Credo, a powerful declaration of beliefs or values, forms the foundation of personal and organizational identity. Understanding its significance can help You align actions with core principles, fostering authenticity and trust. Discover how embracing your credo enhances decision-making by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
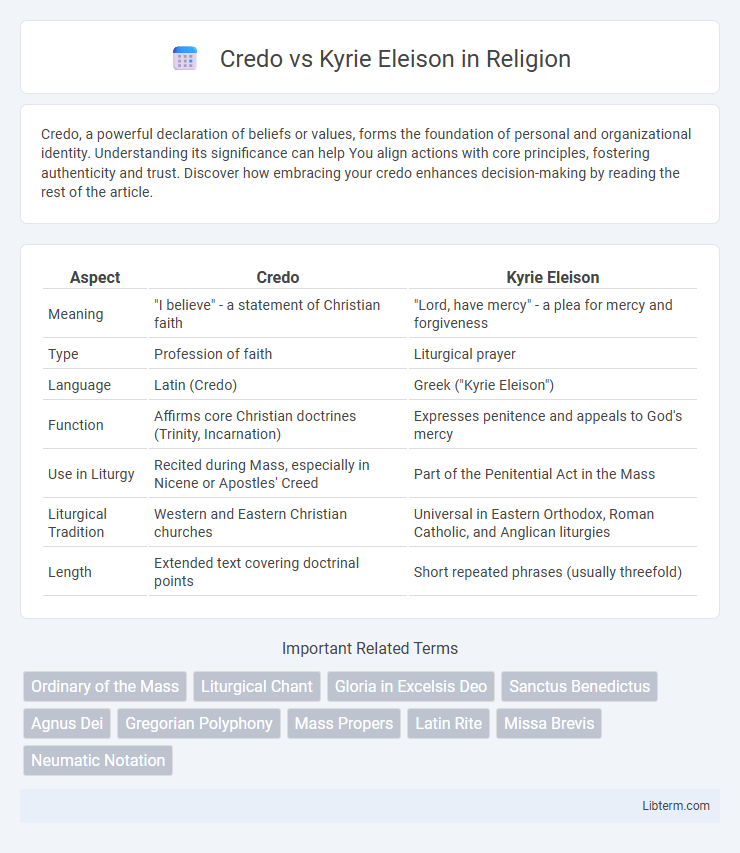
| Aspect | Credo | Kyrie Eleison |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | "I believe" - a statement of Christian faith | "Lord, have mercy" - a plea for mercy and forgiveness |
| Type | Profession of faith | Liturgical prayer |
| Language | Latin (Credo) | Greek ("Kyrie Eleison") |
| Function | Affirms core Christian doctrines (Trinity, Incarnation) | Expresses penitence and appeals to God's mercy |
| Use in Liturgy | Recited during Mass, especially in Nicene or Apostles' Creed | Part of the Penitential Act in the Mass |
| Liturgical Tradition | Western and Eastern Christian churches | Universal in Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and Anglican liturgies |
| Length | Extended text covering doctrinal points | Short repeated phrases (usually threefold) |
Introduction to Credo and Kyrie Eleison
The Credo and Kyrie Eleison are fundamental components of the Christian liturgical tradition, with the Kyrie Eleison serving as a short prayer for mercy, meaning "Lord, have mercy" in Greek, and is typically one of the opening parts of the Mass. The Credo, also known as the Nicene Creed, is a longer profession of faith that outlines the core beliefs of Christianity and is recited during the Mass to affirm the congregation's doctrinal unity. Both parts hold significant theological weight and play key roles in the structure and spiritual focus of Catholic and Orthodox worship services.
Historical Origins of Credo and Kyrie Eleison
The Credo and Kyrie Eleison are integral parts of the Christian Mass with distinct historical origins reflecting early Church development. The Kyrie Eleison, originating in the Greek-speaking Eastern Church, is one of the oldest prayers in Christian liturgy, dating back to the 3rd century, emphasizing a plea for mercy. In contrast, the Credo was formalized following the Council of Nicaea in 325 AD as a profession of faith, encapsulating core Christian doctrines to counter heresies.
