Skepticism encourages questioning assumptions and demands evidence before accepting claims, fostering critical thinking and intellectual curiosity. Embracing skepticism can protect you from misinformation and help develop a more nuanced understanding of complex issues. Explore the full article to discover how skepticism can transform your approach to knowledge and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
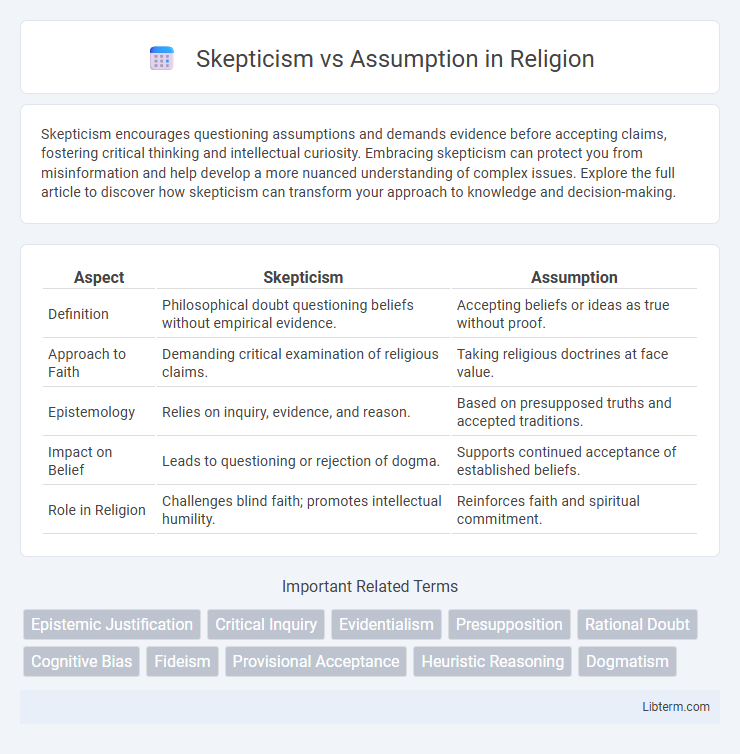
| Aspect | Skepticism | Assumption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical doubt questioning beliefs without empirical evidence. | Accepting beliefs or ideas as true without proof. |
| Approach to Faith | Demanding critical examination of religious claims. | Taking religious doctrines at face value. |
| Epistemology | Relies on inquiry, evidence, and reason. | Based on presupposed truths and accepted traditions. |
| Impact on Belief | Leads to questioning or rejection of dogma. | Supports continued acceptance of established beliefs. |
| Role in Religion | Challenges blind faith; promotes intellectual humility. | Reinforces faith and spiritual commitment. |
Understanding Skepticism: A Rational Approach
Understanding skepticism involves questioning claims and seeking evidence before accepting them as true. This rational approach prioritizes critical thinking and empirical validation over unexamined assumptions. Emphasizing doubt as a tool, skepticism helps prevent cognitive biases and supports more reliable knowledge acquisition.
What Is Assumption? The Basis of Unquestioned Belief
Assumption refers to accepting something as true without requiring proof or evidence, forming the basis of unquestioned belief that influences reasoning and decision-making. Unlike skepticism, which demands critical evaluation and evidence before acceptance, assumptions often operate unconsciously and shape perceptions and actions implicitly. Understanding the role of assumptions is crucial for distinguishing between justified knowledge and beliefs taken for granted.
The Origins of Skeptical Thinking
Skeptical thinking originated in ancient Greece with philosophers like Pyrrho and the Academic Skeptics, who questioned the certainty of knowledge and emphasized inquiry over assumption. This tradition challenged dogmatic beliefs by advocating for continuous questioning and evidence-based conclusions rather than accepting assertions without critical evaluation. The evolution of skepticism significantly influenced modern scientific methods, promoting doubt as a catalyst for deeper understanding and intellectual rigor.
Types of Assumptions in Everyday Life
Assumptions in everyday life often fall into categories such as normative assumptions, which guide behavior based on social norms, and existential assumptions, which relate to beliefs about reality and existence. Predictive assumptions anticipate future events based on past experiences, while interpretive assumptions influence how information and situations are understood. Recognizing these types can help differentiate between unbiased skepticism and unexamined acceptance in decision-making processes.
Cognitive Bias: Fueling Assumptions and Challenging Skepticism
Cognitive biases such as confirmation bias and availability heuristic fuel assumptions by filtering information to fit preexisting beliefs, leading to overconfidence in unverified conclusions. Skepticism challenges these biases by promoting critical thinking and demanding empirical evidence before accepting claims. Recognizing and mitigating cognitive biases is essential to balance healthy skepticism and prevent unfounded assumptions in decision-making.
Benefits of Adopting Skepticism in Decision-Making
Adopting skepticism in decision-making enhances critical thinking by encouraging thorough evaluation of evidence and reducing cognitive biases, leading to more informed and reliable conclusions. Skepticism fosters a culture of questioning assumptions, which minimizes risk and prevents costly errors in judgment. This approach improves problem-solving skills and supports adaptive strategies in dynamic environments by promoting continuous learning and evidence-based decisions.
Assumptions: Risks and Consequences in Reasoning
Assumptions in reasoning pose significant risks by introducing biases that can distort conclusions and hinder critical analysis. Unexamined assumptions often lead to flawed judgments or decisions, especially when they rely on incomplete or incorrect information. Evaluating and challenging these underlying premises is crucial to avoiding errors and ensuring sound, evidence-based reasoning.
Skepticism vs. Assumption in Scientific Inquiry
Skepticism in scientific inquiry demands rigorous evidence and continuous questioning of hypotheses, ensuring conclusions are based on verifiable data rather than preconceived beliefs. Assumption, on the other hand, risks biasing research outcomes by accepting hypotheses without sufficient empirical support, potentially hindering objective analysis. Emphasizing skepticism fosters critical thinking and methodological rigor essential for the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Overcoming the Dangers of Unquestioned Assumptions
Unquestioned assumptions often lead to cognitive biases and flawed decision-making, hindering critical thinking and innovation. Employing skepticism fosters a questioning mindset that challenges preconceived notions, promoting comprehensive analysis and evidence-based conclusions. By actively scrutinizing assumptions, individuals and organizations enhance problem-solving accuracy and reduce the risk of errors rooted in unchecked beliefs.
Cultivating Healthy Skepticism for Critical Thinking
Cultivating healthy skepticism enhances critical thinking by encouraging careful evaluation of information and evidence before accepting claims. Skepticism involves questioning assumptions and seeking verifiable proof, reducing the risk of bias or misinformation. Developing this mindset empowers individuals to make informed decisions and fosters intellectual rigor in problem-solving.
Skepticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com