Idealism emphasizes the primacy of ideas, consciousness, or spiritual reality over the material world, shaping how individuals perceive and interpret existence. This philosophical approach influences various disciplines, including ethics, politics, and art, by asserting that reality is fundamentally mentally constructed. Discover how idealism can transform your understanding of the world by exploring the concepts detailed in this article.
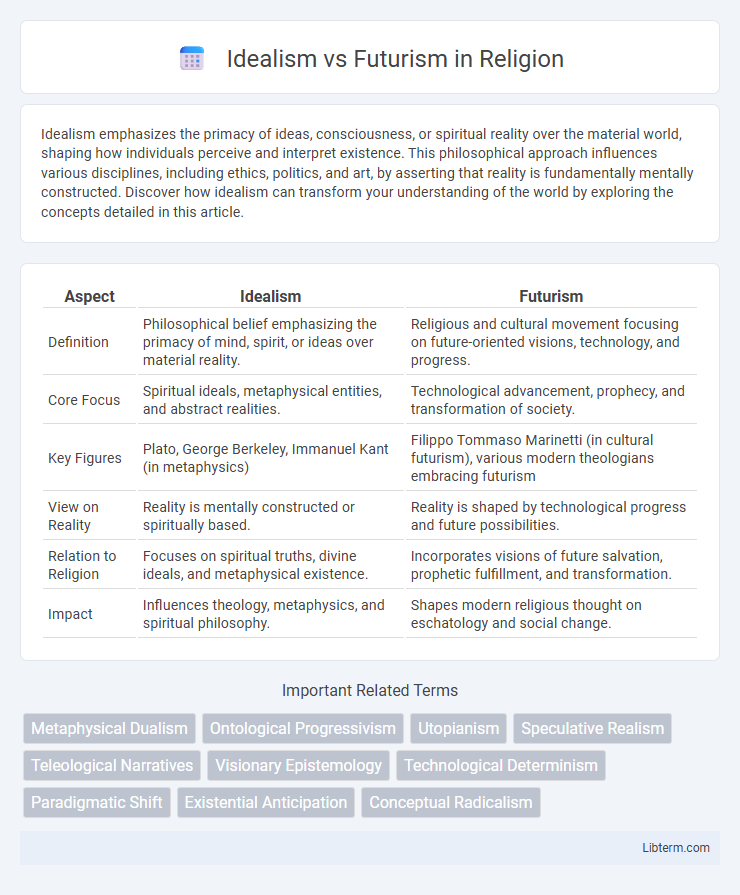
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Idealism | Futurism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical belief emphasizing the primacy of mind, spirit, or ideas over material reality. | Religious and cultural movement focusing on future-oriented visions, technology, and progress. |
| Core Focus | Spiritual ideals, metaphysical entities, and abstract realities. | Technological advancement, prophecy, and transformation of society. |
| Key Figures | Plato, George Berkeley, Immanuel Kant (in metaphysics) | Filippo Tommaso Marinetti (in cultural futurism), various modern theologians embracing futurism |
| View on Reality | Reality is mentally constructed or spiritually based. | Reality is shaped by technological progress and future possibilities. |
| Relation to Religion | Focuses on spiritual truths, divine ideals, and metaphysical existence. | Incorporates visions of future salvation, prophetic fulfillment, and transformation. |
| Impact | Influences theology, metaphysics, and spiritual philosophy. | Shapes modern religious thought on eschatology and social change. |
Understanding Idealism: Core Principles
Idealism centers on the belief that reality is fundamentally shaped by the mind, ideas, and consciousness, emphasizing the primacy of thoughts over material objects. Key principles include the notion that the external world is a manifestation of mental constructs and that knowledge is derived from innate ideas or spiritual insight. Philosophers such as Plato and George Berkeley contribute to the understanding of idealism by asserting that perception and reality are intimately connected through cognitive processes.
