Nifaq, often translated as hypocrisy in Islamic teachings, involves a discrepancy between outward behavior and inner belief, undermining sincerity in faith and community trust. Addressing nifaq is crucial for maintaining genuine relationships and spiritual integrity. Explore the rest of this article to understand how to recognize and overcome nifaq in your life.
Table of Comparison
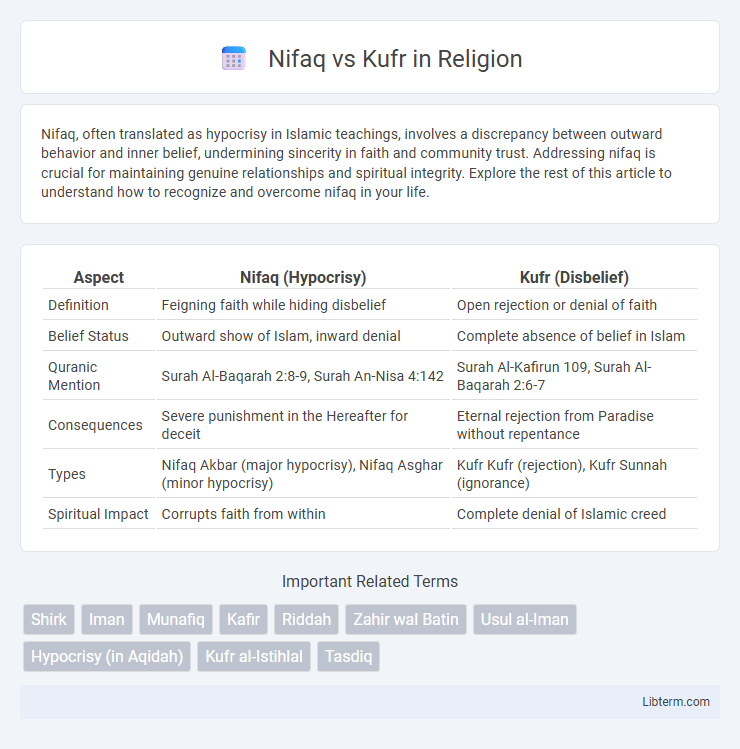
| Aspect | Nifaq (Hypocrisy) | Kufr (Disbelief) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Feigning faith while hiding disbelief | Open rejection or denial of faith |
| Belief Status | Outward show of Islam, inward denial | Complete absence of belief in Islam |
| Quranic Mention | Surah Al-Baqarah 2:8-9, Surah An-Nisa 4:142 | Surah Al-Kafirun 109, Surah Al-Baqarah 2:6-7 |
| Consequences | Severe punishment in the Hereafter for deceit | Eternal rejection from Paradise without repentance |
| Types | Nifaq Akbar (major hypocrisy), Nifaq Asghar (minor hypocrisy) | Kufr Kufr (rejection), Kufr Sunnah (ignorance) |
| Spiritual Impact | Corrupts faith from within | Complete denial of Islamic creed |
Understanding Nifaq and Kufr: Definitions
Nifaq refers to hypocrisy in Islamic theology, characterized by outwardly professing faith while inwardly concealing disbelief or ill intent, posing a significant danger to the integrity of a Muslim's faith. Kufr denotes open disbelief or rejection of Islam's core tenets, which categorizes an individual as a disbeliever, affecting their standing both spiritually and socially in an Islamic context. Understanding the clear distinction between Nifaq (hidden hypocrisy) and Kufr (manifest disbelief) is essential for comprehending accountability and sincerity within Islamic belief systems.
Historical Context of Nifaq and Kufr
Nifaq, or hypocrisy in Islamic terminology, emerged prominently during the early Hijrah period when certain individuals secretly opposed Prophet Muhammad while outwardly professing Islam. Kufr, meaning disbelief or denial of faith, was historically associated with tribes and groups that rejected the message of Islam outright during the Prophet's time. The distinction between nifaq and kufr became critical as the Muslim community sought to identify internal threats from hypocrites who disrupted unity versus external opponents who openly rejected the faith.
