Sunnah refers to the teachings, practices, and examples set by the Prophet Muhammad, serving as a vital guide for Muslims in daily life and spiritual matters. Following the Sunnah helps deepen your faith and align actions with Islamic principles. Discover how embracing the Sunnah can transform your understanding and practice by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
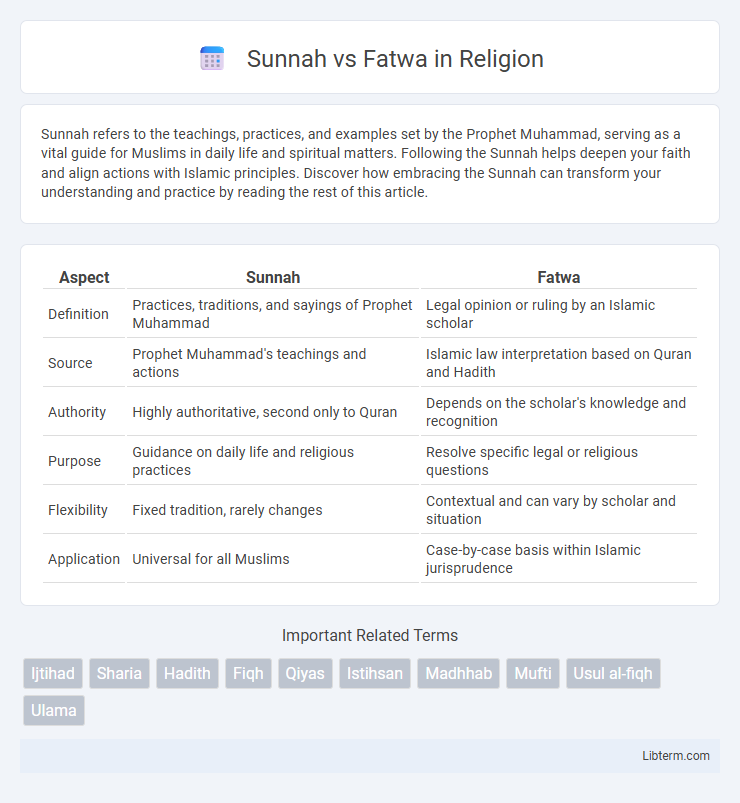
| Aspect | Sunnah | Fatwa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practices, traditions, and sayings of Prophet Muhammad | Legal opinion or ruling by an Islamic scholar |
| Source | Prophet Muhammad's teachings and actions | Islamic law interpretation based on Quran and Hadith |
| Authority | Highly authoritative, second only to Quran | Depends on the scholar's knowledge and recognition |
| Purpose | Guidance on daily life and religious practices | Resolve specific legal or religious questions |
| Flexibility | Fixed tradition, rarely changes | Contextual and can vary by scholar and situation |
| Application | Universal for all Muslims | Case-by-case basis within Islamic jurisprudence |
Introduction to Sunnah and Fatwa
Sunnah refers to the teachings, practices, and examples of the Prophet Muhammad, serving as a primary source of Islamic law alongside the Quran. Fatwa is a formal legal opinion or interpretation provided by a qualified Islamic scholar addressing specific issues or questions within Islamic jurisprudence. Understanding the distinction between Sunnah and Fatwa is essential for comprehending how Islamic guidance is derived and applied in various contexts.
Defining Sunnah: Origins and Importance
Sunnah refers to the practices, teachings, and examples of the Prophet Muhammad, serving as a primary source of Islamic guidance alongside the Quran. Originating from Hadith collections, Sunnah shapes religious rituals, moral conduct, and legal principles within Islamic jurisprudence. It holds paramount importance by providing contextual interpretation of Quranic verses, ensuring adherence to authentic Islamic traditions.
