. |
| Examples | Multiple ballots cast in a single election cycle. | Gerrymandering and racial vote dilution tactics. |
| Detection | Vote audits, ballot reconciliation, eyewitness reports. | Statistical analysis, court challenges, demographic studies. |
Understanding Ballot Stuffing: Definition and Methods
Ballot stuffing is an electoral fraud involving the illegal insertion of multiple ballots into the voting system to artificially inflate votes for a candidate or option. Common methods include the submission of fake ballots, casting votes on behalf of non-existent or ineligible voters, and exploiting weaknesses in vote counting processes. Unlike vote dilution, which reduces the impact of legitimate votes, ballot stuffing directly increases the vote count to manipulate election outcomes.
What Is Vote Dilution? Key Concepts Explained
Vote dilution occurs when the influence of certain voters or demographic groups is weakened, often through tactics like gerrymandering or at-large voting systems that disperse minority votes across many districts. This practice undermines the principle of equal representation by minimizing the electoral power of specific groups, thereby skewing election outcomes. It contrasts with ballot stuffing, which involves the direct addition of fraudulent votes, whereas vote dilution manipulates district boundaries or voting methods to reduce legitimate votes' impact.
Historical Examples of Ballot Stuffing
Ballot stuffing, a fraudulent practice of casting multiple votes illegally to influence election outcomes, has occurred in various historical contexts such as the 1946 Italian general elections and the 1876 U.S. presidential race marked by widespread electoral fraud. This tactic contrasts with vote dilution, where the voting power of certain groups is minimized through district manipulation or restrictive laws rather than direct vote manipulation. Notable cases of ballot stuffing often involve coercion or organized political machines aiming to secure victory by inflating vote totals artificially.
Vote Dilution in Practice: Real-World Cases
Vote dilution occurs when the value of certain votes is minimized, often through practices like gerrymandering or at-large voting systems that weaken minority representation. Real-world cases include the Supreme Court's rulings on racial gerrymandering, such as in Shelby County v. Holder, which addressed the undermining of minority voting power. These instances highlight how vote dilution subtly manipulates electoral boundaries and structures to skew political influence away from marginalized communities.
Comparing Ballot Stuffing and Vote Dilution: Key Differences
Ballot stuffing involves illegal multiple voting to inflate vote counts, directly compromising election integrity by artificially increasing support for a candidate. Vote dilution reduces the impact of legitimate votes by manipulating district boundaries or voter distribution, weakening the electoral influence of specific groups. Both practices undermine democratic processes but differ as ballot stuffing manipulates vote quantity, while vote dilution manipulates vote effectiveness.
Legal Frameworks Against Electoral Manipulation
Legal frameworks against electoral manipulation rigorously address ballot stuffing and vote dilution to safeguard democratic integrity. Ballot stuffing involves illegal addition of ballots, punishable under election fraud statutes that impose strict penalties and oversight mechanisms, such as biometric voter verification and transparent vote counting. Vote dilution, which undermines the value of votes through gerrymandering or discriminatory practices, is countered by constitutional provisions and judicial review processes ensuring equal representation and adherence to the principle of "one person, one vote.
Identifying Signs of Ballot Stuffing
Ballot stuffing is identified by an unusually high number of votes cast from a single location or a sudden surge in voter turnout that exceeds historical patterns. Other signs include identical markings on multiple ballots, discrepancies between the number of votes and the number of voters, and ballot boxes found with more ballots than authorized. Election monitoring authorities should analyze voter lists, verify poll station records, and cross-check surveillance footage to detect potential ballot stuffing incidents effectively.
Recognizing Vote Dilution in Modern Elections
Recognizing vote dilution in modern elections involves identifying tactics that weaken an individual's voting power without outright fraud, such as manipulating district boundaries or purging voter rolls. Unlike ballot stuffing, which inflates vote counts illegally, vote dilution subtly marginalizes specific groups by spreading their votes thinly across multiple districts or imposing restrictive voter ID laws. Detecting these practices requires analyzing election data patterns, demographic shifts, and legal challenges to ensure equitable representation and uphold democratic integrity.
Preventative Measures and Reforms for Fair Elections
Preventative measures against ballot stuffing include centralized biometric voter authentication and secure blockchain-based voting systems to ensure ballot integrity. Reforms targeting vote dilution emphasize redistricting reforms like independent commissions and proportional representation to preserve equal voter influence. Implementing transparent audit trails and public access to election data strengthens accountability and deters both ballot manipulation and vote suppression.
The Impact of Electoral Fraud on Democracy
Ballot stuffing inflates vote counts by submitting multiple fraudulent ballots, directly undermining electoral integrity and skewing election outcomes. Vote dilution weakens individual voting power by manipulating district boundaries or marginalizing certain groups, eroding fair representation. Both forms of electoral fraud compromise democratic legitimacy, reducing public trust and destabilizing governance structures.
Ballot stuffing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com