Confessionalism is a political system that allocates power and representation among religious or ethnic communities to maintain balance and prevent dominance by any single group. This approach aims to foster coexistence and reduce sectarian conflict by ensuring that key governmental positions are shared according to specific community quotas. Discover how confessionalism shapes governance and influences social dynamics in diverse societies by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
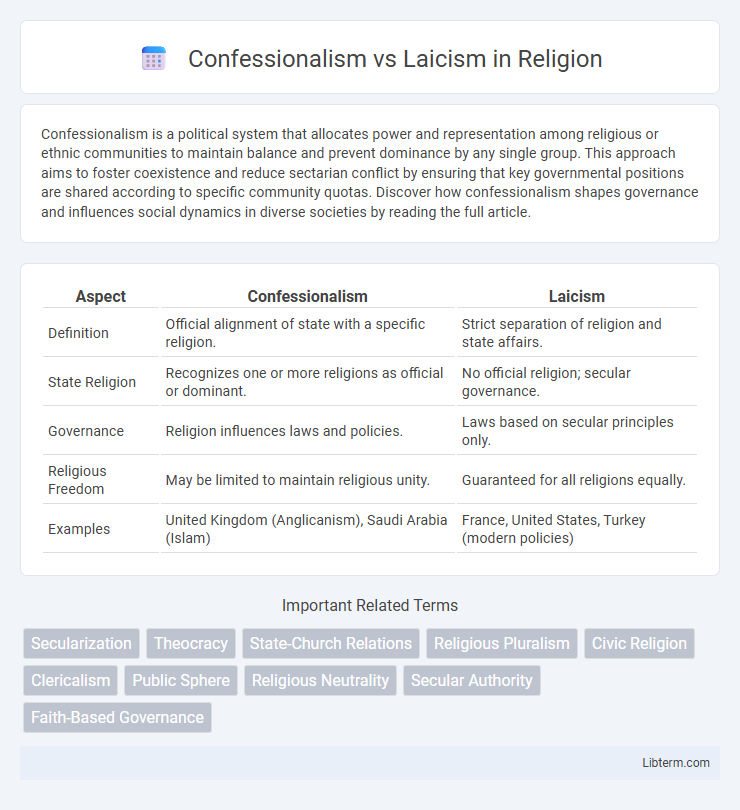
| Aspect | Confessionalism | Laicism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official alignment of state with a specific religion. | Strict separation of religion and state affairs. |
| State Religion | Recognizes one or more religions as official or dominant. | No official religion; secular governance. |
| Governance | Religion influences laws and policies. | Laws based on secular principles only. |
| Religious Freedom | May be limited to maintain religious unity. | Guaranteed for all religions equally. |
| Examples | United Kingdom (Anglicanism), Saudi Arabia (Islam) | France, United States, Turkey (modern policies) |
Understanding Confessionalism: Definition and Origins
Confessionalism is a political and social system where religious groups play a central role in governance, often institutionalizing power-sharing based on distinct confessional communities. Originating in societies marked by deep religious pluralism, such as Lebanon or Switzerland, confessionalism seeks to maintain social harmony by recognizing and balancing the interests of multiple faith-based groups. This system contrasts with laicism, which advocates for the strict separation of religion and state, emphasizing secular governance and equal citizenship without religious considerations.
The Core Principles of Laicism
Laicism centers on the strict separation of religion from state affairs, ensuring that public institutions remain secular and free from religious influence. It upholds the neutrality of the government in religious matters, promoting equal treatment of all citizens regardless of faith. The core principles emphasize the protection of individual freedoms, including freedom of conscience and religion, while preventing religious interference in political decision-making and education.
Historical Evolution of Confessionalism and Laicism
Confessionalism originated in the 19th century primarily in European states as a political system that institutionalized religious affiliations within governmental structures, aiming to balance power among diverse religious communities, especially in deeply divided societies like Lebanon and Belgium. Laicism, emerging from Enlightenment principles in France during the late 18th and early 19th centuries, evolved to advocate for strict separation of religion and state, promoting secularism to ensure neutrality and prevent religious influence in public affairs. The historical evolution of confessionalism reflects attempts to manage religious pluralism through power-sharing agreements, whereas laicism developed as a response to clerical dominance, emphasizing a secular public sphere and uniform citizenship regardless of religious identity.
Impact on Governance and Political Systems
Confessionalism, which integrates religious principles into governance, often leads to political systems where power is distributed based on religious affiliation, affecting legislative processes and minority rights protections. Laicism enforces a strict separation between religion and state, promoting secular policies that aim to ensure equal treatment of all citizens regardless of faith, thereby fostering neutral governance structures. The impact on political systems includes confessionalism's tendency to institutionalize sectarianism, while laicism strives to prevent religious influence in lawmaking and public administration.
Confessional States: Case Studies and Examples
Confessional states, such as Lebanon and Vatican City, institutionalize a specific religion within their political frameworks, often granting official status to a dominant faith and shaping laws accordingly. Lebanon's confessionalism distributes political power among religious communities to maintain sectarian balance, while Vatican City operates as an absolute confessional state under the governance of the Roman Catholic Church. These examples illustrate how confessional states intertwine religious identity with state authority, impacting governance, legal systems, and social cohesion.
Secular Societies: Models of Laicism in Practice
Secular societies implement laicism by separating religious institutions from state affairs, ensuring governance based on neutral, civil principles rather than religious doctrines. Models of laicism in practice vary from strict state secularism, as seen in France's laicite, which prohibits religious symbols in public institutions, to more inclusive secular frameworks like Turkey's constitutional secularism that allows religious expression but limits political influence. These approaches prioritize secular law and public neutrality to promote social cohesion and prevent confessional dominance in political and educational systems.
Religious Freedom vs State Neutrality
Confessionalism entails the explicit recognition and endorsement of a particular religion by the state, which can limit religious freedom by privileging certain faiths over others. Laicism, or secularism, advocates for state neutrality in religious matters, ensuring equal treatment of all religions and non-religious beliefs to protect individual religious freedom. This neutrality fosters an inclusive public sphere where diverse religious identities coexist without state bias or interference.
Social and Cultural Implications of Both Approaches
Confessionalism shapes social structures by aligning political power and cultural identity with specific religious groups, often reinforcing communal affiliations and potentially limiting social integration. Laicism promotes secular governance that separates religion from public institutions, fostering a neutral space for diverse cultural expressions and reducing sectarian conflicts. This secular framework encourages individual freedoms and pluralism but may challenge traditional religious influences on social norms and cultural practices.
Contemporary Challenges: Debates and Conflicts
Contemporary challenges in confessionalism versus laicism manifest through ongoing debates regarding the role of religion in public policy and education, often sparking conflicts over secularism and religious freedoms. Confessionalism emphasizes the recognition and representation of religious identities in governance, while laicism advocates for strict separation of religion and state affairs to ensure neutrality. These opposing views lead to disputes over legal frameworks, minority rights, and the influence of religious institutions in democratic societies.
Future Perspectives: Confessionalism and Laicism in a Changing World
Future perspectives on Confessionalism and Laicism reveal shifting dynamics as global societies increasingly embrace pluralism and secular governance models. Technological advancements and cross-cultural exchanges challenge rigid confessional frameworks while promoting laicism's emphasis on state neutrality and individual rights. Emerging political landscapes indicate a trend toward hybrid approaches that balance religious identity with secular principles to foster social cohesion in diverse populations.
Confessionalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com