Unpacking Futurism: Philosophy and Vision
Futurism, emerging in the early 20th century, champions technological innovation, speed, and the rejection of past conventions to reshape society and culture. This avant-garde movement emphasizes dynamic change, the power of machines, and a vision of progress that challenges traditional idealist perspectives centered on abstract concepts and eternal truths. Key figures like Filippo Tommaso Marinetti articulated Futurism's philosophy as a celebration of modernity and disruption, contrasting sharply with idealism's focus on ideas and metaphysical ideals.
Historical Roots of Idealism and Futurism
Idealism traces its historical roots to ancient philosophers such as Plato, who emphasized the existence of abstract, non-material realities as the foundation of truth and knowledge. Futurism emerged in the early 20th century as an avant-garde movement, originating in Italy with Filippo Tommaso Marinetti's 1909 manifesto promoting speed, technology, and modernity. While Idealism centers on metaphysical concepts and the primacy of ideas, Futurism is grounded in the celebration of technological progress and dynamic change.
Key Differences Between Idealism and Futurism
Idealism centers on the primacy of ideas, consciousness, and subjective experience as the foundation of reality, while Futurism emphasizes progress, technology, and dynamic change as drivers of societal transformation. Idealism often explores metaphysical concepts and moral values, contrasting with Futurism's focus on innovation, speed, and the rejection of traditional norms. The key difference lies in Idealism's inward, philosophical approach versus Futurism's outward, practical vision of a rapidly evolving future.
Influential Thinkers in Idealism and Futurism
Influential thinkers in Idealism include Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, who emphasized the primacy of ideas and consciousness in shaping reality, and Immanuel Kant, who explored the role of perception and the mind in constructing experience. In Futurism, Filippo Tommaso Marinetti stands out as the founder, advocating for a rejection of the past and a celebration of technology, speed, and innovation, while Ray Kurzweil represents modern Futurism through his predictions on artificial intelligence and technological singularity. Both movements have shaped philosophical and cultural narratives, with Idealism focusing on metaphysical ideas and Futurism prioritizing progress and transformation.
Idealism in Modern Society
Idealism in modern society emphasizes the pursuit of ethical principles, human values, and the belief that reality is shaped by the mind and ideas. This philosophical approach influences education, politics, and culture by encouraging visionary thinking and the prioritization of moral goals over material success. Idealism fosters innovation and social progress by inspiring individuals to imagine transformative possibilities beyond current limitations.
Futurism's Impact on Technology and Culture
Futurism, emerging in the early 20th century, profoundly influenced technology and culture by celebrating speed, innovation, and modernity, championing dynamic movement and mechanization. This artistic and social movement inspired advancements in industrial design, architecture, and transportation, pushing boundaries toward the future with optimism about technological progress. Its impact reshaped cultural perceptions by embracing change and the machine age, laying groundwork for the modern relationship between humans and technology.
Idealism vs Futurism: Philosophical Debates
Idealism centers on the belief that reality is fundamentally shaped by the mind, emphasizing ideas, consciousness, and perception as primary. Futurism challenges this by prioritizing technological progress, innovation, and the tangible transformation of society through evolving scientific advancements. Philosophical debates between Idealism and Futurism explore the tension between metaphysical concepts and empirical future-oriented changes in shaping human experience and knowledge.
The Future of Idealism and Futurism
The future of idealism envisions a world guided by ethical values, human consciousness, and the pursuit of meaning beyond materialism, emphasizing metaphysical insights and spiritual growth. Futurism anticipates rapid technological advancements, innovation in artificial intelligence, and transformative societal changes that reshape industries, communication, and daily life. Integrating the visionary aspects of idealism with the pragmatic focus of futurism could inspire sustainable development and ethical frameworks for emerging technologies.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Idealism and Futurism
Striking a balance between idealism and futurism involves harmonizing visionary aspirations with pragmatic innovation to create sustainable progress. Integrating idealism's focus on values and purpose with futurism's emphasis on technological advancements drives holistic development in society and business. This synthesis fosters adaptable strategies that align ethical principles with emerging trends for long-term impact.
Idealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com