Liturgical Roles in Christian Worship
The Credo, or Nicene Creed, serves as a proclamation of faith, affirming core Christian doctrines during the liturgy, particularly within the Mass or Divine Liturgy. Kyrie Eleison, translating to "Lord, have mercy," functions as a penitential prayer, invoking God's mercy and often opening the worship service. Both elements are integral in shaping the spiritual rhythm of Christian worship, with the Credo emphasizing doctrinal unity and the Kyrie fostering humility and supplication.
Structural Differences in Musical Composition
Credo and Kyrie Eleison differ structurally in their musical composition; the Credo is an extended, text-heavy movement with multiple sections reflecting the Nicene Creed's detailed theological statements, requiring varied tempos and dynamic contrasts to emphasize each phrase. Kyrie Eleison, by contrast, features a shorter, repetitive ternary form (ABA) focused on the plea for mercy, often utilizing homophonic textures and a more meditative tempo to evoke solemnity. These structural differences highlight the Credo's narrative complexity versus the Kyrie's meditative simplicity within liturgical music.
Theological Themes in Credo
The Credo emphasizes foundational Christian theological themes such as the nature of the Holy Trinity, the incarnation of Jesus Christ, and the resurrection, highlighting the core doctrines of faith and salvation. It systematically affirms belief in God the Father, Jesus Christ as the Son, and the Holy Spirit, underscoring the unity and distinct persons within the Godhead. The text articulates key elements of Christian dogma including the forgiveness of sins, the resurrection of the body, and eternal life, reflecting its role as a comprehensive statement of faith.
Kyrie Eleison: Meaning and Significance
Kyrie Eleison, meaning "Lord, have mercy" in Greek, is a central prayer in Christian liturgy expressing repentance and supplication for divine mercy. Unlike the Credo, which is a formal statement of faith summarizing core Christian beliefs, Kyrie Eleison emphasizes humility and the acknowledgment of human frailty before God. This plea for mercy has deep roots in early Christian worship and continues to be integral in modern Mass settings across various denominations.
Use in Catholic and Orthodox Traditions
The Credo, or Nicene Creed, is a foundational statement of faith widely recited in Catholic Mass and Eastern Orthodox Divine Liturgy, affirming core Christian doctrines such as the Trinity and the Incarnation. Kyrie Eleison, meaning "Lord, have mercy," is a penitential prayer integral to both traditions, typically chanted or sung during the beginning of the service to invoke God's mercy. In Catholic liturgy, the Credo follows the homily, while the Kyrie is part of the introductory rites; in Orthodox worship, Kyrie Eleison appears frequently throughout the Divine Liturgy, reinforcing themes of repentance and divine grace.
Linguistic Features: Latin vs. Greek
The "Credo" is predominantly written in Latin, featuring classical Latin syntax, morphology, and ecclesiastical vocabulary that reflect the Western Church's tradition. In contrast, "Kyrie Eleison" employs Greek phrases rooted in Byzantine liturgical heritage, using simple, repetitive structures emphasizing plea and supplication. The linguistic contrast between Latin's formal, declensional grammar and Greek's concise, vocative expressions highlights their distinct cultural and theological origins within Christian worship.
Notable Musical Settings Through History
Notable musical settings of the Credo include Johann Sebastian Bach's Mass in B minor and Antonio Vivaldi's Gloria, showcasing rich Baroque counterpoint and expressive choral writing. Kyrie Eleison has been prominently featured in compositions such as Mozart's Requiem and Guillaume de Machaut's Messe de Nostre Dame, highlighting its role as a meditative plea within the liturgical mass. Both texts have inspired a wide range of interpretations from Renaissance polyphony to contemporary sacred music, reflecting their enduring spiritual and musical significance.
Credo vs Kyrie Eleison: Key Contrasts and Similarities
Credo and Kyrie Eleison are central components of the Mass Ordinary, with Credo serving as a profession of faith and Kyrie Eleison as a brief prayer for mercy. The Credo is a lengthy, doctrinal statement outlining Christian beliefs, while Kyrie Eleison consists of repetitive, simple invocations emphasizing penitence. Both elements highlight key aspects of worship, with Credo focusing on faith affirmation and Kyrie Eleison on supplication and humility before God.
Credo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com