Imams play a vital role in guiding and leading Muslim communities through religious duties, spiritual teachings, and community services. Their knowledge of Islamic law and ability to interpret the Quran helps provide clarity and support for daily life and worship practices. Discover more about the significance of imams and how they influence your faith journey in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
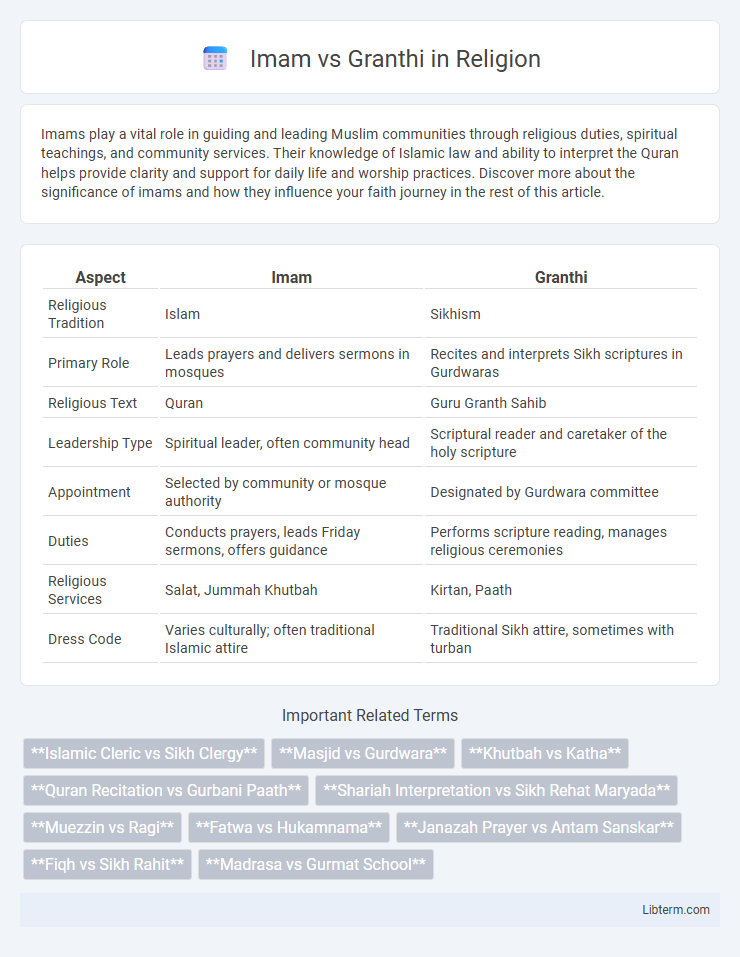
| Aspect | Imam | Granthi |
|---|---|---|
| Religious Tradition | Islam | Sikhism |
| Primary Role | Leads prayers and delivers sermons in mosques | Recites and interprets Sikh scriptures in Gurdwaras |
| Religious Text | Quran | Guru Granth Sahib |
| Leadership Type | Spiritual leader, often community head | Scriptural reader and caretaker of the holy scripture |
| Appointment | Selected by community or mosque authority | Designated by Gurdwara committee |
| Duties | Conducts prayers, leads Friday sermons, offers guidance | Performs scripture reading, manages religious ceremonies |
| Religious Services | Salat, Jummah Khutbah | Kirtan, Paath |
| Dress Code | Varies culturally; often traditional Islamic attire | Traditional Sikh attire, sometimes with turban |
Definition: Imam and Granthi Explained
An Imam is a religious leader in Islam who leads prayers, provides spiritual guidance, and interprets Islamic teachings for the community, often recognized in mosques or Islamic centers. A Granthi is a Sikh scripture reader and custodian responsible for the care and recitation of the Guru Granth Sahib, the central holy scripture of Sikhism, ensuring its proper handling and ceremonial presentation. Both roles serve as key religious authorities within their respective faiths, emphasizing spiritual leadership and scriptural stewardship.
