Mysticism explores the direct, personal experience of the divine or ultimate reality beyond ordinary perception. It emphasizes inner transformation, spiritual insight, and the union of the self with a higher power or truth. Discover how mysticism can deepen Your understanding of spirituality by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
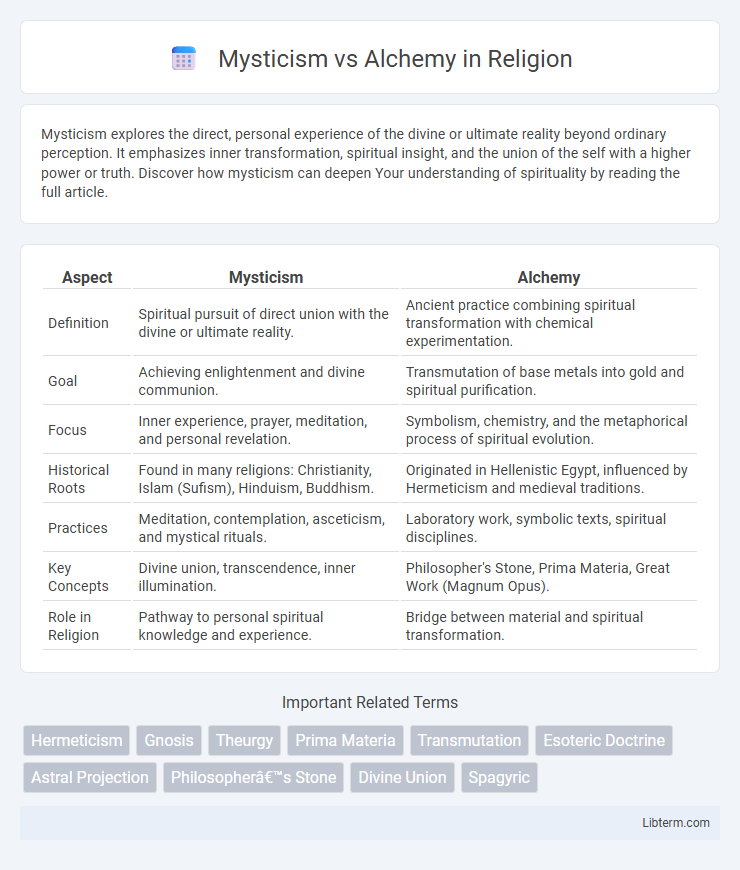
| Aspect | Mysticism | Alchemy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual pursuit of direct union with the divine or ultimate reality. | Ancient practice combining spiritual transformation with chemical experimentation. |
| Goal | Achieving enlightenment and divine communion. | Transmutation of base metals into gold and spiritual purification. |
| Focus | Inner experience, prayer, meditation, and personal revelation. | Symbolism, chemistry, and the metaphorical process of spiritual evolution. |
| Historical Roots | Found in many religions: Christianity, Islam (Sufism), Hinduism, Buddhism. | Originated in Hellenistic Egypt, influenced by Hermeticism and medieval traditions. |
| Practices | Meditation, contemplation, asceticism, and mystical rituals. | Laboratory work, symbolic texts, spiritual disciplines. |
| Key Concepts | Divine union, transcendence, inner illumination. | Philosopher's Stone, Prima Materia, Great Work (Magnum Opus). |
| Role in Religion | Pathway to personal spiritual knowledge and experience. | Bridge between material and spiritual transformation. |
Defining Mysticism: Key Concepts and Foundations
Mysticism centers on the pursuit of direct, personal experience with the divine or ultimate reality through practices such as meditation, contemplation, and prayer. Key concepts include unity with the cosmos, transcendence of the ego, and inner transformation leading to spiritual enlightenment. Foundations of mysticism span diverse traditions but share the goal of achieving profound spiritual insight beyond ordinary perception.
Alchemy Explained: Origins and Core Principles
Alchemy, rooted in ancient Egypt and Hellenistic philosophy, combines elements of science, spirituality, and proto-chemistry aimed at transmuting base metals into noble metals like gold. Central principles include the Philosopher's Stone, believed to enable transformation and immortality, and the concept of the four classical elements--earth, water, air, fire--interacting through processes such as calcination, dissolution, and coagulation. Alchemy's legacy significantly influenced modern chemistry and medicine, intertwining mystical symbolism with early scientific experimentation.
