Blasphemy refers to the act of showing disrespect or irreverence toward sacred beliefs, deities, or religious symbols, often considered offensive in many cultures. Understanding the legal and social implications of blasphemy is essential to navigate sensitive discussions without causing harm. Explore the detailed analysis to learn how blasphemy laws vary worldwide and what they mean for your rights and freedoms.
Table of Comparison
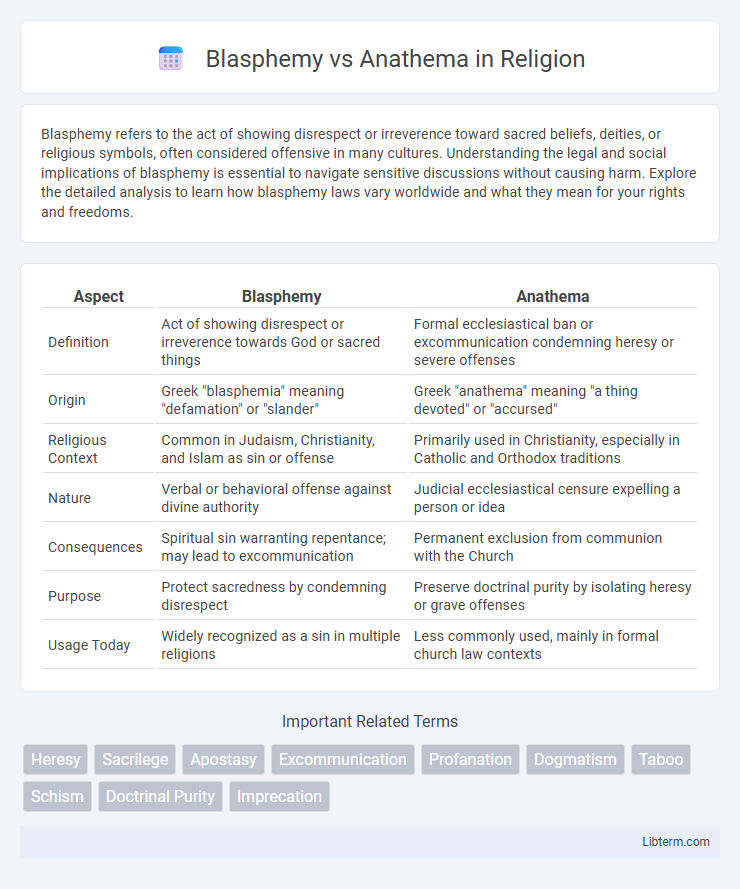
| Aspect | Blasphemy | Anathema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Act of showing disrespect or irreverence towards God or sacred things | Formal ecclesiastical ban or excommunication condemning heresy or severe offenses |
| Origin | Greek "blasphemia" meaning "defamation" or "slander" | Greek "anathema" meaning "a thing devoted" or "accursed" |
| Religious Context | Common in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam as sin or offense | Primarily used in Christianity, especially in Catholic and Orthodox traditions |
| Nature | Verbal or behavioral offense against divine authority | Judicial ecclesiastical censure expelling a person or idea |
| Consequences | Spiritual sin warranting repentance; may lead to excommunication | Permanent exclusion from communion with the Church |
| Purpose | Protect sacredness by condemning disrespect | Preserve doctrinal purity by isolating heresy or grave offenses |
| Usage Today | Widely recognized as a sin in multiple religions | Less commonly used, mainly in formal church law contexts |
Understanding Blasphemy: Definition and Origins
Blasphemy is the act of showing disrespect or irreverence toward sacred entities, religious figures, or divine concepts, often expressed through speech or actions that offend religious sensibilities. Originating from the Greek word *blasphemia*, meaning "evil-speaking" or "slander," blasphemy has historically been considered a serious offense across various religions, including Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. Understanding blasphemy involves recognizing its role as an infringement upon sacred traditions and its potential to provoke social and legal consequences within religious communities.
Anathema Explained: Historical and Theological Roots
Anathema originated in early Christian theology as a formal ecclesiastical ban or excommunication pronounced upon heretics and those deemed irredeemably opposed to Church doctrine. Historically, it identified individuals or teachings that were condemned and separated from the Christian community, often accompanied by solemn curses or declarations of divine judgment. Theologically, anathema represents a total rejection of heretical beliefs and serves as a boundary marker distinguishing orthodox faith from doctrinal deviation, contrasting with blasphemy, which refers primarily to offensive speech against the sacred.
