The hijab is a traditional headscarf worn by many Muslim women as a symbol of modesty and religious faith. It serves both cultural and spiritual purposes, reflecting identity while promoting self-respect and privacy. Discover the deeper meanings and diverse styles of the hijab throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
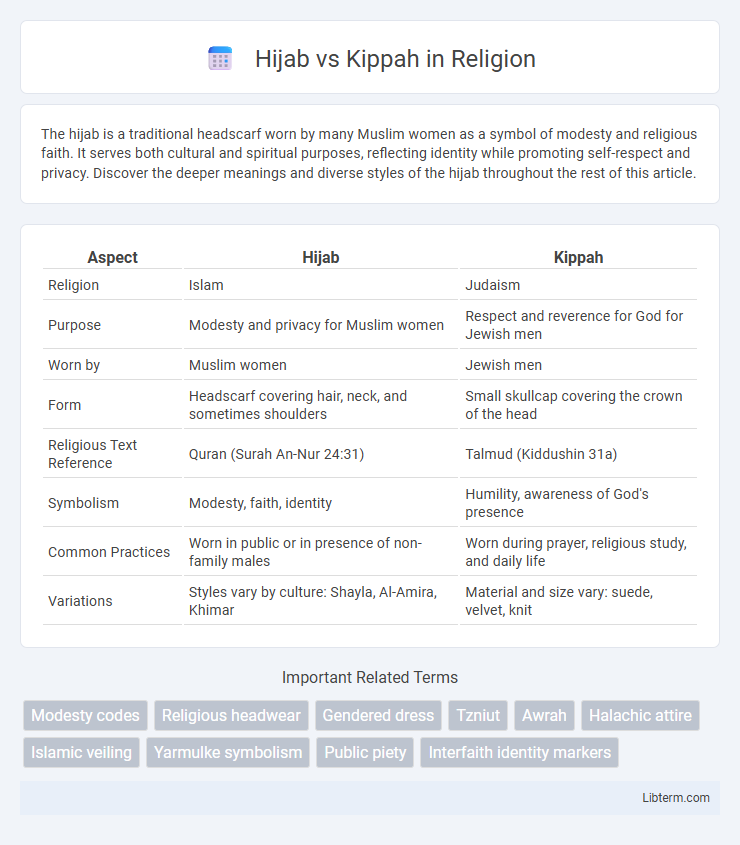
| Aspect | Hijab | Kippah |
|---|---|---|
| Religion | Islam | Judaism |
| Purpose | Modesty and privacy for Muslim women | Respect and reverence for God for Jewish men |
| Worn by | Muslim women | Jewish men |
| Form | Headscarf covering hair, neck, and sometimes shoulders | Small skullcap covering the crown of the head |
| Religious Text Reference | Quran (Surah An-Nur 24:31) | Talmud (Kiddushin 31a) |
| Symbolism | Modesty, faith, identity | Humility, awareness of God's presence |
| Common Practices | Worn in public or in presence of non-family males | Worn during prayer, religious study, and daily life |
| Variations | Styles vary by culture: Shayla, Al-Amira, Khimar | Material and size vary: suede, velvet, knit |
Introduction: Understanding Hijab and Kippah
Hijab and Kippah are distinct religious head coverings symbolizing faith and identity in Islam and Judaism, respectively. The Hijab typically refers to a scarf covering the hair and neck for Muslim women, representing modesty and devotion. The Kippah, a small skullcap worn by Jewish men, signifies reverence and acknowledgment of a higher authority.
Historical Origins of the Hijab and Kippah
The hijab, originating in pre-Islamic Arabian cultures, evolved as a modesty garment codified in Islamic teachings during the 7th century, symbolizing privacy and religious identity for Muslim women. The kippah, also known as a yarmulke, traces back to ancient Jewish tradition, with Talmudic references emphasizing head coverings as a sign of reverence and humility before God. Both head coverings embody deep-rooted religious and cultural significance, reflecting the distinct historical contexts of Islam and Judaism.
Religious Significance in Islam and Judaism
The hijab in Islam symbolizes modesty, privacy, and morality, serving as a visible expression of faith and adherence to Islamic guidelines for women's dress. The kippah, also known as a yarmulke, holds religious significance in Judaism as a sign of reverence and acknowledgment of God's presence, traditionally worn by men during prayer, study, and other religious occasions. Both head coverings reflect deep-rooted spiritual identities and cultural customs within their respective religions, emphasizing devotion and religious observance.
Cultural Interpretations Across Regions
The hijab and kippah serve distinct cultural and religious functions across various regions, reflecting diverse interpretations within Islamic and Jewish communities. In Middle Eastern countries, the hijab symbolizes modesty and identity, often intertwined with socio-political norms, while in Western societies, it also represents personal faith and multiculturalism. Conversely, the kippah is predominantly worn by Jewish men globally as a sign of reverence and communal belonging, with variations in style and usage reflecting regional customs from Eastern Europe to Israel.
Differences in Symbolism and Meaning
The hijab symbolizes modesty, privacy, and religious faith in Islam, often representing a woman's commitment to Islamic principles and identity. The kippah, or yarmulke, signifies reverence and awareness of God's presence in Judaism, worn primarily by men to express humility before the divine. Both serve as visible markers of religious devotion, yet the hijab emphasizes personal modesty while the kippah highlights spiritual consciousness and community belonging.
Gender and Religious Head Coverings
Hijab and kippah serve as significant religious head coverings that reflect distinct gender roles and spiritual identities within Islam and Judaism respectively. The hijab is traditionally worn by Muslim women to express modesty and devotion, symbolizing a gender-specific practice rooted in Islamic teachings. In contrast, the kippah is predominantly worn by Jewish men as a sign of reverence and awareness of God, highlighting differing religious obligations tied to gender in these faiths.
Legal and Social Challenges Worldwide
The hijab and kippah, as religious symbols, face diverse legal restrictions and social challenges across various countries, reflecting differing levels of religious freedom and secularism. In nations like France and Turkey, laws banning conspicuous religious attire target the hijab, impacting Muslim women's rights and sparking international debates on secularism versus religious expression. Conversely, the kippah encounters social discrimination and occasional legal limitations in regions with heightened anti-Semitic sentiments, highlighting ongoing struggles for religious minorities to freely practice their faith worldwide.
Modern Fashion and Identity Expression
The hijab and kippah serve as powerful symbols of religious identity while evolving into significant elements of modern fashion. Contemporary designers incorporate vibrant patterns and diverse materials, allowing wearers to express personal style alongside cultural heritage. This fusion of tradition and trend highlights how both garments empower individuals to navigate faith and identity in today's globalized society.
Stereotypes, Misconceptions, and Media Representation
Hijab and kippah, symbols of Muslim and Jewish identities respectively, often face stereotypes and misconceptions in media representation, where hijab is frequently associated with oppression and kippah with insularity. Misunderstandings arise from generalized portrayals that overlook the cultural, religious, and personal significance of these head coverings, leading to biased narratives. Media narratives tend to simplify these symbols instead of highlighting their diverse meanings, contributing to public prejudice and reducing complex identities to mere visual markers.
Fostering Interfaith Dialogue and Respect
The hijab and kippah serve as powerful symbols of religious identity in Islam and Judaism, respectively, fostering mutual understanding when recognized in interfaith dialogue. Emphasizing their shared role in expressing faith encourages respect and bridges cultural divides between Muslim and Jewish communities. This recognition supports collaborative efforts to promote religious tolerance and challenge stereotypes, enhancing coexistence and peace.
Hijab Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com