Du'a is a powerful act of worship in Islam where believers communicate directly with Allah, seeking guidance, forgiveness, and blessings. It serves as a personal connection that strengthens faith and provides comfort in times of need. Discover how incorporating Du'a into your daily routine can transform your spiritual journey by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
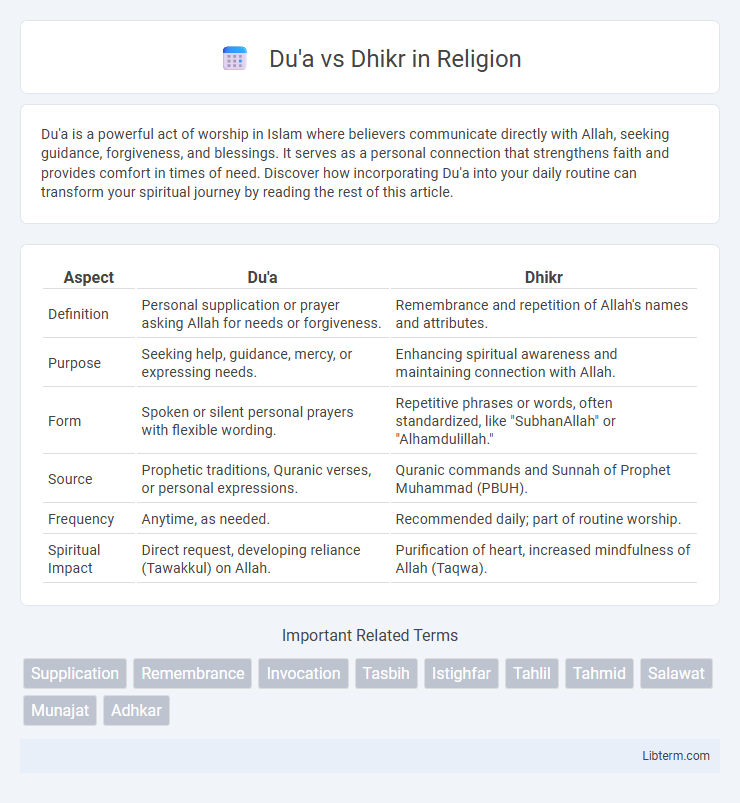
| Aspect | Du'a | Dhikr |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Personal supplication or prayer asking Allah for needs or forgiveness. | Remembrance and repetition of Allah's names and attributes. |
| Purpose | Seeking help, guidance, mercy, or expressing needs. | Enhancing spiritual awareness and maintaining connection with Allah. |
| Form | Spoken or silent personal prayers with flexible wording. | Repetitive phrases or words, often standardized, like "SubhanAllah" or "Alhamdulillah." |
| Source | Prophetic traditions, Quranic verses, or personal expressions. | Quranic commands and Sunnah of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH). |
| Frequency | Anytime, as needed. | Recommended daily; part of routine worship. |
| Spiritual Impact | Direct request, developing reliance (Tawakkul) on Allah. | Purification of heart, increased mindfulness of Allah (Taqwa). |
Understanding the Concepts: What are Du'a and Dhikr?
Du'a is a personal, heartfelt invocation or supplication to Allah, expressing specific requests, gratitude, or seeking forgiveness, while Dhikr involves the repetitive remembrance or glorification of Allah through phrases like "SubhanAllah," "Alhamdulillah," and "Allahu Akbar." Both practices are essential components of Islamic spirituality, aimed at strengthening the believer's connection with the Divine, but Du'a emphasizes direct communication and petitioning, whereas Dhikr focuses on continuously acknowledging and praising God's attributes. Understanding these distinctions highlights how Du'a nurtures a personal dialogue with Allah, and Dhikr cultivates mindfulness and constant awareness of His presence.
The Linguistic Roots of Du'a and Dhikr
Du'a and Dhikr both originate from Arabic linguistic roots that emphasize communication with the Divine; Du'a stems from the root "d-'-w," meaning to call or summon, highlighting a petitionary or supplicatory aspect. Dhikr derives from the root "dh-k-r," meaning to remember or mention, emphasizing continuous remembrance and mindfulness of God. The distinct etymological backgrounds reflect Du'a as an active prayer seeking help and Dhikr as a meditative practice affirming God's presence.
