Krishna represents a central figure in Hindu mythology, embodying divine love, wisdom, and heroism celebrated in texts like the Bhagavad Gita and Mahabharata. His teachings on dharma and devotion guide millions toward spiritual growth and ethical living. Explore the rich stories and profound lessons about Krishna throughout this article to deepen your understanding.
Table of Comparison
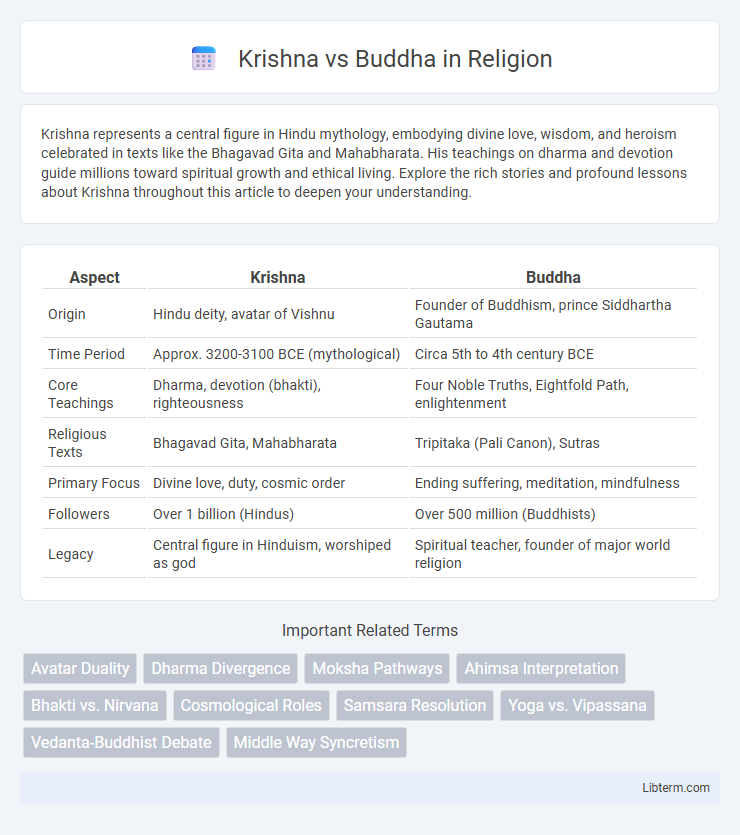
| Aspect | Krishna | Buddha |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Hindu deity, avatar of Vishnu | Founder of Buddhism, prince Siddhartha Gautama |
| Time Period | Approx. 3200-3100 BCE (mythological) | Circa 5th to 4th century BCE |
| Core Teachings | Dharma, devotion (bhakti), righteousness | Four Noble Truths, Eightfold Path, enlightenment |
| Religious Texts | Bhagavad Gita, Mahabharata | Tripitaka (Pali Canon), Sutras |
| Primary Focus | Divine love, duty, cosmic order | Ending suffering, meditation, mindfulness |
| Followers | Over 1 billion (Hindus) | Over 500 million (Buddhists) |
| Legacy | Central figure in Hinduism, worshiped as god | Spiritual teacher, founder of major world religion |
Introduction: Understanding Krishna and Buddha
Krishna is a major deity in Hinduism, revered as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and a central figure in the Bhagavad Gita, symbolizing divine love, duty, and righteousness. Buddha, the founder of Buddhism, is known as Siddhartha Gautama, whose teachings focus on enlightenment through the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path. Both figures represent transformative spiritual leaders whose philosophies have profoundly influenced Indian culture and religious thought.
Historical Contexts of Krishna and Buddha
Krishna is a central figure in Hinduism, traditionally dated around 1500-500 BCE, depicted as a divine prince and charioteer in the Mahabharata, embodying dharma and cosmic order. Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama, emerged in the 6th to 4th century BCE India, specifically in the northeastern region, founding Buddhism with teachings centered on enlightenment and the Four Noble Truths. The historical contexts reveal Krishna's association with ancient Vedic traditions and epic narratives, while Buddha's life marks a shift towards philosophical inquiry and spiritual reform in response to social and religious conditions of ancient India.
