Investigative journalism uncovers hidden truths through in-depth research and fact-checking, exposing corruption, injustice, and social issues that impact society. This form of journalism often requires persistence, critical analysis, and the ability to navigate sensitive information responsibly. Discover how investigative journalism shapes public awareness and accountability in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
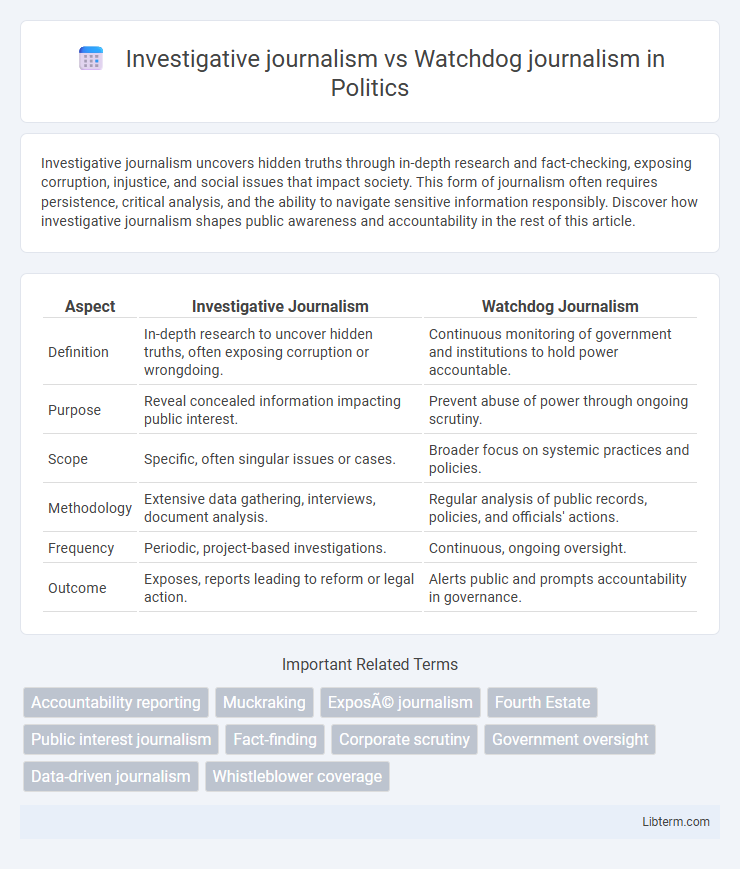
| Aspect | Investigative Journalism | Watchdog Journalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | In-depth research to uncover hidden truths, often exposing corruption or wrongdoing. | Continuous monitoring of government and institutions to hold power accountable. |
| Purpose | Reveal concealed information impacting public interest. | Prevent abuse of power through ongoing scrutiny. |
| Scope | Specific, often singular issues or cases. | Broader focus on systemic practices and policies. |
| Methodology | Extensive data gathering, interviews, document analysis. | Regular analysis of public records, policies, and officials' actions. |
| Frequency | Periodic, project-based investigations. | Continuous, ongoing oversight. |
| Outcome | Exposes, reports leading to reform or legal action. | Alerts public and prompts accountability in governance. |
Defining Investigative Journalism
Investigative journalism is a disciplined process of in-depth research and fact-finding aimed at uncovering hidden truths, corruption, or abuses of power often concealed from the public eye. Unlike watchdog journalism, which continuously monitors institutions for accountability, investigative journalism involves extensive time and resource investment to produce detailed and evidence-based reports that reveal previously unknown information. This form of journalism plays a critical role in democracy by exposing systemic issues and prompting legal or policy reforms through meticulous investigation.
What is Watchdog Journalism?
Watchdog journalism serves as a vital mechanism for holding powerful institutions and public officials accountable by scrutinizing actions that may harm the public interest. It involves continuous monitoring, exposing corruption, abuses of power, and ensuring transparency in government and corporate sectors. This form of journalism empowers citizens with critical information necessary for democratic oversight and civic engagement.
