Polytheism involves the belief in and worship of multiple deities, each often representing different aspects of nature or human experience. This religious system has shaped many ancient civilizations and continues to influence cultural traditions worldwide. Explore the rest of the article to understand how polytheism impacts various societies and your worldview.
Table of Comparison
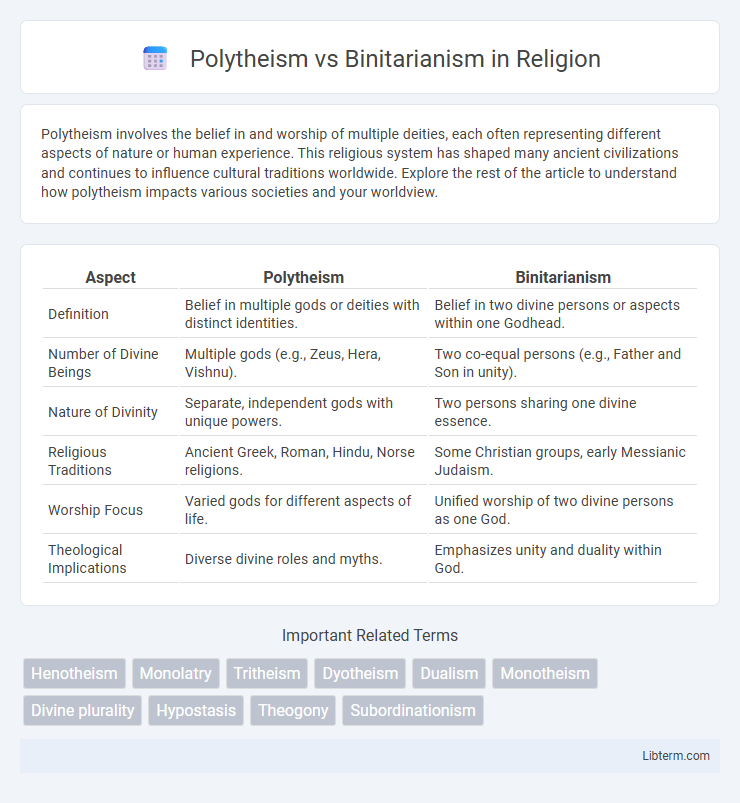
| Aspect | Polytheism | Binitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in multiple gods or deities with distinct identities. | Belief in two divine persons or aspects within one Godhead. |
| Number of Divine Beings | Multiple gods (e.g., Zeus, Hera, Vishnu). | Two co-equal persons (e.g., Father and Son in unity). |
| Nature of Divinity | Separate, independent gods with unique powers. | Two persons sharing one divine essence. |
| Religious Traditions | Ancient Greek, Roman, Hindu, Norse religions. | Some Christian groups, early Messianic Judaism. |
| Worship Focus | Varied gods for different aspects of life. | Unified worship of two divine persons as one God. |
| Theological Implications | Diverse divine roles and myths. | Emphasizes unity and duality within God. |
Understanding Polytheism: Definition and Core Beliefs
Polytheism is the belief in and worship of multiple deities, each representing different aspects of life, nature, and cosmos, often organized into a pantheon with specific roles and attributes. Core beliefs center on the idea that these gods possess distinct personalities, powers, and domains, influencing human affairs and natural phenomena. Polytheistic traditions emphasize rituals, myths, and temples dedicated to various gods, reflecting a diverse and complex spiritual worldview.
Binitarianism Explained: Origins and Tenets
Binitarianism, rooted in early Christian theology, posits that God exists as two distinct persons or aspects--the Father and the Son--united in one divine essence, differing from traditional Trinitarian doctrine. Originating from biblical interpretations emphasizing the close relationship between God the Father and Jesus Christ, binitarianism emphasizes the unity and distinction within the Godhead without the inclusion of a third person, the Holy Spirit as a separate entity. Central tenets include the worship of both divine persons as one God, rejection of polytheism's multiple gods, and adherence to scriptural teachings that highlight the Father-Son bond as foundational to understanding God's nature.
