Incarnation refers to the embodiment of a deity or spirit in a physical form, often seen in religious and philosophical contexts as a divine presence taking human shape. This concept plays a crucial role in various faiths, symbolizing the union of the spiritual and material worlds to convey deeper meanings about existence and salvation. Explore the rest of the article to discover how incarnation shapes beliefs and influences cultures across history.
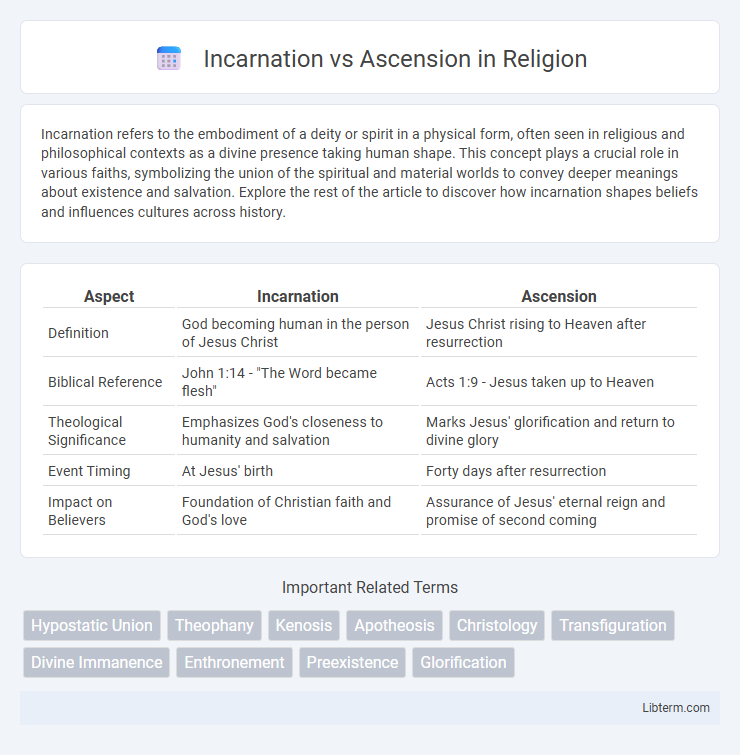
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Incarnation | Ascension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | God becoming human in the person of Jesus Christ | Jesus Christ rising to Heaven after resurrection |
| Biblical Reference | John 1:14 - "The Word became flesh" | Acts 1:9 - Jesus taken up to Heaven |
| Theological Significance | Emphasizes God's closeness to humanity and salvation | Marks Jesus' glorification and return to divine glory |
| Event Timing | At Jesus' birth | Forty days after resurrection |
| Impact on Believers | Foundation of Christian faith and God's love | Assurance of Jesus' eternal reign and promise of second coming |
Understanding Incarnation: Definition and Origins
The Incarnation refers to the Christian doctrine that God became flesh in the person of Jesus Christ, embodying both divine and human natures. Originating from the Greek term "Encarnein," meaning "to make flesh," this concept is central to Christology and foundational to understanding salvation history. The Nicene Creed affirms the Incarnation, emphasizing its significance in God's redemptive plan.
The Concept of Ascension Explained
The concept of Ascension refers to the event where Jesus Christ rose bodily into heaven after His resurrection, signifying His exaltation and divine authority. Unlike the Incarnation, which emphasizes God becoming human through Jesus Christ, Ascension highlights the completion of His earthly mission and His enthronement at the right hand of God. This doctrine underscores the belief in Jesus' ongoing heavenly ministry and the promise of eternal life for believers.
Historical Roots of Incarnation and Ascension
The historical roots of Incarnation trace back to early Christian theology, particularly in the Gospel of John, where Jesus is described as the Word made flesh, symbolizing God becoming human. Ascension finds its origins in post-resurrection narratives, especially in Luke-Acts, depicting Jesus' return to heaven 40 days after resurrection, signifying the completion of his earthly mission and the promise of eternal life. Both doctrines emerged from the early church's efforts to articulate the divine and human nature of Christ and his ongoing spiritual authority.
Key Differences Between Incarnation and Ascension
Incarnation refers to the embodiment of a divine being in human form, most notably seen in Christian theology where God became Jesus Christ. Ascension, on the other hand, describes the event where Jesus Christ rose to heaven in bodily form after his resurrection. The key differences lie in incarnation as the divine entering the human realm, while ascension signifies the departure from the human realm back to the divine, marking two distinct moments in Christian doctrinal history.
Incarnation in Major World Religions
Incarnation in major world religions often signifies a divine being taking human form, with Hinduism highlighting avatars like Krishna as manifestations of Vishnu, while Christianity centers on Jesus Christ as God becoming flesh. This theological concept emphasizes the union of the divine and human, enabling direct interaction with the world. Contrastingly, Ascension typically refers to a divine figure's rise to a transcendental realm after earthly life, underscoring completion rather than embodiment.
Ascension in Spiritual Traditions
The Ascension is a pivotal event in Christian spirituality symbolizing Jesus Christ's return to divine glory, often interpreted as the soul's journey complete with transformation and enlightenment in various spiritual traditions. It reflects the belief in transcendence beyond the physical realm, representing spiritual elevation and reunion with the divine source, resonating in mysticism and esoteric teachings. Emphasizing Ascension highlights the ultimate spiritual goal of unity with the divine, contrasting with Incarnation which focuses on divine manifestation within the human experience.
Theological Implications of Incarnation
The Incarnation, the theological doctrine that God became flesh in the person of Jesus Christ, underscores the union of divine and human natures, enabling redemption through a fully human experience of suffering and grace. This foundational event emphasizes God's willingness to enter human history and offers believers a tangible connection to divine love and salvation. The Ascension, while affirming Christ's exaltation and divine authority, builds upon the Incarnation's premise by demonstrating the completion of the redemptive mission and the promise of the Holy Spirit's guidance.
Ascension: Symbolism and Spiritual Significance
The Ascension symbolizes Christ's triumph over death and His return to divine glory, emphasizing the fulfillment of His redemptive mission and the promise of eternal life. Spiritually, it signifies the believers' hope for transcendence and the call to partake in the heavenly realm through faith and spiritual growth. This event marks the transition from Jesus' earthly ministry to His eternal intercession, serving as a foundational doctrine for Christian hope and the anticipation of the Second Coming.
Modern Interpretations: Incarnation vs Ascension
Modern interpretations of the Incarnation emphasize God's embodiment in Jesus Christ, highlighting themes of divine empathy and relational presence in human experience. Conversely, the Ascension is viewed as the exaltation of Christ, symbolizing the transition from physical presence to spiritual authority and ongoing intercession at the divine right hand. Contemporary theological discourse often explores the Incarnation and Ascension as complementary realities that shape Christian identity, emphasizing the balance between immanence and transcendence in modern faith practice.
Choosing the Path: Personal and Collective Impact
Choosing the path between Incarnation and Ascension shapes both personal growth and collective consciousness by emphasizing grounded human experience versus spiritual transcendence. Incarnation invites deep connection with physical reality and empathy, fostering transformation through lived challenges and relationships. Ascension focuses on elevating awareness and expanding spiritual dimensions, promoting unity and higher states of collective enlightenment.
Incarnation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com