Salafi Islam emphasizes a return to the practices of the earliest Muslim community, focusing on strict adherence to the Quran and Sunnah. It advocates for a literal interpretation of religious texts and rejects later innovations or cultural influences in faith. Discover how Salafi beliefs impact modern Islamic thought and practice throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
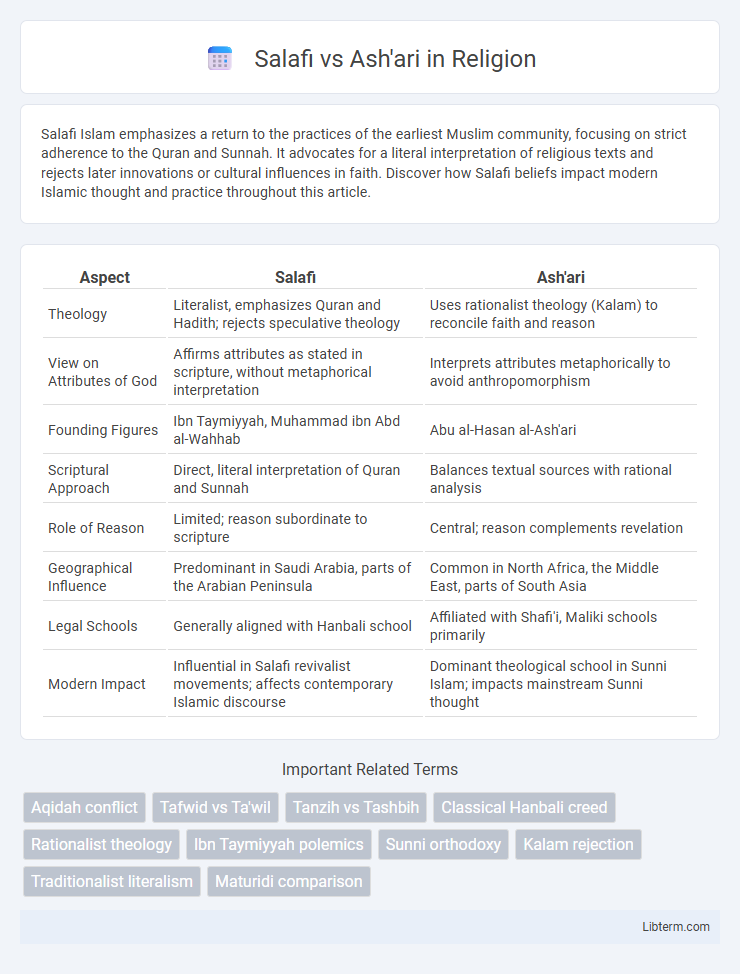
| Aspect | Salafi | Ash'ari |
|---|---|---|
| Theology | Literalist, emphasizes Quran and Hadith; rejects speculative theology | Uses rationalist theology (Kalam) to reconcile faith and reason |
| View on Attributes of God | Affirms attributes as stated in scripture, without metaphorical interpretation | Interprets attributes metaphorically to avoid anthropomorphism |
| Founding Figures | Ibn Taymiyyah, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab | Abu al-Hasan al-Ash'ari |
| Scriptural Approach | Direct, literal interpretation of Quran and Sunnah | Balances textual sources with rational analysis |
| Role of Reason | Limited; reason subordinate to scripture | Central; reason complements revelation |
| Geographical Influence | Predominant in Saudi Arabia, parts of the Arabian Peninsula | Common in North Africa, the Middle East, parts of South Asia |
| Legal Schools | Generally aligned with Hanbali school | Affiliated with Shafi'i, Maliki schools primarily |
| Modern Impact | Influential in Salafi revivalist movements; affects contemporary Islamic discourse | Dominant theological school in Sunni Islam; impacts mainstream Sunni thought |
Understanding Salafism: Core Beliefs and Historical Roots
Salafism emphasizes strict adherence to the Quran and Sunnah as understood by the first three generations of Muslims (Salaf al-Salih), advocating a literal and purist interpretation of Islamic texts. The movement arose in the 18th century through scholars like Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, aiming to purge innovations (bid'ah) and restore authentic monotheism (Tawhid). Salafism contrasts with the Ash'ari theological school, which embraces rationalist methods and occasional metaphorical interpretations in understanding divine attributes.
The Foundations of Ash'ari Theology
Ash'ari theology fundamentally centers on reconciling faith with reason, emphasizing divine omnipotence and occasionalism, where God's will is the ultimate cause of all events. Key doctrines include affirming God's attributes without anthropomorphism and prioritizing textual evidence from the Quran and Hadith while interpreting ambiguous verses metaphorically. Unlike Salafi literalism, Ash'arism employs kalam (rational theology) to defend orthodox Sunni beliefs against philosophical and heretical challenges.