Historical Evolution of Mysticism and Alchemy
Mysticism and alchemy evolved as intertwined yet distinct traditions during the Middle Ages, with mysticism emphasizing direct spiritual experiences and inner transformation, while alchemy focused on the physical transmutation of matter and the pursuit of the philosopher's stone. Alchemy's origins trace back to Hellenistic Egypt, blending Greek philosophy, Egyptian metallurgy, and Islamic science, whereas mysticism draws from diverse religious traditions, including Christian, Jewish Kabbalah, and Sufi practices. The Renaissance period further shaped their evolution, as mysticism deepened the quest for divine knowledge and alchemy advanced proto-scientific experimentation that laid groundwork for modern chemistry.
Philosophical Differences Between Mysticism and Alchemy
Mysticism emphasizes personal spiritual experience and the pursuit of divine union through contemplation and inner knowledge, while alchemy focuses on material transformation and the symbolic process of turning base metals into gold as a metaphor for spiritual refinement. Mysticism values transcendence beyond physical reality, whereas alchemy combines practical experimentation with esoteric philosophy grounded in physical substances. The philosophical divergence lies in mysticism's prioritization of metaphysical enlightenment versus alchemy's integration of spiritual growth with tangible, artisanal processes.
Spiritual Aims: Mystical Union vs Alchemical Transformation
Mysticism centers on achieving a direct, personal union with the divine or ultimate reality, emphasizing spiritual enlightenment and inner transcendence. Alchemy focuses on the transformation of both matter and the self, symbolizing spiritual purification and the attainment of perfection through symbolic processes like the transmutation of base metals into gold. While mysticism seeks experiential knowledge of the sacred, alchemy integrates spiritual goals with physical and symbolic practices aimed at holistic transformation.
Symbolism and Language in Mysticism and Alchemy
Mysticism employs symbolic language rooted in spiritual experience, using metaphors and archetypes to convey ineffable truths and inner transformation. Alchemy utilizes a codified system of symbols and allegories representing physical and chemical processes, aiming to transmute substances and achieve spiritual enlightenment. Both disciplines rely on esoteric symbolism, but mysticism emphasizes direct experiential knowledge, while alchemy integrates symbolic language with material and philosophical experimentation.
Influential Figures in Mysticism and Alchemy
Influential figures in mysticism include Meister Eckhart, whose teachings emphasized direct experience of the divine, and Jakob Bohme, known for integrating Christian mysticism with alchemical symbolism. In alchemy, Paracelsus revolutionized the practice by combining chemical processes with medical applications, while Isaac Newton devoted significant study to alchemical texts alongside his scientific work. The contributions of these key individuals shaped the philosophical and practical foundations of mysticism and alchemy, blending spirituality with early scientific inquiry.
Mysticism and Alchemy in World Religions
Mysticism in world religions emphasizes direct, personal experience of the divine and transcendent states through practices such as meditation, prayer, and contemplation, found prominently in Christianity, Islam (Sufism), Hinduism, and Buddhism. Alchemy, historically interwoven with religious traditions, blends spiritual symbolism with early chemical experimentation aiming at transformation and enlightenment, notably influencing Hermeticism and medieval European Christian mystics. Both mysticism and alchemy seek transcendence and spiritual perfection, yet mysticism prioritizes inner union with the divine while alchemy emphasizes physical and symbolic transformation.
Modern Interpretations and Practices
Modern interpretations of mysticism emphasize personal spiritual experiences and inner transformation, often integrating psychology and meditation techniques to explore consciousness. Alchemy today is viewed less as a literal quest for turning base metals into gold, and more as a symbolic framework for psychological and spiritual growth, particularly in Jungian psychology. Contemporary practitioners blend these traditions to seek holistic understanding, combining ancient esoteric symbolism with modern therapeutic practices.
Mysticism vs Alchemy: Lasting Impact on Culture and Science
Mysticism and alchemy have both shaped culture and science by influencing philosophical thought, spiritual practices, and early scientific experimentation. Mysticism contributed to cultural frameworks through its emphasis on inner experience and transcendence, impacting religious traditions and artistic expressions worldwide. Alchemy laid foundational principles for modern chemistry and medicine by pioneering experimental methods and the search for material transformation.
Mysticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com