Moksha represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth and rebirth in Hindu philosophy, symbolizing spiritual freedom and self-realization. Attaining Moksha involves deep meditation, ethical living, and transcending worldly attachments to unite your soul with the divine consciousness. Explore the article further to understand the profound path and practices leading to Moksha.
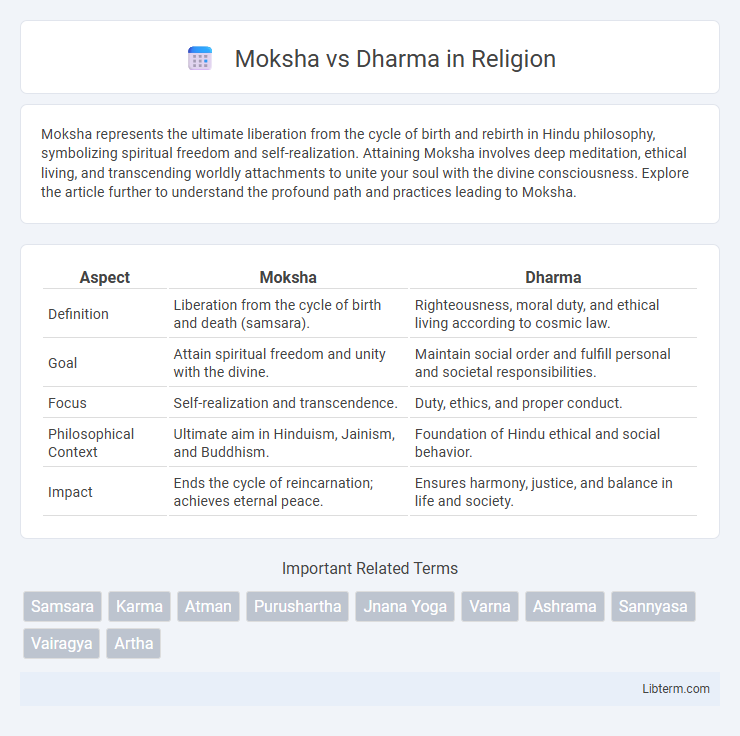
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Moksha | Dharma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Liberation from the cycle of birth and death (samsara). | Righteousness, moral duty, and ethical living according to cosmic law. |
| Goal | Attain spiritual freedom and unity with the divine. | Maintain social order and fulfill personal and societal responsibilities. |
| Focus | Self-realization and transcendence. | Duty, ethics, and proper conduct. |
| Philosophical Context | Ultimate aim in Hinduism, Jainism, and Buddhism. | Foundation of Hindu ethical and social behavior. |
| Impact | Ends the cycle of reincarnation; achieves eternal peace. | Ensures harmony, justice, and balance in life and society. |
Introduction to Moksha and Dharma
Moksha represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth and death, embodying spiritual freedom and self-realization in Hindu philosophy. Dharma signifies the moral and ethical duties guiding individuals in their roles within society and the universe, ensuring order and righteousness. Both concepts are foundational to Indian spiritual thought, shaping personal conduct and the pursuit of life's highest goals.
Defining Moksha: The Ultimate Liberation
Moksha represents the ultimate liberation in Hindu philosophy, signifying freedom from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth (samsara) and the cessation of all suffering and desires. It is achieved through self-realization, detachment from material existence, and union with the supreme consciousness (Brahman). Unlike Dharma, which prescribes moral duties and righteous living, Moksha transcends worldly obligations, embodying spiritual emancipation and eternal bliss.
Understanding Dharma: Duty and Righteousness
Dharma represents the ethical foundation guiding individual actions based on duty, righteousness, and moral law within Hindu philosophy. It emphasizes living in harmony with societal and cosmic order by fulfilling one's responsibilities according to their caste, stage of life, and personal role. Understanding Dharma is crucial for maintaining balance and integrity in life while progressing toward spiritual goals like Moksha.
Historical Contexts of Moksha and Dharma
Moksha and Dharma are pivotal concepts in ancient Indian philosophy, deeply rooted in Vedic traditions and Hindu scriptures such as the Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita. Moksha signifies liberation from the cycle of samsara, representing the ultimate spiritual goal, while Dharma encompasses the moral and ethical duties that sustain societal order and individual righteousness. Historically, interpretations of Dharma have evolved through texts like the Dharmasastras, whereas Moksha has been explored through various schools of Vedanta and Buddhist teachings, reflecting diverse cultural and religious contexts.
Philosophical Differences Between Moksha and Dharma
Moksha represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth and death, emphasizing transcendence and self-realization beyond worldly existence. Dharma refers to the ethical and moral duties one must follow in life, maintaining social order and individual righteousness. While Dharma guides actions within the material world, Moksha signifies the spiritual goal of freedom from all material bindings and suffering.
Interdependence of Moksha and Dharma in Hindu Thought
Moksha and Dharma in Hindu thought are deeply intertwined, with Dharma serving as the ethical and moral foundation necessary for achieving Moksha, the liberation from the cycle of rebirth. Dharma encompasses duties, righteousness, and social responsibilities that guide individuals toward spiritual growth and self-realization, which are essential for attaining Moksha. The pursuit of Moksha is contingent upon the proper observance of Dharma, highlighting their interdependence within Hindu philosophy.
Role of Moksha and Dharma in Daily Life
Moksha represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth and death, guiding individuals toward spiritual freedom and inner peace. Dharma serves as a moral compass, directing daily actions and decisions based on ethical duties and societal responsibilities. Together, Moksha and Dharma balance the pursuit of spiritual goals with practical living, ensuring harmony between personal growth and social order.
Scriptural References to Moksha and Dharma
Moksha, often described in the Upanishads such as the Chandogya and Brihadaranyaka, signifies liberation from the cycle of samsara and the realization of the Atman's unity with Brahman. Dharma, extensively outlined in texts like the Manusmriti and the Bhagavad Gita, embodies the ethical duties and moral law guiding human conduct in accordance with cosmic order. Together, these scriptural references reflect the dual paths of righteous living (dharma) leading toward spiritual liberation (moksha) in Hindu philosophy.
Modern Interpretations of Moksha vs Dharma
Modern interpretations of Moksha emphasize personal liberation and self-realization through mindfulness, meditation, and ethical living, adapting ancient concepts to contemporary spiritual practices. Dharma, in today's context, is understood as one's moral duty and social responsibility, guiding behavior in professional and personal life while fostering social harmony and justice. Both concepts intersect as frameworks for achieving a balanced life with inner freedom and societal contribution.
Conclusion: Balancing the Pursuit of Moksha and Dharma
Balancing the pursuit of Moksha and Dharma involves harmonizing spiritual liberation with ethical living and social responsibility. Moksha represents the ultimate goal of freeing the soul from the cycle of rebirth, while Dharma provides the moral framework guiding righteous action in life. Integrating both ensures a holistic approach to personal growth, combining transcendence with duty.
Moksha Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com