Engaging in regular sexual activity offers numerous physical and mental health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, reduced stress levels, and strengthened emotional intimacy with your partner. Understanding the impact of sexual wellness on overall well-being can empower you to make informed decisions about your sexual health. Discover more about the advantages and tips for maintaining a healthy sexual lifestyle in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
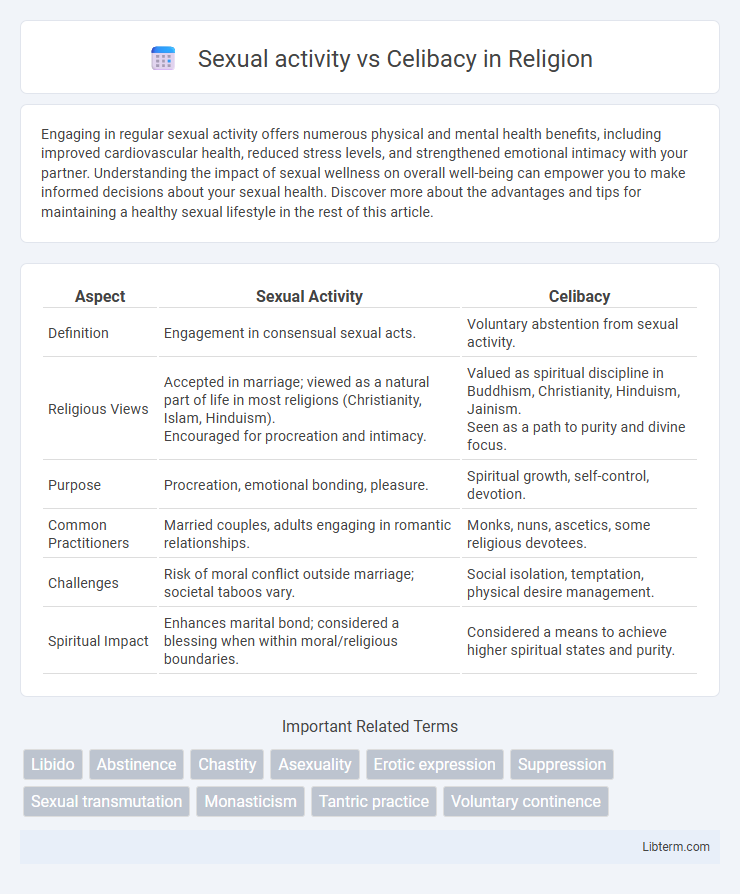
| Aspect | Sexual Activity | Celibacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engagement in consensual sexual acts. | Voluntary abstention from sexual activity. |
| Religious Views |
Accepted in marriage; viewed as a natural part of life in most religions (Christianity, Islam, Hinduism). Encouraged for procreation and intimacy. |
Valued as spiritual discipline in Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Jainism. Seen as a path to purity and divine focus. |
| Purpose | Procreation, emotional bonding, pleasure. | Spiritual growth, self-control, devotion. |
| Common Practitioners | Married couples, adults engaging in romantic relationships. | Monks, nuns, ascetics, some religious devotees. |
| Challenges | Risk of moral conflict outside marriage; societal taboos vary. | Social isolation, temptation, physical desire management. |
| Spiritual Impact | Enhances marital bond; considered a blessing when within moral/religious boundaries. | Considered a means to achieve higher spiritual states and purity. |
Introduction to Sexual Activity and Celibacy
Sexual activity involves physical intimacy between individuals, often driven by biological, emotional, and social factors, and can play a significant role in human relationships and reproduction. Celibacy, by contrast, is the deliberate abstention from sexual activity, commonly practiced for personal, religious, or philosophical reasons to cultivate self-discipline or spiritual growth. Understanding the distinctions between sexual activity and celibacy aids in comprehending diverse lifestyle choices and their impact on physical and mental well-being.
