Manmukh refers to a person who is self-centered and follows worldly desires rather than spiritual wisdom, often ignoring higher moral values. This term highlights the struggle between material attachment and the pursuit of inner enlightenment, emphasizing the importance of self-awareness and mindfulness in personal growth. Discover how understanding the concept of Manmukh can transform Your approach to life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
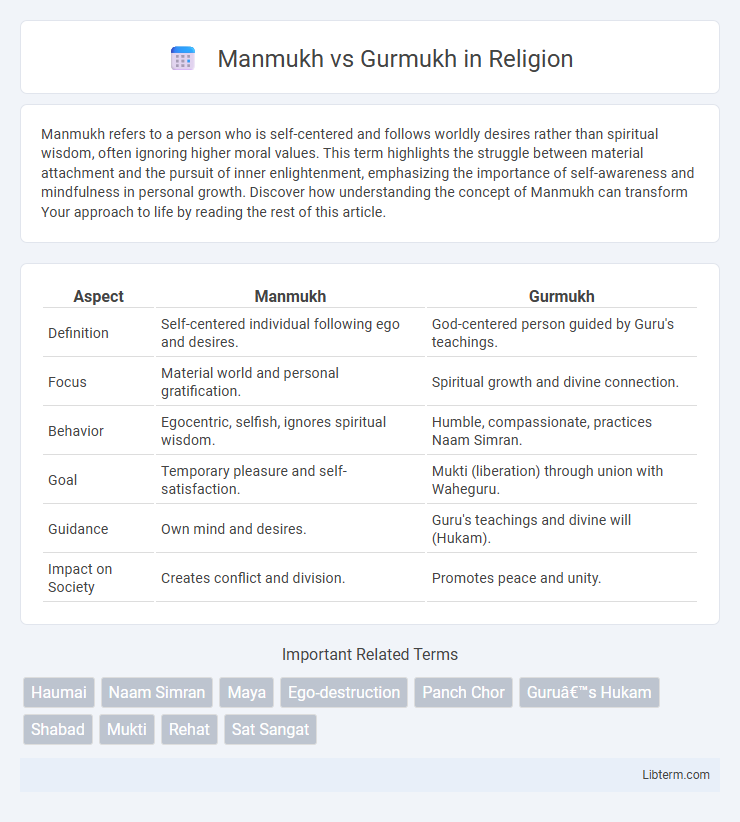
| Aspect | Manmukh | Gurmukh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-centered individual following ego and desires. | God-centered person guided by Guru's teachings. |
| Focus | Material world and personal gratification. | Spiritual growth and divine connection. |
| Behavior | Egocentric, selfish, ignores spiritual wisdom. | Humble, compassionate, practices Naam Simran. |
| Goal | Temporary pleasure and self-satisfaction. | Mukti (liberation) through union with Waheguru. |
| Guidance | Own mind and desires. | Guru's teachings and divine will (Hukam). |
| Impact on Society | Creates conflict and division. | Promotes peace and unity. |
Understanding Manmukh and Gurmukh: Definitions
Manmukh refers to a person who is self-willed and follows their own desires, often ignoring spiritual teachings and righteousness. Gurmukh describes an individual oriented towards the Guru's wisdom, living in accordance with divine guidance and moral principles. These definitions highlight the contrasting mindsets: Manmukh is driven by ego and materialism, while Gurmukh embodies spiritual enlightenment and devotion.
Origins of the Concepts in Sikhism
Manmukh and Gurmukh are fundamental concepts in Sikhism representing contrasting approaches to life and spirituality, with origins rooted in Guru Nanak's teachings. Manmukh refers to individuals who follow their own limited desires and ego, prioritizing the self over divine will, while Gurmukh describes those who align their lives with the Guru's guidance and embody spiritual wisdom and humility. These concepts are extensively discussed in the Guru Granth Sahib, Sikhism's central scripture, emphasizing the transformative journey from self-centeredness to God-centered living.
Core Characteristics of a Manmukh
A Manmukh is characterized by ego, self-centeredness, and attachment to worldly desires, often neglecting spiritual wisdom and divine guidance. This type of person prioritizes material gains, reacts impulsively to emotions, and remains engrossed in the five vices: lust, anger, greed, attachment, and ego. As a result, a Manmukh lacks humility, mindfulness, and detachment, contrasting sharply with the enlightened and God-centered nature of a Gurmukh.
Attributes of a Gurmukh
A Gurmukh embodies virtues such as humility, compassion, and unwavering faith in the Divine, consistently aligning actions with Guru's teachings. This individual practices selflessness, mindfulness, and strives to merge ego with spiritual wisdom, fostering inner peace and harmony with others. The Gurmukh's life reflects discipline, devotion, and a pursuit of truth, contrasting sharply with the self-centered, materialistic tendencies of a Manmukh.
Manmukh vs Gurmukh in Daily Life
Manmukh focuses on selfish desires and materialism, leading to stress, confusion, and a lack of inner peace in daily life. Gurmukh aligns actions with spiritual wisdom and selflessness, fostering harmony, clarity, and contentment. Choosing Gurmukh mentality promotes balanced relationships and mindful decision-making throughout everyday experiences.
Spiritual Implications of Each Path
Manmukh, driven by self-centered desires and ego, often remains trapped in material illusions, hindering spiritual growth and connection with the divine. Gurmukh follows the Guru's wisdom, embracing humility and selfless devotion, leading to inner peace and union with God. The spiritual implications highlight Manmukh's cycle of rebirth and suffering, while Gurmukh attains liberation (moksha) through faith and righteous living.
Teachings of Guru Granth Sahib on Manmukh and Gurmukh
The Guru Granth Sahib describes Manmukh as one who follows self-will, remains engrossed in worldly desires, and is disconnected from spiritual wisdom, leading to cycles of suffering and ignorance. In contrast, a Gurmukh aligns their mind and actions with the Guru's teachings, embracing humility, compassion, and mindfulness of Waheguru, resulting in inner peace and liberation (mukti). The scripture emphasizes that transforming from Manmukh to Gurmukh requires continuous remembrance of Naam, selfless service (seva), and surrender to divine will (Hukam).
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
Many people mistakenly believe that being a Manmukh simply means ignoring spiritual teachings, but it specifically refers to living driven by ego and material desires rather than divine wisdom. A Gurmukh is often misunderstood as merely a religious follower, whereas it truly signifies aligning one's actions and thoughts with the Guru's teachings and inner divine guidance. These clarifications highlight that Manmukh and Gurmukh are not just labels but represent fundamentally different orientations towards life and spirituality.
Steps to Transition from Manmukh to Gurmukh
Transitioning from Manmukh to Gurmukh requires a conscious commitment to aligning actions and thoughts with Gurbani teachings and Sikh principles. Developing consistent meditation on Waheguru's name (Naam Simran) and practicing selfless service (Seva) cultivate spiritual awareness and detach one from ego-driven desires. Embracing humility, ethical living, and compassion fosters the inner transformation necessary to embody the Gurmukh mindset, oriented towards divine will (Hukam).
Importance of the Gurmukh Ideal in Modern Society
The Gurmukh ideal, centered on living according to divine guidance and embodying humility, compassion, and selflessness, offers a transformative framework for modern society's ethical challenges. Embracing Gurmukh principles fosters social harmony, mental peace, and resilient communities by prioritizing collective well-being over individual ego, contrasting sharply with the self-centered Manmukh approach. This shift towards a Gurmukh mindset is crucial in addressing contemporary issues like materialism, environmental degradation, and social fragmentation.
Manmukh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com