Understanding Fatwa: Concept and Purpose
A Fatwa is a formal legal opinion or ruling issued by an Islamic scholar, addressing specific questions or situations within the framework of Islamic law. It serves to guide Muslims in practicing their faith according to Shariah, providing clarity on complex issues where direct evidence from the Quran or Sunnah may not be explicit. Unlike the Sunnah, which consists of the teachings and practices of Prophet Muhammad, a Fatwa is context-specific and can vary based on interpretation and contemporary circumstances.
Sources of Sunnah in Islamic Jurisprudence
The sources of Sunnah in Islamic jurisprudence primarily include the sayings (Hadith), actions, and tacit approvals of Prophet Muhammad, as captured through rigorous chains of narration (Isnad) and documented in authoritative collections like Sahih Bukhari and Sahih Muslim. These authentic Hadith serve as a fundamental source alongside the Quran, guiding Muslim law and morality with detailed practical examples. Fatwa, on the other hand, is a non-binding legal opinion issued by qualified scholars based on the Quran, Sunnah, consensus (Ijma), and analogical reasoning (Qiyas), reflecting contemporary issues within Islamic law.
Authority and Issuance of Fatwa
Sunnah represents the established practices and teachings of Prophet Muhammad, serving as a primary source of Islamic law and moral authority. Fatwa, on the other hand, is a formal legal opinion or ruling issued by qualified Islamic scholars (muftis) based on the Quran, Sunnah, and other jurisprudential sources. The authority of a fatwa is derived from the scholar's expertise and recognition within the Islamic community, while the Sunnah's authority is rooted in its direct connection to the Prophet's example.
Key Differences Between Sunnah and Fatwa
Sunnah refers to the actions, sayings, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad serving as a primary source of Islamic law and guidance, while Fatwa is a formal legal opinion or interpretation issued by qualified Islamic scholars based on the Qur'an, Sunnah, and other sources. The Sunnah holds an authoritative and foundational status in Sharia, whereas Fatwas are advisory and context-specific responses to contemporary issues that may vary among scholars. While Sunnah provides established practices to emulate, Fatwas address new or emerging questions in Islamic jurisprudence, reflecting dynamic scholarly reasoning.
The Role of Sunnah in Daily Life
The Sunnah, comprising the practices and sayings of Prophet Muhammad, serves as a fundamental guide for Muslims in daily life, influencing personal conduct, worship, and social interactions. It complements the Quran by providing practical examples of Islamic principles, shaping rituals such as prayer, fasting, and ethical behavior. Unlike a fatwa, which is a scholarly legal opinion issued to address specific issues, the Sunnah offers a continuous, holistic framework for living according to Islamic values.
Circumstances for Seeking a Fatwa
Seeking a fatwa becomes essential when an individual faces complex or unprecedented issues not explicitly addressed in the Sunnah, the documented practices and sayings of the Prophet Muhammad. Fatwas provide authoritative interpretations by qualified Islamic scholars, taking into account contemporary circumstances, societal changes, and specific details of the situation. Crucial circumstances for seeking a fatwa include legal ambiguities, modern technological developments, and evolving social norms that require contextual Islamic guidance beyond the foundational texts.
Common Misconceptions: Sunnah vs Fatwa
Sunnah refers to the practices, teachings, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad that provide a model for Muslims to follow, while fatwa is a legal opinion or ruling given by an Islamic scholar based on interpretation of Sharia law. A common misconception is that fatwas carry the same religious authority as Sunnah, but fatwas can vary among scholars and contexts and are subject to reinterpretation, unlike the fixed traditions of Sunnah. Understanding the distinction helps prevent confusion between divinely guided practices and human-derived legal judgments.
Conclusion: Harmonizing Sunnah and Fatwa
Harmonizing Sunnah and Fatwa enhances Islamic jurisprudence by balancing the Prophet's traditions with contemporary legal rulings. Integrating Sunnah ensures Fatwas remain rooted in foundational teachings, while Fatwas adapt these principles to modern contexts. This synergy promotes a dynamic yet authentic application of Islamic law that respects tradition and addresses current societal needs.
Sunnah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com