Hermeneutics explores the theory and methodology of interpretation, especially of texts and symbolic expressions, focusing on understanding meaning in context. It is essential for analyzing literature, law, and religious scriptures, enabling deeper insight into complex ideas and cultural nuances. Discover how hermeneutics can transform your perspective by diving into the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
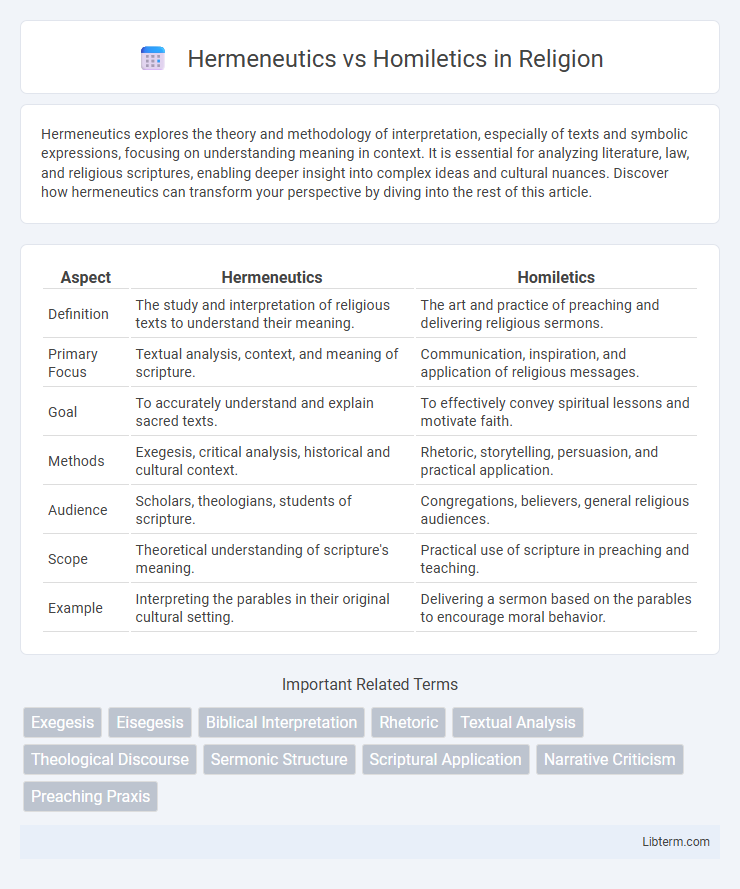
| Aspect | Hermeneutics | Homiletics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The study and interpretation of religious texts to understand their meaning. | The art and practice of preaching and delivering religious sermons. |
| Primary Focus | Textual analysis, context, and meaning of scripture. | Communication, inspiration, and application of religious messages. |
| Goal | To accurately understand and explain sacred texts. | To effectively convey spiritual lessons and motivate faith. |
| Methods | Exegesis, critical analysis, historical and cultural context. | Rhetoric, storytelling, persuasion, and practical application. |
| Audience | Scholars, theologians, students of scripture. | Congregations, believers, general religious audiences. |
| Scope | Theoretical understanding of scripture's meaning. | Practical use of scripture in preaching and teaching. |
| Example | Interpreting the parables in their original cultural setting. | Delivering a sermon based on the parables to encourage moral behavior. |
Introduction to Hermeneutics and Homiletics
Hermeneutics involves the systematic study of interpreting biblical texts, focusing on understanding context, language, and original intent to ensure accurate theological meaning. Homiletics centers on the art and science of preaching, emphasizing the effective communication and application of those interpreted texts to a contemporary audience. Both disciplines are foundational in theological education, where hermeneutics provides critical tools for exegesis, and homiletics transforms exegesis into impactful sermons.
