Pakhandi refers to someone who is deceitful or hypocritical, often pretending to have qualities or beliefs they do not truly possess. Understanding the traits and behaviors associated with pakhandi individuals can help you identify and protect yourself from insincere relationships. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to recognize and deal with pakhandi people effectively.
Table of Comparison
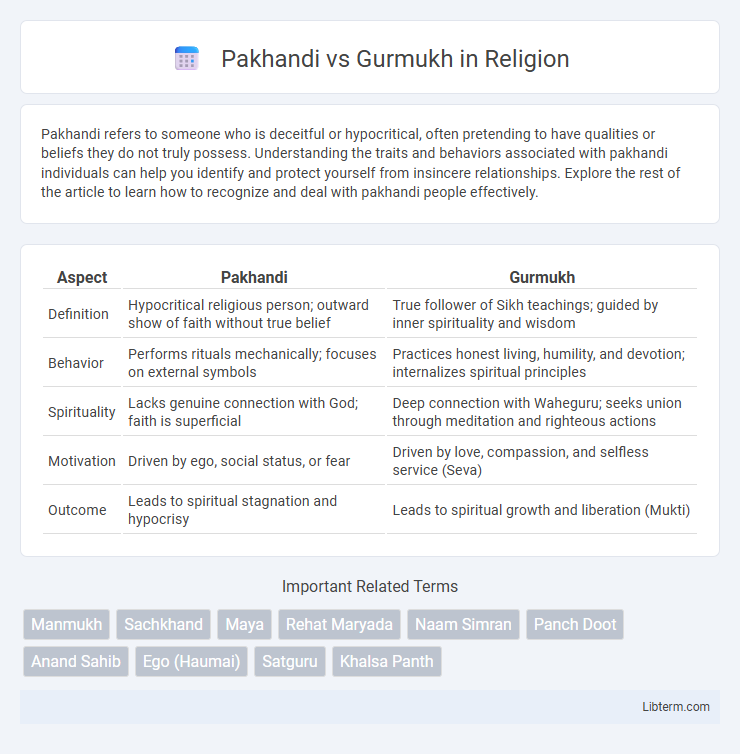
| Aspect | Pakhandi | Gurmukh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hypocritical religious person; outward show of faith without true belief | True follower of Sikh teachings; guided by inner spirituality and wisdom |
| Behavior | Performs rituals mechanically; focuses on external symbols | Practices honest living, humility, and devotion; internalizes spiritual principles |
| Spirituality | Lacks genuine connection with God; faith is superficial | Deep connection with Waheguru; seeks union through meditation and righteous actions |
| Motivation | Driven by ego, social status, or fear | Driven by love, compassion, and selfless service (Seva) |
| Outcome | Leads to spiritual stagnation and hypocrisy | Leads to spiritual growth and liberation (Mukti) |
Understanding Pakhandi: Definition and Origins
Pakhandi refers to individuals who practice hypocrisy or false religiosity, often engaging in ostentatious displays of piety without genuine spiritual intent, a concept rooted deeply in South Asian cultural and religious contexts. The term originates from Punjabi and Urdu languages, historically used to critique superficial religious adherence that diverges from sincere faith practices. Understanding Pakhandi involves recognizing its role in social and religious discourse, where it highlights the tension between outward showmanship and true spiritual commitment.
Who is a Gurmukh? Core Characteristics
A Gurmukh is an individual who lives in alignment with the teachings of the Guru, embodying spiritual wisdom, humility, and selflessness. Core characteristics of a Gurmukh include devotion to truth, compassion for others, and constant remembrance of the Divine, leading to a life of righteousness and inner peace. Unlike a Pakhandi, who is hypocritical and superficial in faith, a Gurmukh demonstrates genuine spiritual integrity and dedication to Sikh principles.