Historical Origins of Imam and Granthi
The historical origins of the Imam trace back to early Islamic leadership, especially within Shia Islam where Imams are considered divinely appointed spiritual successors to Prophet Muhammad, beginning with Imam Ali in the 7th century. Granthis originate from Sikhism, emerging during the 15th and 16th centuries in Punjab as ceremonial readers and custodians of the Guru Granth Sahib, the Sikh holy scripture. Both roles hold deep religious significance but stem from distinct theological frameworks and historical contexts within Islam and Sikhism respectively.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Imams lead Islamic congregational prayers, deliver sermons, and provide spiritual guidance within the Muslim community, ensuring adherence to religious practices and teachings. Granthis serve as ceremonial custodians of the Sikh scriptures, facilitate readings from the Guru Granth Sahib, and assist in conducting Sikh religious services and rituals. Both roles emphasize leadership and religious instruction but differ in scripture focus and specific ritual duties.
Religious Significance in Islam and Sikhism
In Islam, an Imam is a religious leader who leads prayers, delivers sermons, and provides spiritual guidance within the Muslim community, embodying both religious authority and communal leadership. In Sikhism, a Granthi serves as a ceremonial reader and custodian of the Guru Granth Sahib, playing a crucial role in preserving and interpreting the Sikh scripture during religious ceremonies. Both roles hold significant spiritual importance, with the Imam focusing on Islamic worship and jurisprudence, while the Granthi emphasizes scripture stewardship and ritual practice in Sikhism.
Training and Qualifications Required
Imams typically undergo formal religious education in Islamic theology, jurisprudence, and Quranic studies at recognized Islamic seminaries or institutions, attaining certifications such as Ijaza or degrees in Islamic Studies. Granthis receive training primarily in Sikh scriptures, rituals, and ceremonies, often through Sikh religious institutions or under the mentorship of experienced Granthis, mastering the recitation and interpretation of the Guru Granth Sahib. Both roles require a deep understanding of their respective religious texts and traditions, but Imams focus more on Islamic law and community leadership, while Granthis emphasize liturgical expertise and ceremonial duties within the Gurdwara.
Rituals and Ceremonies Led by Imam vs Granthi
Imams lead Islamic rituals such as daily prayers (Salah), Friday congregational prayers (Jumu'ah), and special ceremonies like Eid prayers and Ramadan Taraweeh. Granthis officiate Sikh ceremonies including reading from the Guru Granth Sahib during rituals like weddings (Anand Karaj), Amrit Sanchar (baptism), and Akhand Path (continuous scripture reading). The primary distinction lies in Imams conducting Islamic worship with Quranic recitations, while Granthis focus on Sikh scriptural rites and community prayers.
Community Leadership and Social Influence
Imams serve as religious leaders in Muslim communities, guiding prayers, interpreting Islamic law, and providing spiritual and social counsel that fosters unity and moral conduct. Granthis hold a pivotal role in Sikh gurdwaras, responsible for reading the Guru Granth Sahib and promoting Sikh teachings, which strengthens communal identity and social cohesion. Both positions exemplify influential community leadership by upholding religious traditions and addressing social needs within their respective faith groups.
Gender and Inclusivity Considerations
Imams, traditionally male religious leaders in Islam, guide congregational prayers and community religious practices, while Granthis, often men or women, serve as custodians and readers of the Guru Granth Sahib in Sikhism, reflecting more gender inclusivity. Sikhism's Granthi role actively embraces female participation, promoting gender equality within religious leadership. In contrast, many Islamic communities maintain male-only Imams, highlighting differing gender inclusivity approaches between these faith traditions.
Comparing Daily Duties: Mosque vs Gurdwara
Imams lead daily prayers and deliver sermons in mosques, focusing on Islamic rituals such as Salah, Quranic recitations, and religious education for the Muslim community. Granthis perform similar roles in gurdwaras, reading from the Guru Granth Sahib, conducting ceremonies, and guiding devotees through Sikh teachings and kirtan sessions. Both serve as spiritual leaders, but the Imam's duties center on Islamic practices while the Granthi emphasizes Sikh scripture and communal worship.
Common Misconceptions and Differences
Imams and Granthis both hold significant roles in their respective religious communities, yet their functions and traditions differ markedly; Imams primarily lead prayers and provide spiritual guidance in Islam, while Granthis read from the Guru Granth Sahib and perform rituals in Sikhism. Common misconceptions often arise, such as assuming Granthis have the same authority as Imams, or that both roles involve political leadership, which is generally inaccurate. Understanding these distinctions clarifies their unique contributions to Islamic and Sikh worship practices without conflating their responsibilities or religious contexts.
Imam Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com