Ascension refers to the act of rising to a higher position or level, whether physically, spiritually, or metaphorically. Understanding the different contexts of ascension can deepen your comprehension of growth and progression in various aspects of life. Explore the rest of the article to discover how ascension impacts your journey and development.
Table of Comparison
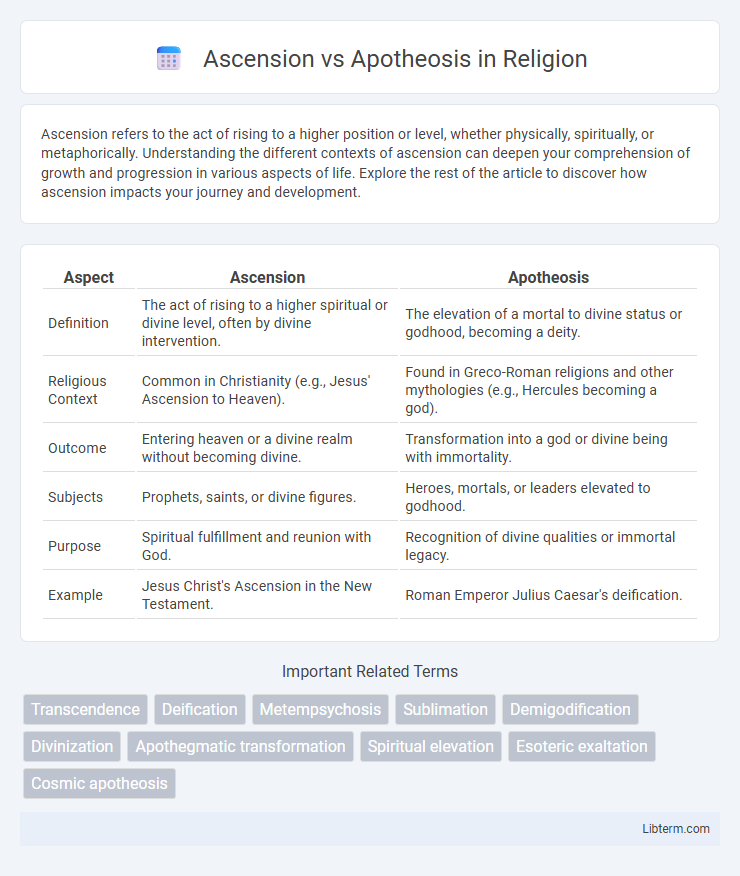
| Aspect | Ascension | Apotheosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The act of rising to a higher spiritual or divine level, often by divine intervention. | The elevation of a mortal to divine status or godhood, becoming a deity. |
| Religious Context | Common in Christianity (e.g., Jesus' Ascension to Heaven). | Found in Greco-Roman religions and other mythologies (e.g., Hercules becoming a god). |
| Outcome | Entering heaven or a divine realm without becoming divine. | Transformation into a god or divine being with immortality. |
| Subjects | Prophets, saints, or divine figures. | Heroes, mortals, or leaders elevated to godhood. |
| Purpose | Spiritual fulfillment and reunion with God. | Recognition of divine qualities or immortal legacy. |
| Example | Jesus Christ's Ascension in the New Testament. | Roman Emperor Julius Caesar's deification. |
Understanding Ascension: A Philosophical Overview
Ascension represents the transformative process of rising to a higher spiritual or metaphysical state, often associated with enlightenment or self-realization. Apotheosis, by contrast, denotes the elevation of an individual to divine status, typically within religious or mythological contexts. Philosophically, ascension emphasizes personal growth and transcendence beyond physical limitations, while apotheosis centers on the deification and ultimate glorification of a figure.
Defining Apotheosis: Concept and Origins
Apotheosis refers to the elevation of an individual to divine status, often characterized by glorification and deification within religious or cultural contexts. Rooted in ancient Greco-Roman traditions and various mythologies, apotheosis signifies the transformation from mortal to godlike being, symbolizing ultimate perfection or supreme honor. This concept underscores the spiritual or symbolic immortalization distinct from the physical or spiritual ascent implied in ascension.