Quranic References to Nifaq and Kufr
Nifaq (hypocrisy) and Kufr (disbelief) are distinct concepts emphasized in the Quran, with Nifaq described as outwardly professing faith while concealing disbelief internally (Surah Al-Baqarah 2:8-9) and Kufr representing outright rejection of faith (Surah Al-Kafirun 109:1-6). The Quran specifically warns against the dangers of Nifaq, labeling hypocrites as the worst of created beings due to their deceit and dual behavior (Surah An-Nisa 4:145), while Kufr is depicted as a complete denial of God's message leading to eternal consequence (Surah Al-Baqarah 2:6-7). Both terms underscore spiritual failings, but Nifaq involves pretense within the community, whereas Kufr signifies clear opposition to belief itself.
Characteristics of a Munafiq (Hypocrite)
A Munafiq (hypocrite) is characterized by deceit, outwardly professing faith while secretly harboring disbelief, often intending to mislead the Muslim community. They exhibit duplicity by concealing true beliefs and manipulating trust through false speech and actions. Unlike outright Kufr (disbelief), Nifaq involves insincerity in faith and deliberate hypocrisy that undermines Islamic principles from within.
Types of Kufr in Islamic Theology
In Islamic theology, kufr refers to disbelief or rejection of faith, categorized into various types including Kufr al-'Inad (stubborn denial), Kufr al-Irthad (apostasy), and Kufr al-Kibr (arrogance). Each type of kufr reflects different degrees of rejection of Allah's guidance, ranging from outright denial of God's existence to rejection of specific tenets of Islam. Distinct from nifaq, which denotes hypocrisy, particularly the concealment of faith while outwardly professing Islam, kufr represents a clear and explicit repudiation of faith principles.
Signs and Consequences of Nifaq
Nifaq, or hypocrisy in Islam, is characterized by clear signs such as persistent dishonesty, deliberate concealment of true beliefs, and inconsistency between public behavior and private sentiments. Consequences of nifaq include severe spiritual harm, social distrust, and ultimate repudiation by Allah on the Day of Judgment, where hypocrites face dire punishment distinct from kufr, or outright disbelief. Unlike kufr, which involves outright rejection of faith, nifaq undermines a believer's sincerity and integrity, resulting in a dual loss both in worldly relations and eternal salvation.
Differentiating Nifaq from Kufr
Nifaq (hypocrisy) involves concealing true disbelief while outwardly professing faith, whereas Kufr (disbelief) is an overt rejection of faith or denial of its core tenets. Nifaq can be internal or external, manifesting as deceit in belief or actions, whereas Kufr explicitly denies belief without pretense. Understanding this distinction is crucial in Islamic theology, as nifaq relates to spiritual hypocrisy within believers, while kufr signifies clear apostasy or disbelief.
Impact of Nifaq and Kufr on the Muslim Community
Nifaq (hypocrisy) erodes trust and unity within the Muslim community by fostering deceit and internal discord, weakening collective faith and social cohesion. Kufr (disbelief) challenges the foundational beliefs of Islam, creating ideological divisions that undermine religious identity and communal solidarity. Both nifaq and kufr significantly impact the spiritual health and social fabric of the Muslim ummah, necessitating vigilance and sincere faith to preserve community strength.
Prevention and Remedies for Nifaq and Kufr
Prevention of Nifaq (hypocrisy) involves strengthening sincere faith, regular self-reflection, and adhering strictly to Islamic teachings through consistent prayer, truthfulness, and good character. Remedies include sincere repentance (Tawbah), seeking Allah's guidance, increasing knowledge of faith, and surrounding oneself with righteous company to reinforce genuine belief. Kufr (disbelief) prevention centers on fostering understanding of Tawheed (monotheism) and the Quran's message, while remedies require firm acceptance of Islam through Shahada, continuous learning, and maintaining strong faith practices to remove doubt and disbelief.
Lessons from Prophetic Teachings on Nifaq and Kufr
Prophetic teachings emphasize the clear distinction between nifaq (hypocrisy) and kufr (disbelief), highlighting that nifaq involves outward affirmation of faith while concealing inner denial, which threatens community cohesion and spiritual integrity. Lessons from Hadith reveal that sincere faith requires aligning both inward belief and outward actions, warning against the destructive consequences of hypocrisy on both personal and societal levels. The Prophet Muhammad taught that recognizing and rectifying nifaq strengthens iman, whereas kufr severs the relationship with Allah, underscoring the importance of genuine faith for salvation.
Nifaq Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com