Key Similarities Between Investigative and Watchdog Journalism
Investigative journalism and watchdog journalism both emphasize uncovering hidden truths and holding powerful entities accountable through thorough research and fact-checking. Each type relies on in-depth analysis of complex issues such as corruption, corporate misconduct, and government malfeasance to inform the public and stimulate reform. Both forms play crucial roles in enhancing transparency and promoting democratic governance by exposing wrongdoing and protecting public interest.
Major Differences: Investigative vs Watchdog Approaches
Investigative journalism involves in-depth research and uncovering hidden truths, often requiring extensive time and resources to expose complex issues such as corruption or corporate malfeasance. Watchdog journalism continuously monitors public institutions and officials to hold them accountable and ensure transparency, focusing on timely reporting of abuses or failures. The major difference lies in investigative journalism's project-based, deep-dive nature versus watchdog journalism's ongoing vigilance and immediate public oversight.
Historical Evolution of Investigative and Watchdog Journalism
Investigative journalism emerged prominently in the early 20th century with landmark exposes like the 1906 publication of Upton Sinclair's "The Jungle," which highlighted systemic issues in the meatpacking industry, setting a precedent for deep-dive reporting that uncovers hidden truths. Watchdog journalism evolved concurrently as a broader journalistic approach aimed at holding institutions accountable through ongoing scrutiny, exemplified by the Watergate scandal coverage by The Washington Post in the 1970s. Both forms have historically intertwined, with investigative journalism often serving as the method through which watchdog journalists expose corruption, abuse of power, and societal injustices.
Core Principles and Ethics in Both Journalism Styles
Investigative journalism centers on in-depth research and uncovering hidden facts through rigorous verification, prioritizing accuracy and transparency to uphold public trust. Watchdog journalism emphasizes vigilant oversight of power by exposing wrongdoing and holding institutions accountable, grounded in ethical responsibility and impartiality. Both styles adhere strictly to principles of truthfulness, fairness, and minimizing harm while ensuring the public's right to know remains paramount.
Skills Required for Investigative and Watchdog Journalists
Investigative journalism demands advanced research skills, critical thinking, and the ability to analyze complex data to uncover hidden truths, often requiring expertise in legal frameworks and ethical considerations. Watchdog journalism relies on meticulous attention to detail, persistence in monitoring public institutions, and strong fact-checking abilities to hold power accountable and expose misconduct. Both fields require excellent communication skills to present findings clearly and compellingly to the public.
Impact on Society: Case Studies and Examples
Investigative journalism uncovers hidden truths through in-depth research, exposing corruption as seen in the Watergate scandal, which led to President Nixon's resignation and reinforced democratic accountability. Watchdog journalism continually monitors public institutions, exemplified by the Boston Globe's Spotlight team revealing systemic abuse in the Catholic Church, prompting widespread reform. Both forms catalyze societal change by increasing transparency, influencing public policy, and empowering citizens with critical information.
Challenges Faced by Investigative and Watchdog Journalists
Investigative and watchdog journalists face significant challenges such as legal threats, intimidation, and limited access to confidential sources, which impede their ability to uncover corruption and hold power accountable. The complexity of verifying sensitive information and navigating ethical dilemmas further complicates their work, often requiring substantial time and resources to produce accurate, impactful reports. Financial constraints and shrinking newsroom budgets also hinder sustained investigative efforts, reducing the capacity to pursue long-term investigations that are crucial for transparency and public trust.
The Future of Investigative and Watchdog Journalism
Investigative journalism and watchdog journalism will increasingly rely on advanced data analytics, AI tools, and collaborative platforms to uncover corruption and hold power accountable. Emerging technologies will enable deeper analysis of large datasets, enhancing transparency and public trust in media. Future developments will emphasize cross-border cooperation and real-time reporting to address complex global issues more efficiently.
Investigative journalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com