Anointing is a sacred ritual symbolizing consecration, healing, and divine blessing through the application of oil. It holds deep spiritual significance in various religious traditions, signifying purification, empowerment, and the presence of holiness. Discover how understanding the power of anointing can enrich your spiritual journey by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
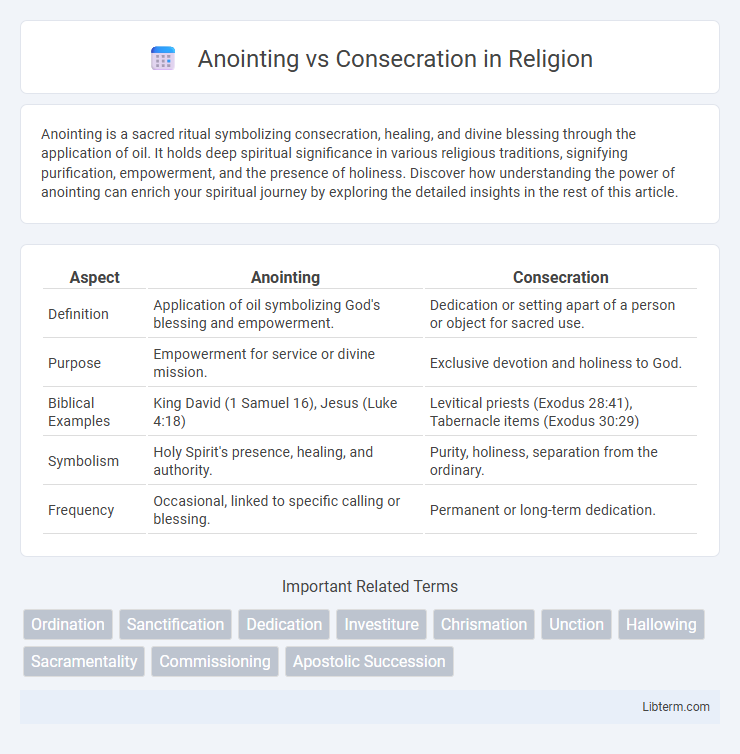
| Aspect | Anointing | Consecration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of oil symbolizing God's blessing and empowerment. | Dedication or setting apart of a person or object for sacred use. |
| Purpose | Empowerment for service or divine mission. | Exclusive devotion and holiness to God. |
| Biblical Examples | King David (1 Samuel 16), Jesus (Luke 4:18) | Levitical priests (Exodus 28:41), Tabernacle items (Exodus 30:29) |
| Symbolism | Holy Spirit's presence, healing, and authority. | Purity, holiness, separation from the ordinary. |
| Frequency | Occasional, linked to specific calling or blessing. | Permanent or long-term dedication. |
Understanding Anointing: Definition and Origins
Anointing involves the ritual application of oil as a symbolic act signifying sanctification, healing, or empowerment, rooted in ancient religious traditions across Judaism and Christianity. Its origins trace back to biblical times when prophets, priests, and kings were anointed to denote divine selection and authority. Understanding anointing requires recognizing its multifaceted role in spiritual identity, ritual purification, and the conferral of God's presence or favor.
What is Consecration? Meaning and Purpose
Consecration is the solemn dedication of a person, object, or place to a sacred purpose, signifying a permanent commitment to divine service. Its primary purpose is to set apart the consecrated entity from ordinary use, establishing it as holy and exclusively devoted to spiritual or religious functions. This ritual often involves specific prayers, blessings, and ceremonies that reinforce the sanctity and intentionality behind the act of consecration.
Historical Significance of Anointing in Spiritual Traditions
Anointing holds profound historical significance in spiritual traditions, symbolizing divine blessing and sanctification across cultures such as ancient Egypt, Judaism, and early Christianity. This ritual, often involving the application of oil, was a key element in consecrating kings, priests, and sacred objects, marking them as chosen by a higher power. The practice underscores a longstanding belief in the transformative power of sacred oil to connect the physical and spiritual realms.
The Biblical Foundation for Anointing and Consecration
The biblical foundation for anointing is rooted in the Old Testament, where oil symbolizes God's presence, empowerment, and sanctification, as seen in the anointing of kings like Saul and David (1 Samuel 10:1; 16:13). Consecration, meanwhile, involves setting people or objects apart for divine purposes, exemplified by the consecration of priests and the tabernacle in Exodus 28-29 and Leviticus 8. Both anointing and consecration underline distinct yet complementary spiritual functions grounded in scripture's emphasis on holiness, divine selection, and empowerment for service.
Key Differences Between Anointing and Consecration
Anointing involves the symbolic act of applying oil to a person or object to signify divine blessing or empowerment, often marking a specific role or mission. Consecration is the formal dedication of a person, place, or item to a sacred purpose, signifying complete separation from ordinary use for religious devotion. Key differences include anointing as a momentary ritual with empowering intent, while consecration represents a permanent, solemn commitment to holiness.
The Process of Anointing: Rituals and Practices
The process of anointing involves the application of sacred oil to a person or object, symbolizing sanctification, healing, or divine empowerment in religious rituals. Typically, anointing is performed by clergy using oils blessed during a liturgical ceremony, with specific prayers and scripture readings enhancing the spiritual significance. This practice is integral in sacraments like baptism, confirmation, and ordination, marking a tangible connection between the individual and God's grace.
Steps and Symbolism in Consecration Ceremonies
Consecration ceremonies involve specific steps such as ritual purification, the formal dedication of objects or individuals to a sacred purpose, and the invocation of divine authority through prayers or chants. Symbolism in consecration often includes the use of holy water, incense, and sacred oils to represent purification, sanctification, and spiritual empowerment. Anointing within consecration is the an application of sacred oil symbolizing the divine presence and blessing, marking a transition to a holy or commissioned state.
Spiritual Impact: Anointing vs. Consecration
Anointing and consecration both hold profound spiritual significance, with anointing symbolizing divine empowerment and healing through the application of oil, often associated with the Holy Spirit's presence and favor. Consecration represents a deeper, lifelong dedication and separation unto God, involving a commitment to holiness, service, and spiritual discipline. The spiritual impact of anointing is often immediate and transformative, while consecration fosters sustained growth and intimate communion with God.
Common Misconceptions About Anointing and Consecration
Common misconceptions about anointing and consecration often confuse the two as identical rituals. Anointing typically involves applying oil as a symbol of divine blessing or empowerment, whereas consecration is a solemn dedication of a person, place, or object to a sacred purpose. Understanding this distinction clarifies their unique spiritual significance in religious practices.
Choosing the Path: When to Seek Anointing or Consecration
Choosing between anointing and consecration depends on the spiritual purpose and context; anointing typically signifies empowerment or healing in specific moments, while consecration involves dedicating a person or object to a sacred purpose permanently. Seek anointing during times of need for divine blessing, protection, or preparation for a particular task, often linked to healing, leadership, or spiritual strengthening. Consecration is appropriate when committing a life, place, or item for ongoing religious service or holiness, reflecting a long-term spiritual commitment within Christian, Jewish, or other liturgical traditions.
Anointing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com