Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence, interprets Sharia law to guide daily conduct and religious practices. It covers all aspects of life, including worship, transactions, and personal behavior, ensuring compliance with Islamic principles. Discover deeper insights into Fiqh's role and its impact on Your spiritual and social life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
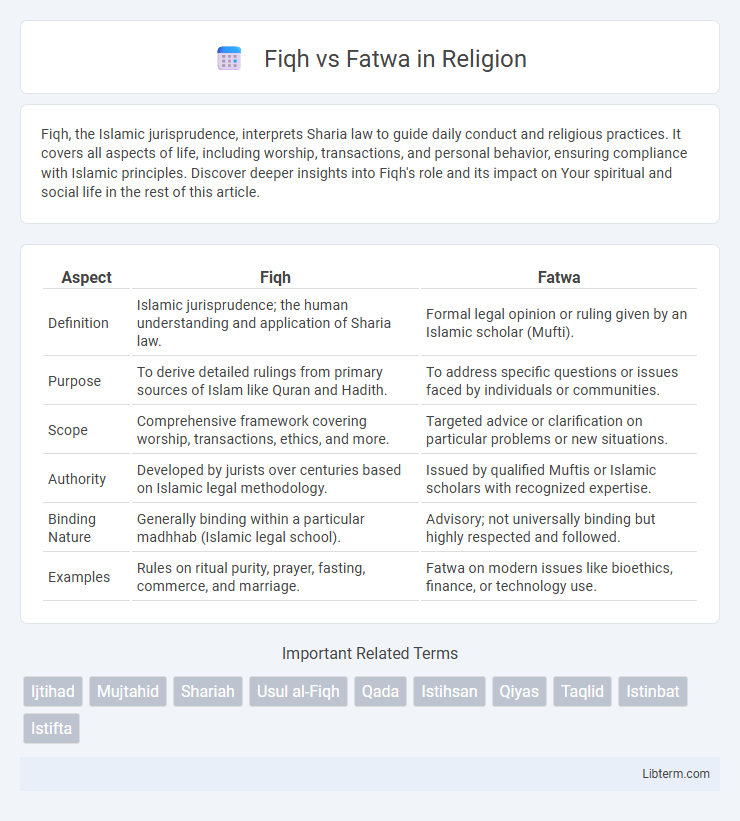
| Aspect | Fiqh | Fatwa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic jurisprudence; the human understanding and application of Sharia law. | Formal legal opinion or ruling given by an Islamic scholar (Mufti). |
| Purpose | To derive detailed rulings from primary sources of Islam like Quran and Hadith. | To address specific questions or issues faced by individuals or communities. |
| Scope | Comprehensive framework covering worship, transactions, ethics, and more. | Targeted advice or clarification on particular problems or new situations. |
| Authority | Developed by jurists over centuries based on Islamic legal methodology. | Issued by qualified Muftis or Islamic scholars with recognized expertise. |
| Binding Nature | Generally binding within a particular madhhab (Islamic legal school). | Advisory; not universally binding but highly respected and followed. |
| Examples | Rules on ritual purity, prayer, fasting, commerce, and marriage. | Fatwa on modern issues like bioethics, finance, or technology use. |
Understanding Fiqh: Definition and Scope
Fiqh refers to the comprehensive Islamic jurisprudence derived from the Quran, Sunnah, consensus (Ijma), and analogical reasoning (Qiyas), which interprets Sharia law to address various aspects of Muslim life such as worship, transactions, and personal conduct. It encompasses detailed rulings and principles that form the foundation for legal decisions in Islamic law. Understanding Fiqh involves recognizing its role in systematically organizing religious duties and ethical guidelines into a coherent legal framework.
What is a Fatwa? Meaning and Purpose
A Fatwa is a formal legal opinion issued by a qualified Islamic scholar (mufti) based on Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh) to address specific questions or issues faced by individuals or communities. It serves the purpose of providing guidance and clarification on religious matters, ensuring that actions comply with Islamic law. Fatwas are context-specific, adaptable to new circumstances, and help Muslims make informed decisions while adhering to Sharia principles.
