Creed is a powerful statement of faith that outlines core beliefs fundamental to many religious traditions, serving as a unifying declaration for communities around the world. Understanding the historical context and theological significance of creeds can deepen your appreciation of their role in shaping spiritual identity. Explore the rest of this article to learn how creeds influence faith and practice across cultures.
Table of Comparison
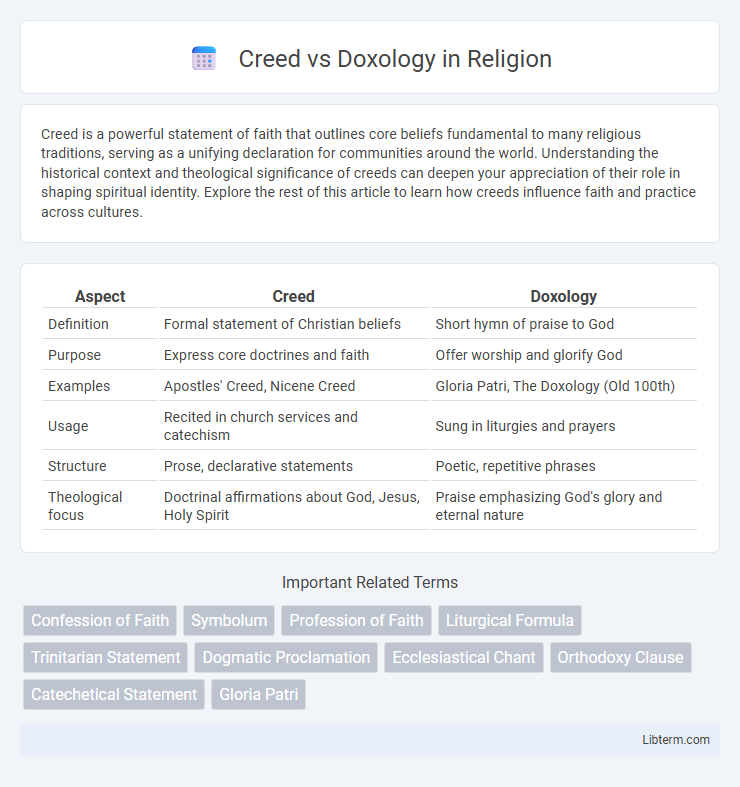
| Aspect | Creed | Doxology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal statement of Christian beliefs | Short hymn of praise to God |
| Purpose | Express core doctrines and faith | Offer worship and glorify God |
| Examples | Apostles' Creed, Nicene Creed | Gloria Patri, The Doxology (Old 100th) |
| Usage | Recited in church services and catechism | Sung in liturgies and prayers |
| Structure | Prose, declarative statements | Poetic, repetitive phrases |
| Theological focus | Doctrinal affirmations about God, Jesus, Holy Spirit | Praise emphasizing God's glory and eternal nature |
Introduction to Creed and Doxology
Creed and doxology represent distinct elements of Christian worship with unique purposes and structures. A creed is a formal statement of faith that summarizes core Christian beliefs, often recited during liturgical services to affirm communal doctrine; examples include the Nicene Creed and Apostles' Creed. Doxology, in contrast, is a short hymn of praise to God, typically expressing worship and glorification, commonly exemplified by the "Gloria Patri" or the "Praise God, from Whom All Blessings Flow.
Defining Creed: Meaning and Purpose
A creed is a formal statement of beliefs that outlines the essential doctrines of a faith, serving as a concise summary of core theological principles. It functions as a unifying declaration, guiding the faith community in shared convictions and affirming foundational truths. Creeds are used in liturgical settings to affirm identity, teach doctrine, and foster spiritual unity among believers.
Defining Doxology: Meaning and Purpose
Doxology is a short hymn or expression of praise to God, often used in Christian worship to glorify the Trinity. Its purpose is to offer a concise and heartfelt acknowledgment of God's holiness, majesty, and eternal nature, typically concluding prayers or hymns. Unlike creeds, which outline beliefs and doctrines, doxologies focus on worship and adoration through poetic, exalted language.
Historical Origins of Creeds
The historical origins of creeds trace back to early Christianity, where concise statements of faith were developed to unify beliefs and counter heresies. The Apostles' Creed, one of the earliest creeds, emerged between the 2nd and 4th centuries as a baptismal declaration summarizing apostolic teachings. Creeds like the Nicene Creed were formulated during significant councils, such as the Council of Nicaea in 325 AD, to address theological disputes and establish orthodox doctrine.
Historical Development of Doxologies
Doxologies originated in early Christian worship as short hymns praising the Trinity, evolving from Jewish liturgical traditions and gaining prominence by the 2nd century. The most well-known doxology, the "Gloria Patri," became a standard element in Western and Eastern liturgies through the Middle Ages, reflecting doctrinal affirmations of the Trinity. The historical development of doxologies highlights their role in expressing communal faith, differentiating liturgical functions from creeds, which serve as formal statements of belief.
Key Differences Between Creed and Doxology
Creeds are formal, structured statements of Christian beliefs that outline essential doctrines such as the Trinity, the nature of Christ, and salvation, while doxologies are short hymns or expressions of praise to God, often used in worship settings. Creeds serve as confessional declarations uniting believers around core theological truths, whereas doxologies function to glorify God and inspire worship through brief, poetic affirmations. The primary distinction lies in creeds providing a doctrinal framework, while doxologies emphasize adoration and liturgical praise.
Role of Creed in Worship and Doctrine
The Creed functions as a foundational statement of Christian faith, outlining essential doctrinal beliefs that unify believers during worship. It serves as a theological anchor, ensuring consistency in teaching across congregations and guiding the interpretation of Scripture. By affirming core doctrines such as the Trinity, incarnation, and resurrection, the Creed reinforces orthodox belief and fosters communal identity within the church.
Role of Doxology in Worship and Praise
Doxology serves as a concise expression of worship and praise, highlighting God's attributes such as holiness, sovereignty, and eternal nature within liturgical settings. It functions to unify congregational voices in a rhythmic declaration of glory to the Trinity, fostering communal participation and spiritual reflection. This singing or recitation emphasizes adoration and thanksgiving, enhancing the worship experience through focused, repetitive affirmation of divine majesty.
Examples of Famous Creeds and Doxologies
Famous creeds include the Apostles' Creed, Nicene Creed, and Athanasian Creed, each articulating core Christian doctrines such as the Trinity, incarnation, and resurrection. Well-known doxologies like the "Gloria Patri" and the "Old 100th" encapsulate praise and worship, often used in liturgical settings to glorify the Trinity. Creeds serve as foundational statements of faith, whereas doxologies function primarily as expressions of worship and praise.
Contemporary Relevance of Creed and Doxology
The contemporary relevance of Creed and Doxology lies in their enduring role as foundational elements in Christian worship and identity formation, with Creeds articulating core theological beliefs and Doxologies offering concise expressions of praise that unify congregations. Modern liturgical practices incorporate Creeds to affirm shared faith across denominational lines while Doxologies enhance spiritual experience through melodic affirmations of God's glory. Both serve as vital tools for catechesis and communal worship, fostering a sense of continuity and doctrinal clarity in diverse contemporary Christian contexts.
Creed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com