Historical Perspectives on Sexual Practices and Abstinence
Historical perspectives on sexual activity and celibacy reveal diverse cultural values where many ancient societies, including early Christian and Buddhist traditions, revered celibacy as a path to spiritual purity and enlightenment. In contrast, other civilizations such as Ancient Rome and Greece often embraced sexual activity as a natural and integral aspect of social and religious life. These varying attitudes highlight how historical contexts influenced societal norms surrounding sexual practices and abstinence, shaping moral frameworks and personal conduct across eras.
Physical Health Implications of Sexual Activity
Sexual activity contributes to improved cardiovascular health by increasing heart rate and circulation, which can reduce the risk of heart disease. Regular sexual activity also supports a stronger immune system by boosting immunoglobulin A (IgA) levels, enhancing the body's defense against infections. Celibacy, while offering benefits such as reduced risk of sexually transmitted infections, lacks these physical health benefits derived from the physiological responses during sexual activity.
Physical Health Benefits and Risks of Celibacy
Celibacy can contribute to physical health by reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections and allowing the body to focus on healing and immune function. However, prolonged celibacy might also lead to increased stress and potential hormonal imbalances affecting cardiovascular health. Scientific studies connect both sexual activity and celibacy to distinct physiological outcomes, emphasizing the importance of personalized health strategies.
Mental and Emotional Effects of Sexual Relationships
Engaging in sexual activity can enhance mental well-being through the release of endorphins and oxytocin, which reduce stress and promote feelings of intimacy and emotional connection. Conversely, celibacy may offer emotional clarity and reduce anxiety related to sexual pressures or relationship complexities, supporting mental focus and personal growth. Both sexual activity and celibacy uniquely influence psychological health, shaped by individual preferences, emotional needs, and relationship contexts.
Psychological Impact of Choosing Celibacy
Choosing celibacy can lead to enhanced self-awareness and emotional clarity, fostering psychological resilience and personal growth. Studies indicate that celibate individuals often experience reduced anxiety related to romantic relationships and greater focus on long-term goals. However, maintaining celibacy requires strong coping strategies to manage societal pressures and potential feelings of isolation.
Relationship Dynamics: Intimacy vs. Abstinence
Sexual activity enhances relationship dynamics by fostering physical intimacy, emotional bonding, and mutual vulnerability, which often lead to increased trust and satisfaction between partners. Celibacy, on the other hand, shifts focus toward emotional connection, shared values, and non-physical forms of closeness, promoting self-discipline and personal growth within the relationship. Both approaches influence attachment styles and communication patterns, shaping the overall dynamics and stability of the partnership.
Societal and Cultural Views on Sex and Celibacy
Sexual activity is often viewed as a natural and essential part of human relationships across many societies, symbolizing intimacy, reproduction, and social bonding, while celibacy is embraced in various cultures and religions as a means of spiritual discipline, personal purity, or social status. In Western cultures, sex is increasingly normalized and celebrated through media and liberal attitudes, whereas celibacy may be perceived as a personal choice linked to morality or religious conviction. Contrastingly, in conservative or traditional societies, celibacy can be highly respected for its association with self-control and virtue, while sexual activity outside socially sanctioned relationships might be stigmatized or regulated.
Religious and Spiritual Approaches to Sexuality and Celibacy
Religious and spiritual frameworks often approach sexuality and celibacy as distinct pathways to personal and divine fulfillment, with many traditions viewing celibacy as a means to spiritual purity and heightened focus on meditation, prayer, or service. In Christianity, Catholic clergy embrace celibacy to dedicate themselves fully to God, while Hinduism respects both celibate ascetics and those engaged in sacred marital relations. Buddhism emphasizes celibacy in monastic life to transcend desire, whereas many indigenous religions integrate sexual activity within rituals to honor creation and fertility cycles.
Making an Informed Personal Choice: Sexual Activity or Celibacy
Making an informed personal choice between sexual activity and celibacy involves understanding the physical, emotional, and psychological impacts associated with each lifestyle. Sexual activity can enhance intimacy, promote emotional bonding, and provide health benefits such as improved cardiovascular health, while celibacy may offer opportunities for personal growth, focused energy, and reduced risk of sexually transmitted infections. Evaluating personal values, health considerations, and relationship goals helps guide a balanced decision aligned with individual well-being and life priorities.
Sexual activity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com