Philosophical Differences: Pakhandi vs Gurmukh
Pakhandi individuals exhibit hypocrisy by outwardly professing religious beliefs while internally lacking true spiritual understanding or devotion, contrasting sharply with Gurmukh who lives in alignment with divine wisdom and embody virtues such as humility and selflessness. The Pakhandi approach centers on superficial rituals and external appearances aimed at social recognition, whereas the Gurmukh pursues sincere inner transformation and union with the divine essence. Philosophically, Pakhandi represents ego-driven behavior rooted in maya (illusion), while Gurmukh reflects a soul-centered consciousness oriented towards truth, compassion, and liberation.
Scriptural Perspectives on Pakhandi and Gurmukh
Scriptural perspectives on Pakhandi emphasize deceit and hypocrisy, condemning those who manipulate spiritual teachings for personal gain, as highlighted in Guru Granth Sahib where such behavior is described as turning away from divine truth. Gurmukh, in contrast, is portrayed in Sikh scriptures as one who lives in harmony with God's will, embodying humility, truth, and genuine devotion. The dichotomy between Pakhandi and Gurmukh underscores the importance of inner sincerity and adherence to authentic spiritual practice in Sikh theology.
Signs of Pakhandi Behavior in Daily Life
Pakhandi behavior often manifests through hypocrisy, where individuals outwardly display piety but act deceitfully or selfishly in private, undermining trust in social and religious settings. Common signs include insincerity in rituals, excessive self-promotion, and judgmental attitudes that contradict their claimed virtues, highlighting a disconnect between appearance and reality. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for distinguishing genuine Gurmukh qualities, which emphasize humility, sincerity, and consistent ethical conduct in daily life.
Living as a Gurmukh: Spiritual Practices
Living as a Gurmukh involves embracing daily spiritual practices that align with Sikh teachings, such as Naam Simran (meditative repetition of God's name) and Seva (selfless service) to promote inner peace and community harmony. This path emphasizes humility, truthfulness, and devotion to Waheguru, fostering a connection that transcends ego and material attachments common in Pakhandi behaviors. Constant mindfulness of divine presence helps Gurmukhs cultivate virtues like compassion and contentment, anchoring their lives in spiritual growth rather than external rituals or hypocrisy.
Social Impact: Pakhandi vs Gurmukh in Society
Pakhandi, characterized by hypocrisy and false religiosity, erodes social trust and fosters division within communities, often leading to cynicism and weakened social cohesion. In contrast, Gurmukh embodies authenticity and spiritual integrity, promoting unity, compassion, and ethical behavior that strengthen societal bonds and encourage collective well-being. The social impact of Gurmukh enhances communal harmony and moral accountability, while Pakhandi fuels mistrust and fragmentation in society.
Identifying True Spirituality: Beyond Appearances
Pakhandi, often characterized by superficial displays of spirituality, focuses on external rituals and ostentatious behavior, whereas Gurmukh embodies true spirituality by internalizing the teachings of the Guru and living a life of humility, compassion, and self-awareness. True spirituality transcends mere appearances and rituals, emphasizing an authentic connection with the divine through consistent practice of virtues and mindfulness. Identifying true spirituality requires discernment to differentiate between hollow showmanship and genuine inner transformation aligned with Sikh principles.
The Path to Transformation: From Pakhandi to Gurmukh
The path to transformation from Pakhandi to Gurmukh centers on rejecting hypocrisy and embracing genuine spirituality as taught in Sikh scriptures. A Pakhandi is marked by superficial religious practices and ego-driven behavior, while a Gurmukh aligns actions with divine wisdom, humility, and selflessness. This journey involves deep self-reflection, sincere devotion, and living in harmony with the teachings of Guru Granth Sahib, fostering inner purity and liberation.
Lessons from Sikh Gurus on Authentic Living
Sikh Gurus emphasized the importance of authentic living by contrasting Pakhandi (hypocrisy) with Gurmukh (God-oriented) conduct, urging followers to embody sincerity, humility, and selfless devotion. The Gurus taught that Pakhandi behavior, marked by outward displays of religiosity without inner truth, leads to spiritual deception, whereas a Gurmukh lives in alignment with divine will, practicing honest actions and maintaining a heartfelt connection with Waheguru. These teachings highlight that true spirituality arises from inner transformation and consistent ethical living, not mere external performance.
Pakhandi Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com