Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, cultural heritage, and established social orders as foundations for stability and continuity. This political philosophy values cautious change, advocating for policies that uphold individual responsibility, free markets, and limited government intervention. Explore the rest of this article to understand how conservatism shapes contemporary political debates and influences your community.
Table of Comparison
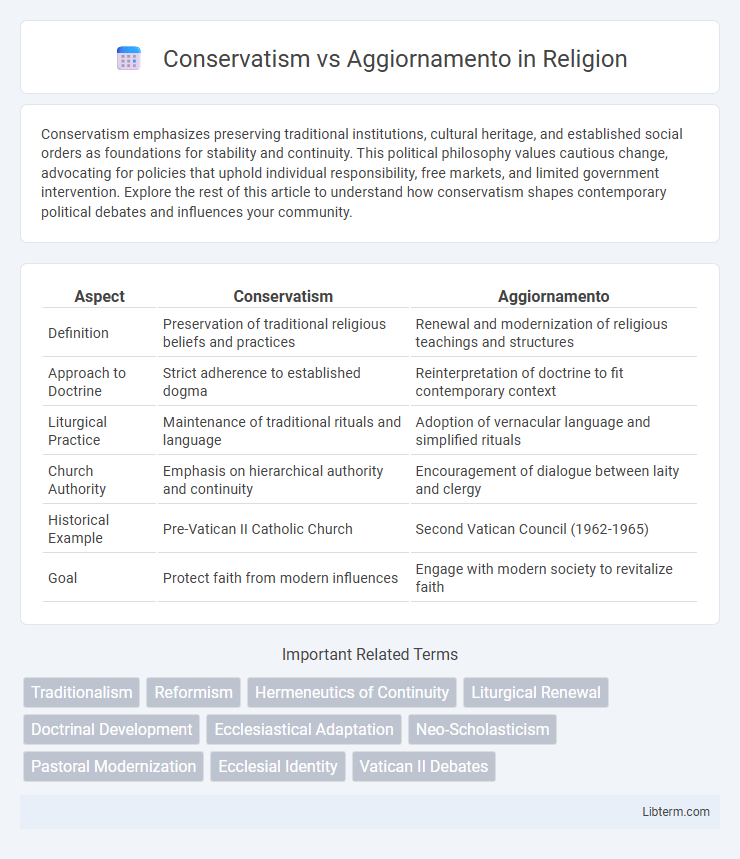
| Aspect | Conservatism | Aggiornamento |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preservation of traditional religious beliefs and practices | Renewal and modernization of religious teachings and structures |
| Approach to Doctrine | Strict adherence to established dogma | Reinterpretation of doctrine to fit contemporary context |
| Liturgical Practice | Maintenance of traditional rituals and language | Adoption of vernacular language and simplified rituals |
| Church Authority | Emphasis on hierarchical authority and continuity | Encouragement of dialogue between laity and clergy |
| Historical Example | Pre-Vatican II Catholic Church | Second Vatican Council (1962-1965) |
| Goal | Protect faith from modern influences | Engage with modern society to revitalize faith |
Introduction: Conservatism and Aggiornamento Defined
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional values, institutions, and practices to maintain social stability and continuity. Aggiornamento, derived from the Italian word meaning "bringing up to date," advocates for reform and modernization within established structures to respond to contemporary challenges. These contrasting approaches shape debates in politics, religion, and social policy, reflecting tensions between maintaining heritage and embracing change.
Historical Roots of Conservatism
Conservatism traces its historical roots to the reaction against the French Revolution, emphasizing the preservation of traditional institutions, social order, and religious values. The ideology champions continuity and skepticism toward rapid change, often advocating for established legal frameworks and hierarchical structures. Its foundations are deeply embedded in the defense of cultural heritage and the maintenance of political stability.
Origins and Meaning of Aggiornamento
Aggiornamento, an Italian term meaning "bringing up to date," originated during the Second Vatican Council (1962-1965) under Pope John XXIII, symbolizing the Church's effort to modernize and engage contemporary society while preserving core doctrines. This concept contrasts with conservatism, which emphasizes maintaining traditional beliefs and practices without significant change. Aggiornamento influenced reforms in liturgy, ecumenism, and Church governance, marking a shift towards renewal and openness within Catholicism.
Key Principles of Conservative Thought
Conservative thought emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, valuing social stability, and respecting established customs and cultural heritage to maintain societal continuity. It prioritizes gradual change over radical reform, advocating for institutions that have demonstrated enduring value rather than experimental innovation. Key principles include a belief in limited government intervention, the importance of moral order, and skepticism towards rapid social transformation.
Core Tenets of Aggiornamento
Aggiornamento, a core concept in modern Catholic reform, emphasizes renewal through engagement with contemporary culture and aggiornamento of Church teachings to address modern challenges. Key tenets include openness to dialogue, adaptation of liturgy, and a pastoral approach prioritizing mercy and inclusivity while maintaining doctrinal continuity. This framework contrasts conservatism's focus on preserving traditional practices, underscoring a dynamic balance between tradition and progress within ecclesiastical contexts.
Conservatism vs Aggiornamento: Points of Conflict
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional doctrines and institutional continuity, while Aggiornamento advocates for updating and reforming practices to address contemporary challenges. The primary conflict lies in resistance from conservative factions against changes proposed to modernize liturgy, social teachings, and ecclesiastical governance. This tension highlights a broader struggle between maintaining established religious identity and embracing adaptation for relevancy in the modern world.
Areas of Convergence and Dialogue
Conservatism and Aggiornamento converge in their shared commitment to preserving core doctrines while addressing contemporary challenges within the Church. Both approaches facilitate dialogue through liturgical renewal and pastoral care, enabling a balanced integration of tradition and modernity. This ongoing exchange fosters unity by promoting thoughtful adaptation without compromising foundational beliefs.
Impact on Society and Culture
Conservatism preserves traditional values and social structures, reinforcing cultural continuity and resistance to rapid change, which often stabilizes societies but may hinder progress and inclusion. Aggiornamento, emphasizing renewal and modernization, drives cultural adaptation and social reform, fostering innovation and inclusivity while challenging established norms. The tension between these approaches shapes societal evolution by balancing heritage preservation with the need for transformation in response to contemporary challenges.
Contemporary Examples and Case Studies
Conservatism in contemporary politics often manifests through policies that prioritize tradition, cultural heritage, and incremental change, as seen in Hungary's emphasis on national identity under Viktor Orban. Aggiornamento, exemplified by Pope Francis' reforms in the Catholic Church, advocates for modernization and engagement with current social issues, such as environmental stewardship and economic inequality. Case studies highlight how conservative governments resist rapid globalization, while aggiornamento-driven institutions pursue adaptability to evolving societal norms.
Future Directions: Balancing Tradition and Renewal
Conservatism prioritizes preserving established traditions and institutional values, ensuring stability and continuity in societal frameworks. Aggiornamento advocates for progressive renewal, emphasizing adaptation to contemporary challenges and fostering innovation within existing structures. Future directions require a strategic balance that integrates enduring cultural principles with necessary reforms to address evolving social, political, and technological landscapes.
Conservatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com