Key Differences between Du'a and Dhikr
Du'a is a personal supplication where a believer directly asks Allah for specific needs or forgiveness, reflecting a conscious and intentional prayer. Dhikr involves the repetitive recitation of Allah's names, phrases, or praises, serving as a constant remembrance and spiritual mindfulness practice. While du'a seeks particular outcomes, dhikr fosters ongoing connection with Allah and internalizes faith through ritual repetition.
The Role of Du'a in Islamic Worship
Du'a serves as a direct, personal supplication to Allah, allowing believers to express their needs, gratitude, and repentance in Islamic worship. Unlike dhikr, which involves repetitive remembrance and glorification of Allah's names and attributes, du'a emphasizes individual communication and heartfelt petition. This intimate form of worship strengthens a Muslim's faith and reliance on divine mercy and guidance.
The Power and Virtue of Dhikr in Daily Life
Dhikr, the remembrance of Allah through repeated phrases and prayers, holds immense power and virtue in daily life by fostering spiritual mindfulness and bringing peace to the heart. Consistent engagement in Dhikr strengthens one's connection with the Divine, purifies the soul, and provides protection from negative influences. Scholars emphasize that Dhikr's rhythmic repetition cultivates inner tranquility, spiritual resilience, and an enduring sense of gratitude, making it essential for holistic well-being in Islamic practice.
Scriptural Evidence: Qur'an and Hadith References
Du'a is a direct supplication to Allah, exemplified in Qur'an 2:186 where Allah says, "Call upon Me; I will respond to you," highlighting personal prayers. Dhikr refers to the remembrance of Allah through repeated phrases such as "SubhanAllah," "Alhamdulillah," and "Allahu Akbar," supported by hadiths like Sahih Muslim 2699, which emphasize constant remembrance for spiritual closeness. Both practices are integral, with Qur'an 13:28 affirming that hearts find tranquility in the remembrance of Allah, underscoring the significance of Dhikr alongside the personal appeals of Du'a.
When to Practice Du'a vs. Dhikr
Du'a is best practiced during specific moments of need, such as before meals, during prayer, or in times of distress, reflecting personal supplication to Allah. Dhikr, involving repetitive remembrance of Allah through phrases or names, is suited for continuous daily practice, helping to maintain spiritual mindfulness throughout routine activities. Both serve complementary spiritual purposes, with Du'a focusing on direct requests and Dhikr fostering constant awareness of the Divine.
Benefits and Rewards of Du'a and Dhikr
Du'a and Dhikr enrich the spiritual life by fostering a deep connection with Allah, with Du'a serving as a direct supplication for personal needs and forgiveness, and Dhikr involving the remembrance of Allah through repeated phrases that increase mindfulness and tranquility. The benefits of Du'a include receiving divine mercy, guidance, and fulfillment of heartfelt desires, while Dhikr strengthens faith, purifies the heart, and grants inner peace. Both practices offer immense rewards in the hereafter, promising the closeness of Allah, forgiveness of sins, and elevated ranks among the righteous.
Common Misconceptions about Du'a and Dhikr
Many people mistakenly believe that du'a and dhikr are interchangeable, but du'a specifically refers to personal supplications asking Allah for needs, while dhikr involves the repetitive remembrance of Allah's names and attributes. Another common misconception is that du'a must follow a strict formula, whereas it can be spontaneous and personalized according to one's circumstances and intentions. Furthermore, some assume dhikr is only for formal worship, but it can be performed anytime to cultivate constant awareness of Allah.
Integrating Du'a and Dhikr into Your Spiritual Routine
Integrating Du'a and Dhikr into your spiritual routine deepens your connection with Allah by combining heartfelt supplications with the mindful remembrance of His names and attributes. Consistent practice involves setting specific times for Du'a to express personal needs and gratitude, while embedding Dhikr throughout daily activities maintains spiritual awareness and tranquility. Utilizing both practices harmoniously enhances inner peace, strengthens faith, and fosters a continuous bond with the Divine presence.
Du'a Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com