Defining Hermeneutics: Principles and Purpose
Hermeneutics involves the study and interpretation of biblical texts, focusing on uncovering original meanings through contextual analysis, linguistic examination, and historical-cultural insights. It establishes principles such as grammatical-historical interpretation, authorial intent, and textual coherence to accurately grasp Scripture's message. The purpose of hermeneutics is to provide a clear, objective understanding of biblical passages that informs sound theological conclusions and preaching.
Understanding Homiletics: Art and Application
Homiletics, as the art of preaching, emphasizes the effective communication and application of biblical texts to inspire and instruct congregations. It integrates rhetorical skills with theological insights to craft sermons that resonate with diverse audiences and address their spiritual needs. Mastery of homiletics requires understanding both the message's theological depth and the cultural context to facilitate meaningful engagement and transformation.
Historical Development of Hermeneutics
Hermeneutics, originating from ancient Greek philosophy and biblical interpretation, evolved significantly through the works of Friedrich Schleiermacher and Wilhelm Dilthey in the 19th century, emphasizing understanding texts within their historical and cultural contexts. Its development contrasts with homiletics, which centers on the art of preaching and practical application of biblical messages rather than comprehensive textual analysis. Hermeneutics' historical trajectory highlights a shift from strict scriptural exegesis to a broader philosophical methodology for interpreting human communication and meaning.
The Evolution of Homiletics in Preaching
Homiletics has evolved significantly from its origins in ancient rhetorical principles to a specialized discipline focused on the effective communication of biblical messages in preaching. Whereas hermeneutics centers on the interpretation and understanding of scriptural texts, homiletics applies these interpretations to craft sermons that engage and inspire congregations. Modern homiletics integrates theological insights, cultural context, and rhetorical strategies, reflecting its ongoing development as a vital tool for impactful preaching.
Core Differences Between Hermeneutics and Homiletics
Hermeneutics centers on the interpretation and explanation of biblical texts, emphasizing context, language, and historical background to uncover meaning. Homiletics focuses on the art and practice of preaching, transforming interpretive insights into effective, engaging sermons that communicate spiritual truths to an audience. The core difference lies in hermeneutics as a theoretical framework for understanding scripture, while homiletics applies that understanding in practical communication.
How Hermeneutics Shapes Biblical Interpretation
Hermeneutics shapes biblical interpretation by providing a systematic framework for understanding scripture's historical context, language, and literary genres, ensuring accurate and meaningful exegesis. It emphasizes the original intent of biblical authors, enabling interpreters to bridge cultural and temporal gaps while avoiding anachronistic readings. This rigorous analytical approach contrasts with homiletics, which centers on applying and communicating biblical truths effectively within a preaching context.
The Role of Homiletics in Sermon Delivery
Homiletics plays a crucial role in sermon delivery by shaping the interpretation of biblical texts into clear, compelling messages tailored for congregational engagement. It involves the practical application of hermeneutical insights to structure sermons that are both theologically sound and pastorally relevant. Effective homiletics ensures that sermons communicate core scriptural truths in ways that inspire reflection, spiritual growth, and ethical action among listeners.
Integration of Hermeneutics and Homiletics in Ministry
Integration of hermeneutics and homiletics in ministry enhances the effectiveness of preaching by ensuring biblical texts are accurately interpreted and contextually communicated. Hermeneutics provides the critical framework for understanding scriptural meaning, while homiletics translates these insights into compelling sermons that resonate with diverse congregations. This synergy deepens theological insight, enriches spiritual formation, and fosters impactful pastoral engagement.
Conclusion: Impact on Contemporary Christian Communication
Hermeneutics enhances contemporary Christian communication by providing deep, contextually accurate interpretations of biblical texts, ensuring messages are theologically sound and relevant. Homiletics transforms these interpretations into engaging, practical sermons that resonate with diverse congregations and inspire spiritual growth. Together, hermeneutics and homiletics bridge scholarly exegesis and effective public preaching, enriching modern faith expression and community understanding.
Hermeneutics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com