Philosophical Foundations: Krishna vs Buddha
Krishna's philosophy centers on Bhakti Yoga and the concept of Dharma, emphasizing devotion, righteous duty, and the unity of the individual soul with the Supreme Being as outlined in the Bhagavad Gita. In contrast, Buddha's teachings focus on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, promoting the cessation of suffering through mindfulness, ethical conduct, and mental discipline without reliance on a personal deity. These foundational differences highlight Krishna's theistic framework rooted in cosmic order versus Buddha's non-theistic approach aimed at enlightenment and liberation from samsara.
Core Teachings and Doctrines
Krishna's teachings in the Bhagavad Gita emphasize dharma (duty), bhakti (devotion), and karma yoga (selfless action) as paths to spiritual liberation. Buddha's core doctrines center on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, which guide individuals to overcome suffering through ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom. While Krishna's message integrates devotion to a personal deity, Buddha advocates for a non-theistic approach focused on personal enlightenment and liberation from samsara.
Approaches to Spiritual Liberation
Krishna's approach to spiritual liberation emphasizes bhakti yoga, or devotion to God, as outlined in the Bhagavad Gita, where surrender to the divine and performing one's dharma without attachment leads to moksha. Buddha's path centers on the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, promoting self-discipline, ethical conduct, and meditation to eradicate suffering and achieve Nirvana. Both traditions highlight inner transformation but diverge in their reliance on divine grace versus personal enlightenment through mindfulness and wisdom.
Ethical Practices: Dharma vs Dhamma
Krishna's teachings in the Bhagavad Gita emphasize Dharma as the cosmic law governing duty, righteousness, and social order, guiding individuals to fulfill their roles with moral integrity and devotion. Buddha's concept of Dhamma centers on ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom aimed at overcoming suffering and achieving enlightenment through the Noble Eightfold Path. Both concepts promote ethical living but Krishna's Dharma integrates duty with spiritual devotion, while Buddha's Dhamma focuses on personal liberation through mindfulness and moral purity.
Roles in Indian Culture and Society
Krishna embodies the divine hero and supreme deity in Hinduism, symbolizing love, dharma, and cosmic order, profoundly influencing Indian art, literature, and religious practices. Buddha represents enlightenment and spiritual awakening, founding Buddhism as a path to overcome suffering and attain Nirvana, shaping Indian philosophy and ethical conduct. Both figures profoundly shape Indian cultural values by offering distinct spiritual paradigms--Krishna through devotional worship and mythic narratives, Buddha through ethical teachings and meditation practices.
Depictions in Art, Literature, and Folklore
Krishna is often depicted in vibrant art as a youthful, blue-skinned god playing the flute, symbolizing divine love and joy, while Buddha is portrayed with serene expressions and specific mudras, emphasizing enlightenment and inner peace. Literary works like the Bhagavad Gita highlight Krishna's role as a divine guide in Hinduism, contrasting with Buddhist scriptures such as the Jataka tales that narrate Buddha's past lives and teachings. Folklore surrounding Krishna includes playful and heroic episodes like his childhood antics and the Ras Lila dance, whereas Buddha's stories focus on his journey from prince to enlightened teacher and his compassionate interactions.
Influence on Modern Spirituality
Krishna and Buddha have significantly shaped modern spirituality by offering distinct paths: Krishna emphasizes bhakti yoga, devotion, and the inner divine, influencing practices like meditation and devotional chanting worldwide. Buddha's teachings on mindfulness, suffering, and enlightenment form the foundation of contemporary mindfulness-based stress reduction and secular meditation techniques. Together, their philosophies inspire a fusion of self-realization and compassionate awareness embraced by millions seeking spiritual growth today.
Conclusion: Legacy of Krishna and Buddha
Krishna's legacy endures through the Bhagavad Gita, influencing Hindu philosophy, devotion, and cultural practices worldwide. Buddha's teachings form the foundation of Buddhism, promoting mindfulness, compassion, and the path to enlightenment across diverse cultures. Both figures profoundly shaped spiritual thought, ethical values, and religious traditions for billions throughout history.
Krishna Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com