Historicism interprets historical events and cultural phenomena by placing them within their specific social, political, and economic contexts, emphasizing how these factors shape human experience over time. This approach challenges ideas that history follows universal laws or timeless patterns, focusing instead on the uniqueness of each period. Explore the rest of the article to discover how historicism influences contemporary thought and your understanding of history.
Table of Comparison
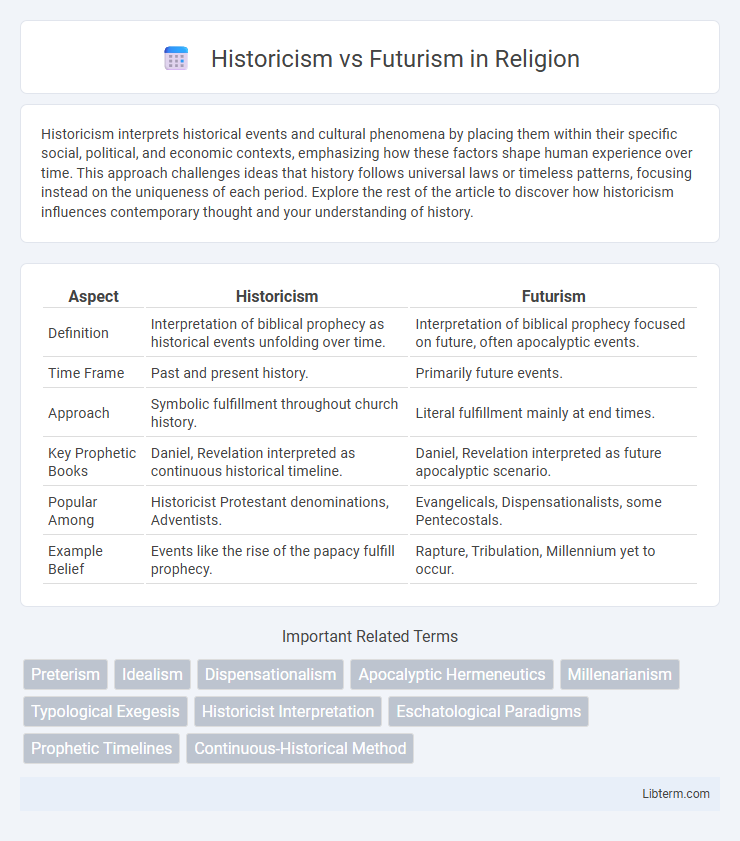
| Aspect | Historicism | Futurism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpretation of biblical prophecy as historical events unfolding over time. | Interpretation of biblical prophecy focused on future, often apocalyptic events. |
| Time Frame | Past and present history. | Primarily future events. |
| Approach | Symbolic fulfillment throughout church history. | Literal fulfillment mainly at end times. |
| Key Prophetic Books | Daniel, Revelation interpreted as continuous historical timeline. | Daniel, Revelation interpreted as future apocalyptic scenario. |
| Popular Among | Historicist Protestant denominations, Adventists. | Evangelicals, Dispensationalists, some Pentecostals. |
| Example Belief | Events like the rise of the papacy fulfill prophecy. | Rapture, Tribulation, Millennium yet to occur. |
Introduction to Historicism and Futurism
Historicism emphasizes the importance of historical context and cultural heritage in shaping art, architecture, and literature, advocating for a deep understanding of past traditions. Futurism, originating in early 20th century Italy, rebels against historical constraints by celebrating technology, speed, and modernity to envision a dynamic, forward-looking future. These movements represent contrasting approaches: Historicism anchors creativity in the past, while Futurism drives innovation through radical breaks from tradition.
Defining Historicism: Key Principles
Historicism emphasizes understanding historical contexts by analyzing cultural, social, and material conditions that shape events and ideas over time. It prioritizes the continuity and influence of past traditions, asserting that historical development is crucial for interpreting present realities. Key principles include the rejection of universal truths, the importance of temporal specificity, and the belief that knowledge is deeply rooted in historical experience.
Understanding Futurism: Core Concepts
Futurism emphasizes dynamic movement, technological innovation, and the rejection of traditional artistic forms rooted in historicism, seeking to capture the energy of modern life. Central concepts include speed, industrial progress, and a break from the past to embrace a forward-looking vision that celebrates machinery and urbanization. This avant-garde movement profoundly influenced literature, visual arts, and architecture by promoting radical experimentation and the glorification of the future.
Origins and Development of Historicism
Historicism originated in the 19th century as a scholarly approach emphasizing the understanding of historical context in shaping culture, art, and societal developments. It developed through the works of historians and philosophers like Leopold von Ranke and Wilhelm Dilthey, who stressed the importance of chronological accuracy and cultural specificity. This movement laid the foundation for modern historiography by prioritizing detailed analysis of historical events and rejecting universalist theories.
The Rise of Futurism in Historical Context
The rise of Futurism emerged as a radical artistic and social movement in early 20th-century Italy, rejecting Historicism's emphasis on traditional forms and classical heritage. Influenced by rapid industrialization, technological advancements, and the dynamic energy of urban life, Futurism celebrated speed, innovation, and modernity while opposing the nostalgia of past eras. This shift reflected broader cultural transformations during a period marked by political upheaval and the dawn of mechanized society.
Major Differences: Historicism vs Futurism
Historicism emphasizes understanding art and culture through historical context, valuing tradition, and continuity, while Futurism rejects the past, celebrating modernity, technology, and dynamic change. Historicism relies on detailed analysis of historical influences and continuity, whereas Futurism embraces innovation, speed, and a break from conventional forms. These opposing perspectives shape their distinct approaches to aesthetics, cultural significance, and societal progress.
Interpretations of Prophecy: A Comparative Analysis
Historicism interprets prophecy as a chronological unfolding of events predetermined by divine will, emphasizing detailed correlations between biblical texts and historical occurrences. Futurism views prophecy primarily as forecasts of imminent eschatological events yet to transpire, often highlighting symbolic and apocalyptic imagery in scriptural predictions. This comparative analysis reveals historicism's methodological reliance on past and present historical data, while futurism prioritizes future-oriented theological expectations within prophetic literature.
Impact on Theology and Philosophy
Historicism emphasizes the contextual and temporal development of theological doctrines, asserting that religious truths evolve with historical circumstances, which challenges static interpretations of faith and encourages dynamic philosophical inquiry. Futurism, by contrast, projects theological concepts into anticipated eschatological events, focusing on prophetic fulfillment and influencing philosophies that prioritize future-oriented ethics and existential hope. Both frameworks significantly shape theological discourse by offering contrasting lenses--historicism grounds theology in past realities, while futurism orients it toward forthcoming possibilities--thereby enriching philosophical debates on temporality and meaning.
Criticisms and Controversies
Historicism faces criticism for its deterministic approach, often accused of overemphasizing past events while neglecting future possibilities, which some argue stifles innovation and adaptability. Futurism, on the other hand, is controversial for its sometimes unrealistic and idealistic predictions, leading to challenges in practical application and accusations of disregarding historical context. Both perspectives generate debate over the balance between learning from history and embracing forward-looking innovation in shaping society and culture.
Conclusion: Relevance Today
Historicism emphasizes the importance of understanding past events and cultural contexts to interpret current phenomena, while Futurism champions innovation and anticipates transformative changes shaping future societies. Both perspectives remain relevant today as Historicism provides valuable lessons for avoiding previous mistakes and preserving cultural heritage, whereas Futurism drives technological advancement and progressive thinking. Balancing these approaches enables a comprehensive understanding of societal evolution, promoting sustainable development and adaptive strategies in an ever-changing world.
Historicism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com