Historical Contexts: Ascension and Apotheosis in Mythology
Ascension and apotheosis both represent transcendence but differ in historical contexts within mythology; ascension often describes a mortal being elevated to a divine realm or status through divine will or merit, such as Jesus Christ's rise to heaven in Christian tradition. Apotheosis, prevalent in Greco-Roman mythology, involves a hero or ruler being deified posthumously, exemplified by Julius Caesar's elevation to godhood by the Roman Senate. These concepts reflect ancient cultural understandings of divinity, immortality, and the human-divine relationship, influencing religious and imperial ideology.
Key Differences Between Ascension and Apotheosis
Ascension refers to the act of rising or moving upward, often implying a literal or spiritual elevation to a higher position, whereas apotheosis signifies the process of deification or glorification, transforming an individual into a divine status. Key differences lie in ascension being primarily a physical or metaphysical ascent, while apotheosis involves the elevation to god-like qualities and ultimate reverence. Ascension is commonly depicted in religious or mythological contexts as ascendant travel, whereas apotheosis connotes the transformation into an immortal, worshipped figure.
Similarities and Overlapping Themes
Ascension and Apotheosis both represent transformative processes signifying a transition from a mortal or ordinary state to a divine or exalted condition, often involving spiritual elevation and enlightenment. Both concepts emphasize transcendence, immortality, and the attainment of higher power or status within religious or mythological frameworks. They share overlapping themes of rebirth, purification, and the merging of human and divine qualities, illustrating humanity's aspiration for ultimate spiritual perfection.
Ascension in Religion and Spirituality
Ascension in religion and spirituality refers to the process by which an individual transcends the physical realm to achieve a higher state of existence or divine status, often accompanied by spiritual enlightenment and closeness to the divine. It is a significant concept in Christianity, exemplified by the Ascension of Jesus Christ, symbolizing the transition from earthly life to a heavenly, glorified state. Ascension emphasizes the transformative journey of the soul, highlighting spiritual growth, liberation, and union with higher powers.
Apotheosis in Art and Literature
Apotheosis in art and literature represents the elevation of a character or figure to divine status, often symbolizing ultimate heroism or transcendence. This theme is prevalent in classical works such as Dante's "Divine Comedy," where mortal souls achieve godlike enlightenment, and in Renaissance art, exemplified by Raphael's frescoes depicting deified figures. Apotheosis serves as a powerful metaphor for transformation and idealized perfection, contrasting with the more literal concept of ascension often linked to physical or spiritual rise.
Cultural Interpretations and Symbolism
Ascension represents the lifting of a mortal being to a divine or higher state, commonly seen in Christian theology as Christ's transition from earthly life to heaven, symbolizing spiritual elevation and redemption. Apotheosis, often rooted in classical Greco-Roman culture, involves the deification of a human, such as emperors or heroes, symbolizing ultimate honor and immortalization within a pantheon. Both concepts reflect cultural interpretations of transformation, where ascension emphasizes a spiritual journey and apotheosis highlights the bestowal of divine status and eternal glory.
Modern Perspectives on Transcendence
Modern perspectives on transcendence distinguish Ascension as a physical or spiritual elevation often linked to religious contexts, while Apotheosis emphasizes the transformation into a divine or god-like status. Scholars analyze Ascension through psychological frameworks highlighting self-improvement and enlightenment journeys, whereas Apotheosis is explored in cultural studies as symbolic of ultimate human potential and societal ideals. Contemporary spirituality integrates both concepts, reflecting evolving understandings of transcendence that merge personal growth with collective transcendental aspirations.
Ascension vs Apotheosis: Which Resonates Today?
Ascension and apotheosis represent distinct spiritual concepts: ascension refers to the process of rising to a higher state of consciousness or existence, while apotheosis denotes the elevation of an individual to divine status. In contemporary discourse, ascension resonates more deeply as it aligns with personal growth, awakening, and transformative experiences that emphasize inner evolution rather than external deification. The modern emphasis on self-realization and holistic spirituality underscores ascension as a more relevant framework compared to traditional apotheosis narratives.
Ascension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com