Historical Development of Fiqh and Fatwa
Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence, developed through rigorous scholarly interpretation of the Quran, Hadith, consensus (ijma), and analogical reasoning (qiyas) to establish comprehensive legal frameworks by the 8th century. Fatwa, a non-binding legal opinion issued by qualified muftis, evolved as a practical tool to address specific issues and adapt Islamic law to changing social contexts across various Muslim societies. The historical development of fiqh provided the theoretical basis, while fatwa allowed dynamic application and flexibility within the Islamic legal tradition.
Sources of Fiqh in Islamic Law
Fiqh in Islamic law is derived from primary sources such as the Quran and Sunnah, which provide foundational texts for legal rulings. Secondary sources include Ijma (consensus of scholars) and Qiyas (analogical reasoning), enabling jurists to interpret and apply principles to new situations. Fatwas are scholarly opinions issued based on Fiqh principles, reflecting the interpretation and application of these sources to specific cases.
Who Issues a Fatwa? The Role of the Mufti
A fatwa is an Islamic legal opinion issued by a qualified mufti, an expert in Islamic jurisprudence trained to interpret Sharia law. The mufti uses fiqh, the detailed jurisprudential framework derived from the Quran, Hadith, and scholarly consensus, to provide specific rulings on contemporary issues. This authoritative guidance helps Muslims navigate complex legal and ethical questions within the bounds of Islamic law.
Differences Between Fiqh and Fatwa
Fiqh refers to the comprehensive Islamic jurisprudence derived from the Quran, Sunnah, consensus, and analogical reasoning, forming the theoretical framework for understanding Sharia law. Fatwa, on the other hand, is a specific legal opinion or ruling issued by a qualified Islamic scholar (mufti) in response to a particular question or situation based on established fiqh principles. The key difference lies in fiqh being the body of jurisprudence itself, while fatwa represents a case-specific application or interpretation of that jurisprudence.
Relationship Between Fiqh, Fatwa, and Sharia
Fiqh represents the comprehensive understanding and interpretation of Islamic law derived from the Quran and Sunnah, while fatwa consists of specific legal rulings or opinions issued by qualified scholars based on fiqh principles. Both fiqh and fatwa function within the framework of Sharia, where fiqh serves as the theoretical foundation and fatwa as the practical application responding to contemporary issues. The relationship between them ensures that Islamic jurisprudence remains dynamic and relevant, balancing divine law with contextual human circumstances.
Real-World Examples: Fiqh and Fatwa in Practice
Fiqh represents the comprehensive Islamic jurisprudence system derived from the Quran, Hadith, Ijma, and Qiyas, guiding daily worship and societal laws, such as prayer methods and business transactions. Fatwa serves as a specific, authoritative legal opinion issued by qualified muftis in response to contemporary issues, like modern banking or bioethical dilemmas, reflecting contextual application of fiqh principles. For instance, the fatwa permitting organ donation addresses new health challenges by interpreting fiqh rulings on preserving life and bodily integrity.
Common Misconceptions About Fiqh and Fatwa
Common misconceptions about Fiqh and Fatwa often confuse their roles; Fiqh represents the comprehensive Islamic jurisprudence derived from the Quran and Sunnah, while a Fatwa is a specific legal opinion issued by a qualified scholar based on Fiqh principles. Many mistakenly believe Fatwas carry universal authority, but they are advisory and context-dependent, reflecting situational rulings rather than fixed laws. Understanding this distinction clarifies that Fiqh forms the theoretical framework, whereas Fatwas apply that framework to real-life issues.
Contemporary Relevance: Fiqh and Fatwa Today
Fiqh, the Islamic jurisprudence framework, continues to guide legal and ethical decision-making by interpreting foundational texts in light of modern contexts. Fatwa, as expert legal opinions issued by qualified scholars, addresses contemporary issues ranging from bioethics to financial transactions, offering practical solutions within Islamic law. The dynamic interaction between fiqh and fatwa enables Muslims worldwide to navigate complex social, technological, and economic challenges while remaining rooted in Sharia principles.
Fiqh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com