Hadith are the recorded sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, serving as a fundamental source for Islamic law and guidance. They complement the Quran by providing context and detailed instructions for various aspects of daily life and spirituality. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of Hadith and their significance in Islam.
Table of Comparison
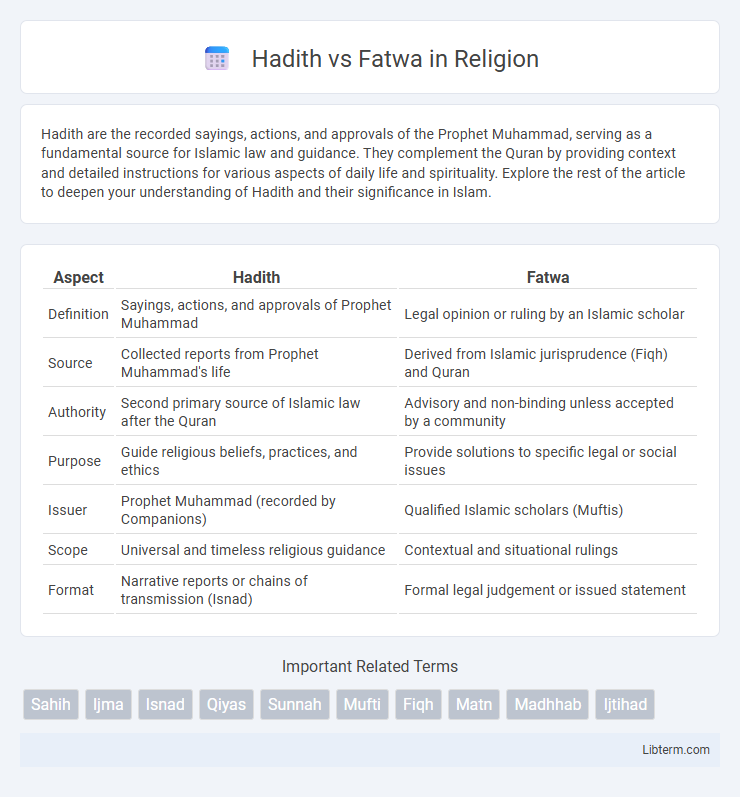
| Aspect | Hadith | Fatwa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sayings, actions, and approvals of Prophet Muhammad | Legal opinion or ruling by an Islamic scholar |
| Source | Collected reports from Prophet Muhammad's life | Derived from Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh) and Quran |
| Authority | Second primary source of Islamic law after the Quran | Advisory and non-binding unless accepted by a community |
| Purpose | Guide religious beliefs, practices, and ethics | Provide solutions to specific legal or social issues |
| Issuer | Prophet Muhammad (recorded by Companions) | Qualified Islamic scholars (Muftis) |
| Scope | Universal and timeless religious guidance | Contextual and situational rulings |
| Format | Narrative reports or chains of transmission (Isnad) | Formal legal judgement or issued statement |
Understanding the Foundations: What Are Hadith and Fatwa?
Hadith are recorded sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, serving as primary sources of Islamic jurisprudence alongside the Quran. Fatwa refers to a formal legal opinion or ruling issued by a qualified Islamic scholar (mufti) to address specific questions or issues in Islamic law. Understanding the foundational difference, Hadith provides the scriptural basis, while Fatwa applies interpretative authority to guide contemporary practice.
Historical Origins of Hadith and Fatwa
Hadith are recorded sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad, forming a foundational source of Islamic law and theology developed during the 7th and 8th centuries following his death. Fatwa emerged as legal opinions issued by qualified Islamic scholars (muftis) based on the Quran, Hadith, and other jurisprudential sources to address specific legal questions within Muslim communities. The historical origins of Hadith lie in early Islamic oral traditions transitioned into written collections, while Fatwa evolved as a formalized juristic response to new situations and societal needs over centuries.
Core Differences Between Hadith and Fatwa
Hadith are recorded sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, serving as primary sources of Islamic teachings and law. Fatwa refers to a formal legal opinion or ruling issued by an Islamic scholar (mufti) to address specific questions or issues based on Quran, Hadith, and other jurisprudential sources. The core difference lies in Hadith being original prophetic guidance, while Fatwa constitutes interpretive legal advice rooted in scholarly analysis.
The Role of Hadith in Islamic Jurisprudence
Hadith plays a critical role in Islamic jurisprudence by providing the sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, which serve as primary sources of law alongside the Quran. These narrations offer detailed guidance on legal, moral, and ritual matters, enabling scholars to derive rulings and principles foundational to Shariah. Fatwa, issued by qualified jurists, interprets and applies these sources, including Hadith, to address specific legal questions within contemporary contexts.
The Process of Issuing a Fatwa
The process of issuing a fatwa begins with a qualified Islamic scholar interpreting relevant Hadith and Quranic texts to address contemporary issues. Scholars analyze the context, linguistic nuances, and authenticity of Hadith to ensure rulings align with Islamic jurisprudence principles. This methodical approach guarantees that fatwas remain authoritative and applicable to modern legal and ethical dilemmas within the Muslim community.
Sources of Authority: How Hadith and Fatwa Derive Legitimacy
Hadith derive legitimacy from being recorded sayings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad, authenticated through rigorous chains of narration (isnad) and classification by Islamic scholars. Fatwa legitimacy stems from the knowledge, expertise, and interpretative authority of qualified Islamic jurists (muftis) who issue legal opinions based on primary sources like the Quran, Hadith, consensus (ijma), and analogical reasoning (qiyas). The authority of Fatwa is contextual and dynamic, relying on juristic reasoning, whereas Hadith's authority is fixed as historical testimony of prophetic tradition.
Interpretation: Static Hadith vs. Dynamic Fatwa
Hadith are static texts consisting of Prophet Muhammad's sayings and actions, preserved with fixed wording and context that guide Islamic law and moral principles. Fatwa represents dynamic scholarly interpretations and rulings derived from Hadith and other Islamic sources, adapting to changing social, cultural, and legal circumstances. This difference highlights Hadith as foundational, while Fatwa evolves to address contemporary challenges in Islamic jurisprudence.
Famous Examples: Influential Hadith and Landmark Fatwas
The Hadith "Actions are judged by intentions" remains one of the most influential sayings of Prophet Muhammad, guiding Islamic jurisprudence and daily life. Landmark fatwas such as the 20th-century ruling on organ transplantation by Sheikh Abdul Aziz ibn Baz have significantly shaped modern medical ethics within Islamic law. These examples highlight the enduring authority of Hadith in spiritual matters and the practical application of fatwas in adapting Sharia to contemporary issues.
Modern Relevance: Hadith and Fatwa in Contemporary Issues
Hadith, as recorded sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad, serve as primary sources for Islamic jurisprudence, providing foundational guidance on ethical and legal matters. Fatwa, a formal legal opinion issued by qualified Islamic scholars, interprets Hadith and other sources to address new and complex issues arising in modern society, such as bioethics, finance, and technology. Together, Hadith and Fatwa enable Muslims to navigate contemporary challenges while maintaining fidelity to Islamic principles and adapting to evolving contexts.
Misconceptions and Clarifications: Hadith vs. Fatwa
Hadith represents the recorded sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad, serving as primary sources for Islamic teachings, while fatwa denotes a legal opinion or ruling issued by qualified scholars to address specific issues. A common misconception is that fatwas carry the same authoritative weight as hadith; however, fatwas are interpretative and context-dependent, often varying between scholars and regions. Clarifying the distinction is essential to understanding Islamic jurisprudence, where hadith form foundational texts and fatwas provide applied guidance based on those texts.
Hadith Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com