Samsara is a fundamental concept in several Eastern philosophies, representing the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma. Understanding this cycle offers profound insights into the nature of existence and the path to spiritual liberation. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how samsara influences life and spiritual growth.
Table of Comparison
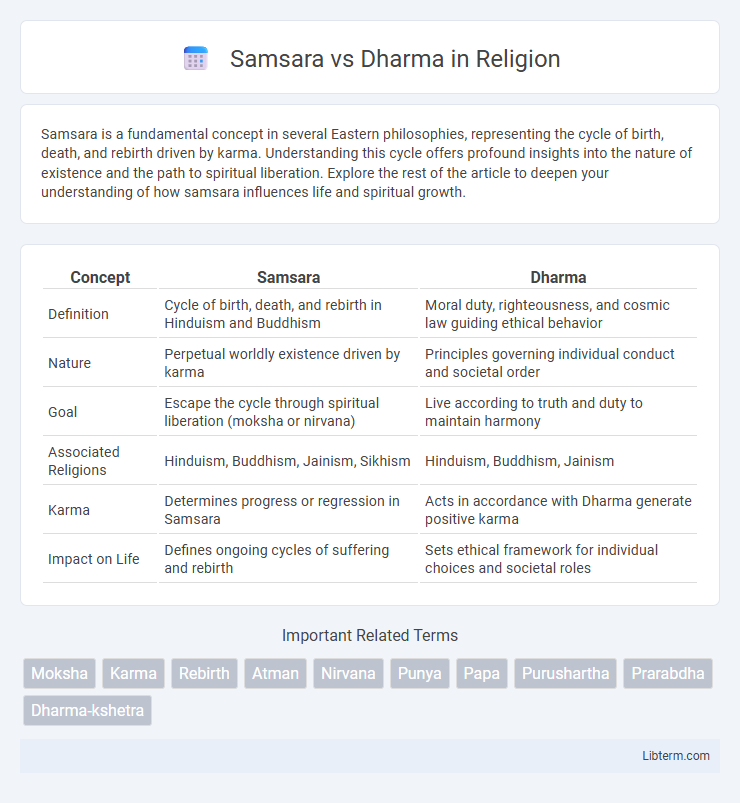
| Concept | Samsara | Dharma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cycle of birth, death, and rebirth in Hinduism and Buddhism | Moral duty, righteousness, and cosmic law guiding ethical behavior |
| Nature | Perpetual worldly existence driven by karma | Principles governing individual conduct and societal order |
| Goal | Escape the cycle through spiritual liberation (moksha or nirvana) | Live according to truth and duty to maintain harmony |
| Associated Religions | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism |
| Karma | Determines progress or regression in Samsara | Acts in accordance with Dharma generate positive karma |
| Impact on Life | Defines ongoing cycles of suffering and rebirth | Sets ethical framework for individual choices and societal roles |
Understanding Samsara: The Cycle of Birth and Death
Samsara refers to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma, where beings experience suffering and attachment. It represents the fundamental problem in Buddhist and Hindu philosophies, emphasizing the impermanence and pain inherent in worldly existence. Understanding Samsara highlights the urgent need for liberation through spiritual practices that lead to enlightenment and freedom from this cycle.
What Is Dharma? Foundations and Principles
Dharma refers to the moral law combined with spiritual discipline that guides one's life in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, emphasizing righteous living and duties aligned with cosmic order. It encompasses ethical principles, social responsibilities, and personal virtues that sustain harmony and balance within society and the universe. Unlike Samsara, which represents the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, Dharma offers the foundational path to break free from this cycle by fulfilling one's duties and living righteously.
The Interplay Between Samsara and Dharma
Samsara represents the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, driven by karma and desires, while Dharma refers to the moral and spiritual duties that guide individuals toward righteousness and liberation. The interplay between Samsara and Dharma lies in how adherence to Dharma can influence one's karma, thereby affecting the quality and progression within Samsara. Following Dharma acts as a pathway to transcend Samsara, enabling the achievement of Moksha or Nirvana, the ultimate freedom from the cycle of existence.
Key Differences: Samsara vs. Dharma
Samsara refers to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, characterized by suffering and attachment in Hinduism and Buddhism. Dharma signifies the moral law, ethical duties, and righteous path that guides individuals toward spiritual growth and liberation from Samsara. The key difference lies in Samsara representing the worldly cycle of existence, while Dharma embodies the principles that help transcend this cycle.
Samsara in Hinduism and Buddhism
Samsara in Hinduism refers to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma, with liberation achieved through moksha by realizing one's true self (Atman) and unity with Brahman. In Buddhism, Samsara represents the endless cycle of suffering and rebirth caused by desire and ignorance, where liberation (nirvana) is attained by following the Noble Eightfold Path to extinguish cravings. Both traditions emphasize Samsara as a fundamental concept explaining life's impermanence and the spiritual goal of transcending this cycle.
Dharma’s Role in Escaping Samsara
Dharma serves as the moral and ethical path guiding individuals toward liberation from Samsara, the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. By adhering to Dharma--righteous duties, spiritual laws, and virtuous conduct--one reduces negative karma, which is the cause of continued existence within Samsara. Mastery of Dharma leads to spiritual evolution and ultimately Moksha, the release from Samsara's endless cycle.
Practical Steps to Align with Dharma
Aligning with Dharma involves cultivating mindfulness, ethical living, and self-awareness to break free from Samsara's cycle of suffering and rebirth. Practicing daily meditation, adhering to moral principles like non-violence and truthfulness, and embracing one's duty promote harmony with universal laws. Consistent reflection on actions and embracing compassion foster spiritual growth and liberation from Samsara's repetitive patterns.
Philosophical Interpretations: Samsara Versus Dharma
Samsara represents the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, symbolizing the soul's continuous journey through suffering and ignorance in Hinduism and Buddhism. Dharma signifies the ethical and moral duties or the universal law that guides individuals toward righteousness and the cessation of samsara. Philosophically, samsara embodies the problem of existence, while dharma offers the practical path to liberation and spiritual harmony.
Common Misconceptions About Samsara and Dharma
Samsara is often misunderstood as mere physical rebirth, while it fundamentally represents the ongoing cycle of birth, death, and suffering driven by ignorance and desires. Dharma is frequently misinterpreted as a rigid set of rules, but it actually denotes the cosmic law and ethical duties guiding individuals towards liberation. Confusing Samsara and Dharma leads to overlooking the transformative role of practicing Dharma to transcend Samsara's cycle of suffering.
Real-Life Applications: Living by Dharma Beyond Samsara
Living by Dharma provides practical guidance for ethical decision-making and mental clarity, enabling individuals to navigate life's challenges with integrity and purpose. It promotes mindfulness, compassion, and self-discipline, which enhance personal growth and social harmony beyond the cyclical suffering associated with Samsara. Applying Dharma in real life cultivates resilience and inner peace, fostering a balanced existence that transcends desire and attachment.
Samsara Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com