Key Doctrinal Differences Between Salafis and Ash'aris
Salafis emphasize a literal interpretation of the Quran and Sunnah, advocating for a return to the practices of the Salaf (early Muslims), while Ash'aris adopt rational theology (kalam) to reconcile faith with reason. Salafis reject metaphorical explanations of divine attributes, affirming them as they appear, whereas Ash'aris interpret these attributes metaphorically to avoid anthropomorphism. The Salafi creed underscores strict adherence to textual evidence, contrasting with the Ash'ari approach that balances revelation and rational interpretation in creed formulation.
Interpretations of Divine Attributes
Salafi interpretations emphasize a literal understanding of divine attributes, affirming them as they appear in the Quran and Sunnah without metaphorical explanation, aiming to avoid any distortion or negation. Ash'ari theology employs a more metaphorical or allegorical approach, asserting that divine attributes should be interpreted in a manner befitting God's transcendence, often invoking ta'wil (rational reinterpretation) to prevent anthropomorphism. This fundamental difference shapes their respective theological frameworks and influences broader Islamic thought on God's nature.
Approaches to Quranic Text and Hadith
The Salafi approach to the Quranic text and Hadith emphasizes a literal and textually apparent interpretation, advocating for understanding scripture in its clear, direct meaning without metaphorical or allegorical readings. In contrast, the Ash'ari methodology incorporates interpretative principles, allowing for metaphorical explanations and rational analysis to reconcile scriptural descriptions with theological concepts. Salafis prioritize strict adherence to the earliest generations' practices, while Ash'aris integrate kalam (theological discourse) to systematize belief with a balance between textual evidence and reason.
Views on Reason and Theological Inquiry
Salafi theology prioritizes strict adherence to the Quran and Sunnah, emphasizing literal interpretation and generally cautions against extensive rational speculation in theological matters to avoid innovation (bid'ah). Ash'ari theology embraces rational inquiry and kalam (Islamic scholastic theology), permitting the use of reason to interpret divine attributes and resolve theological dilemmas while maintaining scriptural fidelity. The Ash'ari approach allows metaphorical interpretation and theological debate, whereas Salafism advocates for clear, apparent meanings to preserve orthodox beliefs.
Historical Evolution of the Salafi-Ash'ari Discourse
The historical evolution of the Salafi-Ash'ari discourse traces back to early Islamic theological debates where Ash'arism, founded by Imam al-Ash'ari in the 10th century, sought a middle path emphasizing rationality within Sunni orthodoxy. Salafism emerged later, primarily in the 18th century under scholars like Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, advocating a return to the practices of the Salaf (the first three generations of Muslims) and rejecting Ash'ari kalam theology as an unwarranted innovation (bid'ah). This discourse intensified through colonial and modern eras, influencing contemporary Sunni thought, with Salafism promoting scriptural literalism and Ash'arism emphasizing theological nuance and interpretative tradition.
Modern-Day Influence and Geographic Distribution
Salafi Islam holds significant influence in regions such as Saudi Arabia, the Gulf States, and parts of North Africa, where its emphasis on a literal interpretation of the Quran and Hadith shapes contemporary religious education and practices. Ash'ari theology predominantly influences areas like Egypt, Jordan, and parts of the Levant, promoting a rationalist approach to creed that blends tradition with philosophical inquiry. Both movements play crucial roles in shaping modern Islamic discourse, educational curricula, and inter-sectarian relations across the Muslim world.
Intra-Muslim Relations: Dialogue and Tensions
Salafi and Ash'ari theological schools represent significant currents within Sunni Islam, often generating both dialogue and tension in intra-Muslim relations due to differing emphases on scriptural interpretation and rationalism. Salafis advocate a literalist approach to the Quran and Hadith, stressing the practices of the early Muslim community, while Ash'aris adopt a more metaphorical and rationalist framework, integrating theological reasoning to harmonize faith and intellect. These divergent methodologies contribute to debates on creed and jurisprudence, occasionally leading to intra-Muslim conflicts, but also fostering ongoing theological discussions essential for religious pluralism and unity in the Muslim world.
Impact on Contemporary Islamic Thought
Salafi and Ash'ari schools have significantly shaped contemporary Islamic thought by influencing theological interpretations and jurisprudential approaches. Salafi emphasis on scriptural literalism fosters a return to early Islamic practices, impacting modernist and revivalist movements globally. Ash'ari theology, advocating rationalism and theological moderation, underpins many mainstream Sunni institutions, promoting intellectual integration and coexistence within diverse Muslim societies.
Salafi Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com