Inclusivism promotes embracing diverse perspectives and fostering a culture where all individuals feel valued and respected regardless of their background. It encourages open-mindedness and the breaking down of barriers that separate groups, enhancing social cohesion and mutual understanding. Discover how inclusivism can transform your community and relationships by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
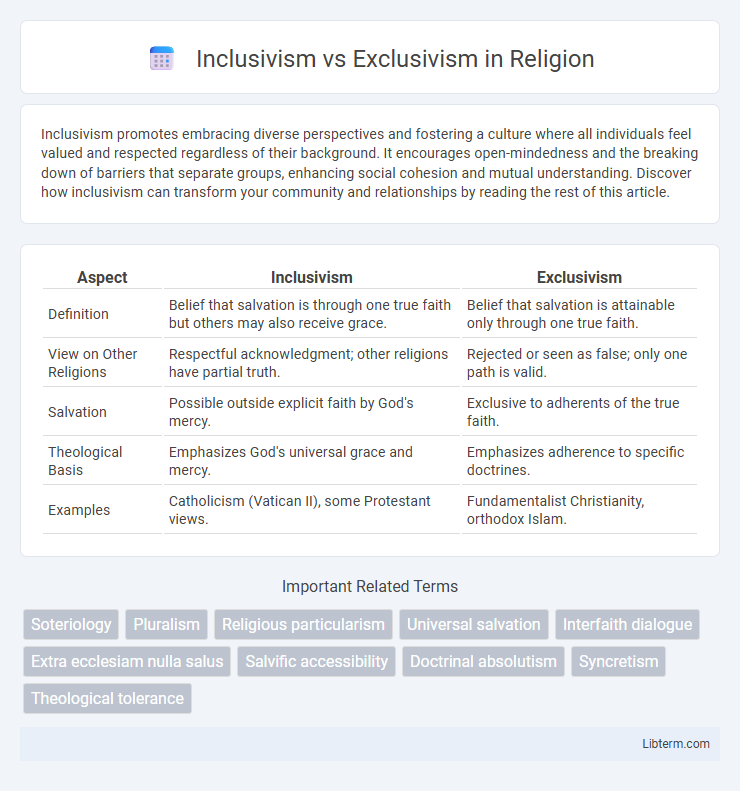
| Aspect | Inclusivism | Exclusivism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that salvation is through one true faith but others may also receive grace. | Belief that salvation is attainable only through one true faith. |
| View on Other Religions | Respectful acknowledgment; other religions have partial truth. | Rejected or seen as false; only one path is valid. |
| Salvation | Possible outside explicit faith by God's mercy. | Exclusive to adherents of the true faith. |
| Theological Basis | Emphasizes God's universal grace and mercy. | Emphasizes adherence to specific doctrines. |
| Examples | Catholicism (Vatican II), some Protestant views. | Fundamentalist Christianity, orthodox Islam. |
Understanding Inclusivism and Exclusivism
Inclusivism recognizes the validity of multiple religious paths while affirming the ultimate truth of one tradition, promoting acceptance and coexistence. Exclusivism asserts that only one religion provides the definitive path to truth and salvation, often rejecting other beliefs as invalid. Understanding these perspectives reveals their impact on interfaith dialogue, tolerance, and religious identity formation.
Historical Foundations of Inclusivism
Historical foundations of inclusivism trace back to early Christian theologians like St. Augustine and St. Thomas Aquinas, who proposed that salvation is possible outside explicit Christian faith through God's grace. This theological stance emphasizes God's universal salvific will, acknowledging that elements of truth and goodness exist in other religions and cultures. Inclusivism historically contrasts with exclusivism by promoting a broader view of divine mercy and human redemption beyond rigid doctrinal boundaries.
Origins and Development of Exclusivism
Exclusivism originated in early Christian theology, emphasizing salvation solely through explicit faith in Jesus Christ, rooted in biblical interpretations such as John 14:6. It developed as a reaction to pluralistic religious environments, asserting doctrinal boundaries to maintain theological purity and identity. Over centuries, exclusivism evolved through church councils and reform movements, reinforcing the notion that truth and salvation are accessible only within orthodox Christian teachings.
Key Theological Arguments for Inclusivism
Key theological arguments for inclusivism emphasize the belief that salvation through Jesus Christ extends beyond explicit Christian confession, recognizing God's grace as accessible to all humanity. Inclusivists argue that divine justice and mercy allow individuals with sincere faith and moral integrity, regardless of religious affiliation, to receive salvation through Christ's redemptive work. This perspective is supported by biblical passages highlighting God's impartial love and the universal offer of salvation, such as Romans 2:14-16 and 1 Timothy 2:4, affirming that salvation is not limited to conscious Christian believers.
Core Beliefs Underpinning Exclusivism
Exclusivism is grounded in the belief that salvation is attainable only through explicit faith in a particular religious tradition, often emphasizing the unique truth of its doctrines. Core beliefs underpinning exclusivism include the conviction that divine revelation is confined to one faith, and that other religions either lack salvific validity or are fundamentally false. This perspective asserts a clear boundary between true believers and non-believers, prioritizing doctrinal purity and exclusive access to salvation.
Inclusivism in Major World Religions
Inclusivism in major world religions emphasizes the acceptance of diverse beliefs while recognizing one's own religion as the ultimate truth, fostering a more open and tolerant approach. Christianity often exemplifies inclusivism by acknowledging that salvation can be available to non-Christians through Christ, even if they do not explicitly follow Christian teachings. Hinduism embraces inclusivism through its acceptance of various deities and paths to liberation, highlighting the belief that multiple religious practices can lead to spiritual truth and enlightenment.
Exclusivism and Interfaith Relations
Exclusivism asserts that salvation is attainable solely through a specific religious tradition, often leading to challenges in interfaith relations due to its rigid doctrinal boundaries. This perspective can create tensions by rejecting the validity of other faiths, hindering meaningful dialogue and cooperation among diverse religious communities. Understanding Exclusivism's impact on interfaith dynamics is crucial for fostering respect and peaceful coexistence in pluralistic societies.
Sociocultural Impact of Inclusivist Approaches
Inclusivist approaches promote social cohesion by embracing cultural diversity and fostering mutual respect across different religious and ethnic groups, which helps reduce social tensions and conflicts. These approaches encourage inclusive policies that support minority rights and equal participation in societal institutions, enhancing social integration and empowerment. Studies show that societies adopting inclusivism exhibit higher levels of social capital, tolerance, and collaborative civic engagement compared to those with exclusive frameworks.
Criticisms Faced by Inclusivism and Exclusivism
Inclusivism faces criticism for potentially diluting religious distinctiveness and undermining the fidelity of exclusive truth claims by accommodating multiple belief systems. Exclusivism is often challenged for fostering intolerance, limiting interfaith dialogue, and disregarding the validity of other religious experiences. Both approaches grapple with balancing doctrinal integrity and the complexities of pluralistic religious landscapes.
Navigating the Future: Toward Pluralistic Dialogue
Navigating the future of religious and cultural discourse necessitates a shift from exclusivism, which asserts a single truth, toward inclusivism that acknowledges multiple perspectives within a pluralistic dialogue. Inclusivism fosters mutual respect and understanding across diverse belief systems, enabling collaborative solutions to global challenges. Embracing pluralistic dialogue promotes peaceful coexistence and enriches collective knowledge by integrating diverse spiritual and ethical insights.
Inclusivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com