Doctrine defines a structured set of principles guiding beliefs or actions within various fields, such as law, religion, or politics. Understanding doctrine helps clarify complex concepts and ensures consistent application of rules or practices. Discover how doctrine shapes your perspective and influences key decisions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
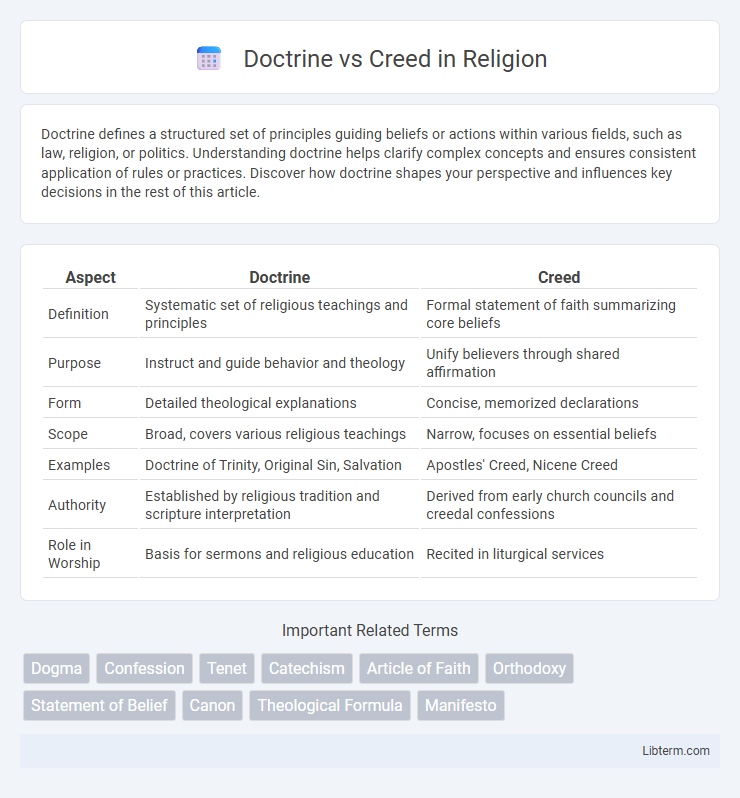
| Aspect | Doctrine | Creed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic set of religious teachings and principles | Formal statement of faith summarizing core beliefs |
| Purpose | Instruct and guide behavior and theology | Unify believers through shared affirmation |
| Form | Detailed theological explanations | Concise, memorized declarations |
| Scope | Broad, covers various religious teachings | Narrow, focuses on essential beliefs |
| Examples | Doctrine of Trinity, Original Sin, Salvation | Apostles' Creed, Nicene Creed |
| Authority | Established by religious tradition and scripture interpretation | Derived from early church councils and creedal confessions |
| Role in Worship | Basis for sermons and religious education | Recited in liturgical services |
Understanding Doctrine and Creed
Doctrine represents a set of official teachings or beliefs formally established by a religious organization, guiding the faith and practice of its adherents. Creed is a concise statement or profession of faith that summarizes core doctrinal beliefs, often recited in communal worship to affirm shared convictions. Understanding the distinction between doctrine and creed is essential for comprehending how religious beliefs are articulated, taught, and confessed within faith communities.
Historical Origins of Doctrines and Creeds
Doctrines originated from early theological debates and councils aiming to establish authoritative teachings, such as the Nicene Creed formed during the First Council of Nicaea in 325 AD to combat Arianism. Creeds function as concise, formal statements of faith that summarize essential doctrines, exemplified by the Apostles' Creed and Nicene Creed, which emerged to unify Christian belief and practice. These historical developments reflect the Church's effort to define orthodoxy and maintain doctrinal consistency across diverse communities.
Key Differences Between Doctrine and Creed
Doctrine refers to a set of formal, authoritative teachings or principles systematically developed and officially endorsed by religious organizations, guiding beliefs and practices. Creed is a concise, declarative statement of faith summarizing core religious beliefs that adherents affirm publicly, often during worship or rites. The key difference lies in doctrine's comprehensive and detailed nature versus creed's brief, formulaic expression of fundamental convictions.
The Role of Doctrine in Religious Practice
Doctrine serves as the structured body of beliefs and teachings that guide religious practice, providing clarity and consistency in interpreting sacred texts and rituals. It shapes moral behavior, ritual observance, and theological understanding, ensuring adherents maintain a cohesive spiritual framework. By defining fundamental principles, doctrine helps preserve religious identity and facilitates communal unity within faith traditions.
The Purpose and Function of a Creed
A creed serves as a concise declaration of core beliefs, providing a unified framework for faith communities to identify and affirm shared doctrines. It functions as a tool for teaching essential theological principles and guiding moral conduct, ensuring consistency across generations. Unlike broader doctrinal systems, creeds distill complex doctrines into accessible, authoritative statements that reinforce communal identity and doctrinal integrity.
Examples of Famous Doctrines and Creeds
The Nicene Creed and the Apostles' Creed stand as prominent examples of Christian creeds, outlining foundational beliefs about the Trinity and the nature of Christ. Famous doctrines such as the Doctrine of the Trinity and the Doctrine of Original Sin define essential theological principles that guide faith and practice within Christianity. These creeds and doctrines serve as authoritative statements that unify believers and clarify core religious tenets.
How Doctrines and Creeds Shape Belief Systems
Doctrines define specific theological principles that guide religious teachings and practices, establishing a detailed framework for interpreting faith. Creeds function as concise, formal statements of core beliefs that unify adherents by summarizing essential doctrines in an accessible format. Both doctrines and creeds shape belief systems by providing authoritative benchmarks that influence religious identity, communal cohesion, and individual faith expression.
Controversies Surrounding Doctrines vs Creeds
Controversies surrounding doctrines versus creeds often stem from their differing roles in defining religious beliefs; doctrines are typically detailed theological teachings subject to interpretation and debate, while creeds are concise, formal statements of faith intended to unify believers. Disputes arise when doctrinal interpretations diverge, leading to schisms, whereas creeds tend to face less controversy due to their fixed, foundational nature. The tension between evolving doctrinal insights and the static authority of creeds highlights ongoing conflicts in religious tradition and authority.
Modern Perspectives on Doctrines and Creeds
Modern perspectives on doctrines emphasize their role as evolving frameworks shaped by contemporary contexts, focusing on adaptability and practical application within religious communities. Creeds function as concise, unifying declarations of core beliefs designed to foster identity and communal cohesion, often resisting frequent alteration to maintain tradition. Both doctrines and creeds continue to influence theological discourse, with doctrines inviting reinterpretation while creeds anchor collective faith through established affirmations.
Doctrine vs Creed: Which Matters More Today?
Doctrine outlines the fundamental beliefs and principles that define a religious or philosophical system, providing a structured framework for faith and practice. Creed, often encapsulated in concise statements like the Nicene Creed, serves as a formal declaration of shared beliefs, fostering unity and identity among adherents. In contemporary contexts, doctrine typically matters more as it guides ethical behavior and theological interpretation, while creed functions as a foundational touchstone that maintains communal coherence.
Doctrine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com