Key Differences: Blasphemy vs Anathema
Blasphemy involves speech or actions that show disrespect or irreverence toward God or sacred things, often considered a sin in many religions. Anathema refers to a formal ecclesiastical curse or excommunication, signifying a person or doctrine that is officially condemned by the church. The key difference lies in blasphemy being an individual offensive act or utterance, while anathema is an institutional judgment imposing religious exclusion or denunciation.
Religious Contexts: How Faiths Interpret Blasphemy
Blasphemy is commonly understood in religious contexts as the act of showing disrespect or irreverence toward sacred entities, deities, or doctrines, often considered a grave offense across many faiths such as Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. Anathema, originating primarily in early Christian traditions, refers to a formal ecclesiastical ban or excommunication, designating a person or belief as accursed and outside the community of faith. While blasphemy denotes the act of profane speech or behavior against the divine, anathema represents the institutionalized condemnation used by religious authorities to maintain doctrinal purity and communal boundaries.
Anathema in Religious Doctrine and Practice
Anathema in religious doctrine refers to a formal ban or excommunication pronounced by ecclesiastical authority, often implying everlasting condemnation and separation from the faith community. It differs from blasphemy, which is an act of disrespect or irreverence toward sacred entities, as anathema carries institutional weight in enforcing doctrinal purity and discipline within the church. Historical examples include the Eastern Orthodox Church's use of anathemas to condemn heresies, highlighting its role in preserving theological orthodoxy.
Legal Implications: Blasphemy Laws Around the World
Blasphemy laws remain in force in over 30 countries, often carrying severe penalties such as imprisonment or fines for speech or actions deemed disrespectful to sacred beliefs. Nations like Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and Iran enforce strict blasphemy statutes, frequently resulting in legal prosecution and sometimes capital punishment. Conversely, many Western countries have abolished blasphemy laws, emphasizing freedom of expression while navigating complex debates on religious tolerance and hate speech regulations.
Historical Examples: Cases of Blasphemy and Anathema
Historical cases of blasphemy include the trial of Galileo Galilei in 1633, where his heliocentric views were condemned as heretical by the Catholic Church, reflecting accusations of disrespect toward established religious doctrine. The Council of Ephesus in 431 AD pronounced the anathema against Nestorius for advocating the separation of Christ's human and divine natures, marking an early example of religious excommunication and condemnation. In medieval Europe, the Cathars were anathematized for their dualistic beliefs, while figures like Giordano Bruno faced charges of blasphemy for challenging orthodox theological concepts.
Modern Perspectives on Blasphemy and Anathema
Modern perspectives on blasphemy emphasize its evolving legal and social ramifications, with many countries shifting from strict penalties to prioritizing freedom of speech and religious tolerance. Anathema, traditionally a formal ecclesiastical curse or excommunication, is increasingly viewed as a historical concept rather than a contemporary tool in religious or social contexts. Contemporary discourse often distinguishes blasphemy's public impact from anathema's internal religious function, reflecting a broader move towards pluralism and human rights.
Cultural Impact: Society's Response to Blasphemy
Blasphemy, often viewed as a direct offense against sacred beliefs, frequently triggers social outrage, legal repercussions, and cultural censorship across various societies. The response to blasphemy ranges from public protests and social ostracism to stringent laws in countries with dominant religious influences, reflecting the deep intertwining of religion and cultural identity. In contrast, anathema carries a formal religious condemnation with lasting communal exclusion, shaping social dynamics primarily within specific religious contexts rather than broader societal frameworks.
Navigating Controversy: Debates Surrounding Blasphemy and Anathema
Blasphemy and anathema are often debated in religious and legal contexts due to their implications on freedom of expression and doctrinal authority. Blasphemy involves irreverence or disrespect toward sacred entities or deities, whereas anathema signifies formal excommunication or condemnation by religious authorities, highlighting differing scopes and responses to perceived heresy. Navigating controversy requires understanding their historical usage in various cultures and legal frameworks, balancing respect for religious beliefs with protection of individual rights.
Blasphemy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com