Historical Development of Polytheistic Religions
Polytheistic religions emerged in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece, characterized by the worship of multiple gods representing natural forces, human experiences, and societal roles. These religions developed intricate mythologies and priesthoods that influenced cultural, political, and social structures over millennia. Polytheism's historical development contrasts with binitarianism, which centers on the worship of two divine persons, primarily seen in early Christian theological debates.
Scriptural Foundations of Binitarianism
Binitarianism finds its scriptural foundation primarily in passages that highlight the unity and distinction of God's two persons, such as in Matthew 28:19, where Jesus commands baptizing "in the name of the Father, and of the Son, and of the Holy Spirit," emphasizing a triadic yet unified divine identity. John 1:1 and John 10:30 illustrate the divine coexistence and oneness of the Father and the Son, underpinning the Binitarian view that God exists as two distinct persons sharing one essence. Unlike Polytheism, which posits multiple gods with separate divine wills, Binitarianism maintains monotheism through scriptural affirmations of one God in two persons.
Key Differences in Divine Structure
Polytheism posits multiple gods with distinct powers and personalities, often governing different aspects of the universe, while Binitarianism centers on two divine persons or entities coexisting within one Godhead. In polytheistic systems, gods operate independently or in complex hierarchies, whereas Binitarianism emphasizes unity and coequality between the two persons, such as the Father and the Son. The core distinction lies in polytheism's multiplicity of deities versus Binitarianism's dual-person unity within a singular divine essence.
Worship Practices: Many Gods vs. Two Persons
Polytheism involves the worship of many gods, each with distinct roles, attributes, and rituals, often requiring diverse ceremonies and offerings tailored to different deities. In contrast, Binitarianism centers on the worship of two divine persons within one Godhead, typically emphasizing a unified devotional practice focused on both figures simultaneously. This difference results in polytheistic practices being more varied and numerous, while Binitarian worship maintains a more centralized and dual-focused liturgy.
Philosophical Implications of Polytheism and Binitarianism
Polytheism presents a philosophical framework that emphasizes a multiplicity of divine agents, fostering a worldview where diverse and often competing forces shape reality, which raises questions about the nature of unity and moral absolutes. Binitarianism, by contrast, posits a dual-aspect unity within the divine, suggesting a more integrated approach to understanding relationality and personhood in theology, challenging strict monotheistic and polytheistic boundaries. The philosophical implications of these beliefs impact metaphysics, ethics, and epistemology by influencing concepts of divine interaction, authority, and the source of moral law.
Influence on Culture and Society
Polytheism deeply shaped ancient civilizations by fostering diverse mythologies, rituals, and artistic expressions that reinforced social hierarchies and community cohesion. Binitarianism, emphasizing a dual divine nature, influenced religious doctrines and liturgical practices, particularly within early Christian contexts, promoting theological debates on unity and distinction in the Godhead. Both belief systems impacted societal values and governance, with polytheism encouraging pluralism and binitarianism shaping monotheistic frameworks centered on dual divine aspects.
Modern Interpretations and Controversies
Modern interpretations of polytheism emphasize the worship of multiple deities, each representing distinct aspects of life and nature, often found in contemporary Pagan and Neopagan movements. Binitarianism, recognizing two divine persons within one Godhead, especially in some Christian sects, faces controversy over its theological divergence from traditional Trinitarian doctrine, challenging mainstream Christian orthodoxy. Debates continue on the scriptural validity and historical development of both beliefs, influencing interfaith dialogues and religious identity in modern spiritual landscapes.
Comparative Analysis: Polytheism vs. Binitarianism
Polytheism encompasses the belief in multiple gods, each with distinct roles and attributes, while Binitarianism centers on the worship of two divine persons coexisting within a single Godhead, typically the Father and the Son. Polytheistic systems often involve a pantheon of gods influencing various aspects of life and nature, contrasting with Binitarianism's emphasis on a dual divine unity reflecting a complex monotheistic framework. This comparative analysis reveals fundamental differences in theological structure, divine plurality, and the nature of divine relationships within each belief system.
Polytheism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com