Soteriology examines the doctrine of salvation, exploring how humanity is redeemed from sin and its consequences through divine intervention. This theological study delves into concepts of grace, faith, and redemption, highlighting their roles in spiritual transformation. Discover more about the profound implications of soteriology and its impact on your understanding of faith throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
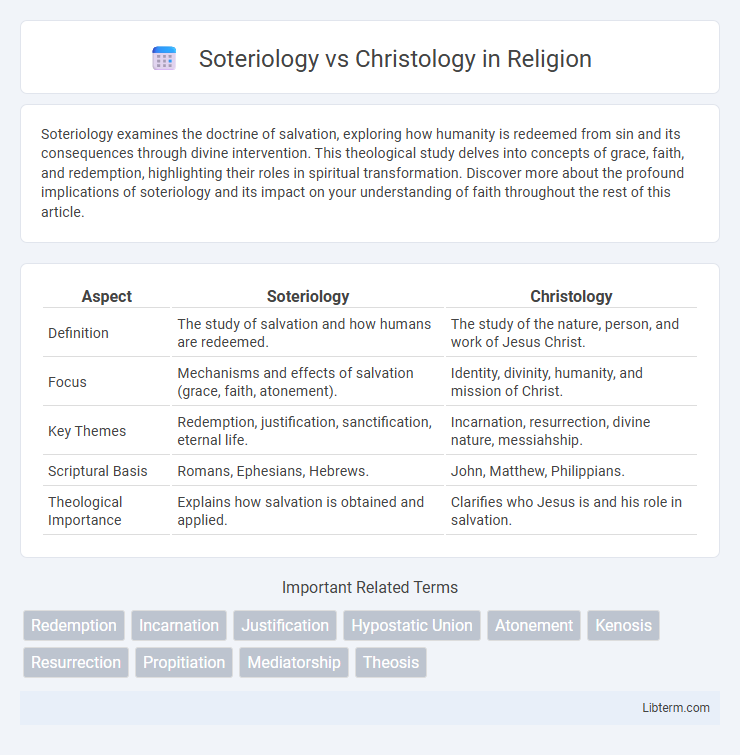
| Aspect | Soteriology | Christology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study of salvation and how humans are redeemed. | The study of the nature, person, and work of Jesus Christ. |
| Focus | Mechanisms and effects of salvation (grace, faith, atonement). | Identity, divinity, humanity, and mission of Christ. |
| Key Themes | Redemption, justification, sanctification, eternal life. | Incarnation, resurrection, divine nature, messiahship. |
| Scriptural Basis | Romans, Ephesians, Hebrews. | John, Matthew, Philippians. |
| Theological Importance | Explains how salvation is obtained and applied. | Clarifies who Jesus is and his role in salvation. |
Introduction to Soteriology and Christology
Soteriology explores the doctrine of salvation, examining how redemption is achieved through faith, grace, and the work of Jesus Christ. Christology focuses on the nature, person, and role of Jesus as the Messiah and Son of God, emphasizing his divine and human attributes. Understanding these theological disciplines provides insight into the relationship between Jesus' identity and the means of salvation in Christian theology.
Defining Soteriology: The Study of Salvation
Soteriology is the theological study focused on the doctrine of salvation, exploring how humanity is redeemed from sin and its consequences. It examines key biblical concepts such as atonement, grace, justification, and sanctification, highlighting the role of Jesus Christ in the salvific process. In contrast, Christology centers on the person and nature of Christ, emphasizing His divinity and humanity, which are foundational for understanding salvation in soteriology.
Defining Christology: Understanding the Nature of Christ
Christology centers on the study of the person, nature, and work of Jesus Christ, emphasizing his dual nature as fully divine and fully human. Soteriology, while related, specifically explores the doctrine of salvation and how Christ's redemptive work reconciles humanity with God. Defining Christology involves examining key theological affirmations such as the Incarnation, the hypostatic union, and the implications of Christ's nature for salvation history.
Historical Development of Soteriology
The historical development of soteriology traces its roots through early Christian debates on salvation, beginning with Pauline epistles emphasizing justification by faith and evolving through Augustine's doctrines of grace and original sin. Medieval scholasticism, particularly Thomas Aquinas, integrated Aristotelian philosophy, refining the understanding of salvation's mechanics, while the Reformation sparked a critical reassessment of soteriology, highlighting sola fide and sola gratia. Modern theological discourse continues to explore soteriology's diverse interpretations within Christology, reflecting evolving doctrines about Christ's role in human redemption.
Historical Evolution of Christological Thought
Christological thought evolved significantly from the early Church Councils, particularly Nicaea (325 AD) and Chalcedon (451 AD), which defined the dual nature of Christ as fully divine and fully human. This historical development influenced Soteriology by framing salvation through the lens of Christ's incarnation, atonement, and resurrection. Debates on Christ's personhood shaped theological understandings of redemption, emphasizing the necessity of both divine and human natures for effective salvation.
Key Doctrinal Differences: Soteriology vs Christology
Soteriology centers on the doctrine of salvation, examining how humanity is redeemed through faith, grace, and the work of Christ, while Christology focuses on the person and nature of Jesus Christ as both fully divine and fully human. Key doctrinal differences include Soteriology's emphasis on atonement, justification, and sanctification, contrasted with Christology's exploration of the incarnation, hypostatic union, and the dual nature of Christ. Theological discussions in Soteriology address the application of salvation to believers, whereas Christology underpins these concepts by defining who Christ is and his role in the redemptive plan.
Interrelationship Between Salvation and the Person of Christ
Soteriology explores the doctrine of salvation, emphasizing how Christ's nature and redemptive work achieve human redemption. Christology focuses on the person and nature of Jesus Christ, central to understanding how salvation is accomplished through his incarnation, atonement, and resurrection. The interrelationship reveals that salvation is inseparable from Christ's identity as both fully divine and fully human, providing the foundation for theological interpretations of redemption.
Major Debates in Soteriological and Christological Theology
Major debates in soteriology center on the nature of salvation, including issues like predestination versus free will, the extent of atonement, and justification by faith or works. Christological discussions focus on the person and nature of Christ, addressing controversies such as the dual nature of Jesus as fully divine and fully human, the hypostatic union, and the implications of Christ's role in redemption. These theological disputes significantly shaped doctrines like the Chalcedonian Definition and Reformed soteriology, influencing Christian orthodoxy and denominational identities.
Soteriology and Christology in Contemporary Theology
Soteriology in contemporary theology emphasizes the multifaceted aspects of salvation, analyzing its implications in personal redemption and social justice through the lens of Christ's salvific work. Christology focuses on the person and work of Jesus Christ, exploring his dual nature as fully divine and fully human, and interpreting his role in salvation history with renewed theological and contextual sensitivity. Both disciplines intersect as contemporary theologians strive to understand how Christ's identity and salvific mission address modern existential and ethical challenges.
Conclusion: The Significance of Integrating Soteriology and Christology
Integrating soteriology and christology reveals the inseparable connection between the person of Jesus Christ and the doctrine of salvation, emphasizing that understanding who Christ is directly impacts how salvation is perceived and received. The study of Christ's nature, incarnation, and redemptive work informs soteriological concepts such as atonement, justification, and sanctification, underscoring that salvation is rooted in Christ's person and work. This integration enhances theological coherence and deepens faith, highlighting that effective salvation theology must account for the fullness of Christ's identity and mission.
Soteriology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com