Apologetics defends and explains the rational basis of religious beliefs, particularly in Christianity, addressing challenges from skepticism and secular critiques. It equips Your mind with thoughtful responses to objections, strengthening faith through evidence and reasoned arguments. Explore the rest of the article to deepen Your understanding of apologetics and its role in intellectual and spiritual growth.
Table of Comparison
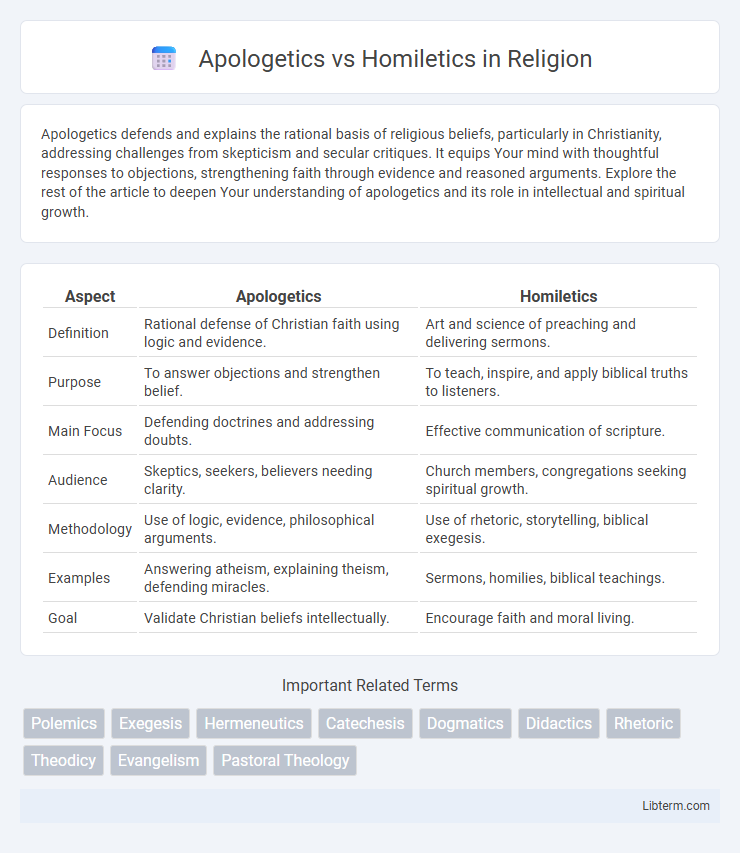
| Aspect | Apologetics | Homiletics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rational defense of Christian faith using logic and evidence. | Art and science of preaching and delivering sermons. |
| Purpose | To answer objections and strengthen belief. | To teach, inspire, and apply biblical truths to listeners. |
| Main Focus | Defending doctrines and addressing doubts. | Effective communication of scripture. |
| Audience | Skeptics, seekers, believers needing clarity. | Church members, congregations seeking spiritual growth. |
| Methodology | Use of logic, evidence, philosophical arguments. | Use of rhetoric, storytelling, biblical exegesis. |
| Examples | Answering atheism, explaining theism, defending miracles. | Sermons, homilies, biblical teachings. |
| Goal | Validate Christian beliefs intellectually. | Encourage faith and moral living. |
Understanding Apologetics: Definition and Purpose
Apologetics involves the reasoned defense of Christian faith through logical arguments and evidence, aiming to address doubts and objections. Its purpose is to demonstrate the truthfulness and rationality of Christianity to both believers and skeptics. This discipline seeks to clarify doctrinal truths while engaging contemporary philosophical and cultural challenges.
Key Principles of Homiletics
Homiletics centers on the art of preaching, emphasizing clear communication, biblical fidelity, and audience engagement to effectively convey scriptural truths. Core principles include sermon structure, such as introduction, body, and conclusion, along with the use of rhetorical devices and illustrative examples to enhance understanding. Homiletics prioritizes application and spiritual impact, ensuring messages resonate and inspire transformation within congregations.
Historical Development of Apologetics
The historical development of apologetics traces back to early Christian writers like Justin Martyr and Tertullian, who defended the faith against pagan criticism and philosophical objections. Apologists systematically addressed challenges from Greco-Roman philosophies and emerging heresies, shaping the discipline into a rational defense of Christianity. Over centuries, apologetics evolved through medieval scholasticism and Reformation debates, emphasizing scriptural authority and reasoned argumentation against skepticism and secular ideologies.
Evolution of Homiletics in Christian Tradition
The evolution of homiletics in the Christian tradition reflects a shift from merely delivering doctrinal defenses, as seen in apologetics, to crafting sermons that engage both the intellect and the emotions of the congregation. Early church fathers emphasized rhetorical skills and scriptural interpretation to persuade and educate believers, while modern homiletics integrates cultural context and communication theory to enhance message effectiveness. This development underscores the transition from argumentative discourse to transformative preaching that fosters spiritual growth and communal identity.
Core Differences between Apologetics and Homiletics
Apologetics centers on defending and rationally explaining the Christian faith against objections using evidence and logical argumentation, while Homiletics focuses on the art and method of preaching or delivering sermons to inspire and instruct a congregation. The core difference lies in Apologetics' emphasis on intellectual defense and proof, whereas Homiletics prioritizes effective communication and spiritual edification through clearly structured messages. Apologists engage audiences by addressing doubts and questions, whereas homileticians craft sermons that apply biblical truths to everyday life.
Objectives: Defending Faith vs. Preaching Faith
Apologetics centers on defending the Christian faith through reasoned arguments and evidence, addressing doubts and objections to strengthen believers' confidence. Homiletics emphasizes preaching faith by effectively communicating biblical truths to inspire spiritual growth and transformation within congregations. Both disciplines aim to deepen faith, but apologetics targets intellectual validation while homiletics focuses on devotional application.
Essential Skills for Effective Apologists
Effective apologists master critical thinking, persuasive communication, and deep theological knowledge to address challenges to faith and clarify doctrines. They develop skills in engaging cultural contexts, managing objections, and articulating reasoned arguments with clarity and respect. Proficiency in Scripture interpretation and familiarity with philosophical concepts enhance their ability to defend beliefs compellingly against skepticism.
Homiletical Techniques for Impactful Sermons
Homiletical techniques such as storytelling, vivid imagery, and rhetorical questions enhance sermon engagement and retention, making messages more impactful. Utilizing scriptural exposition combined with practical application ensures relevance and spiritual growth for congregants. Effective homiletics balance theological depth with relatable illustrations, maximizing the sermon's influence on listeners' faith and daily lives.
Common Challenges in Apologetics and Homiletics
Common challenges in apologetics include addressing deeply held worldviews and overcoming skepticism without alienating the audience. In homiletics, difficulties often arise in crafting sermons that are both theologically rich and relatable to diverse congregations. Both fields require skillful communication to effectively convey complex religious truths while engaging listeners meaningfully.
Integrating Apologetics and Homiletics in Modern Ministry
Integrating apologetics and homiletics in modern ministry enhances the effectiveness of sermons by addressing both the intellectual and spiritual needs of the congregation. Apologetics strengthens homiletics by providing reasoned arguments that defend the faith, enabling preachers to engage skeptics and deepen believers' understanding. This synergy fosters a comprehensive approach that equips pastors to communicate biblical truths persuasively and confidently in contemporary cultural contexts.
Apologetics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com