Hyperdulia is a term in Catholic theology that denotes the special veneration given uniquely to the Virgin Mary, distinguishing her from the worship reserved for God alone and the veneration offered to other saints. This heightened honor recognizes Mary's exceptional role as the Mother of Jesus and her intercessory power. Discover how understanding hyperdulia can deepen your appreciation of Marian devotion throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
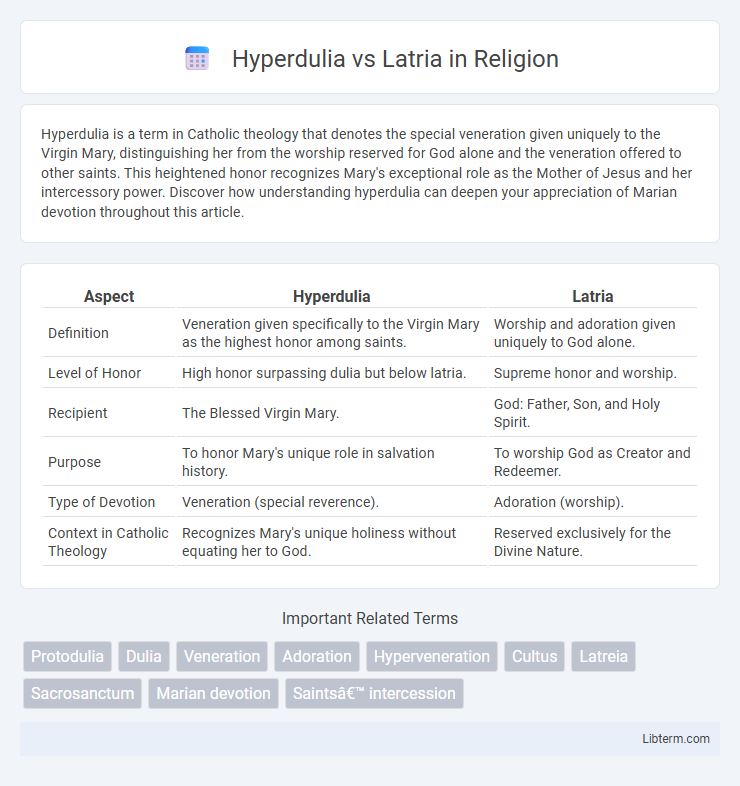
| Aspect | Hyperdulia | Latria |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Veneration given specifically to the Virgin Mary as the highest honor among saints. | Worship and adoration given uniquely to God alone. |
| Level of Honor | High honor surpassing dulia but below latria. | Supreme honor and worship. |
| Recipient | The Blessed Virgin Mary. | God: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. |
| Purpose | To honor Mary's unique role in salvation history. | To worship God as Creator and Redeemer. |
| Type of Devotion | Veneration (special reverence). | Adoration (worship). |
| Context in Catholic Theology | Recognizes Mary's unique holiness without equating her to God. | Reserved exclusively for the Divine Nature. |
Understanding Hyperdulia and Latria: Key Definitions
Hyperdulia is a form of veneration specifically reserved for the Virgin Mary, recognizing her unique role and holiness without equating her to divine worship. Latria represents the highest form of worship due exclusively to God, involving adoration and supreme reverence. Understanding the distinction between Hyperdulia's veneration and Latria's worship is essential for accurately interpreting Catholic devotional practices and theology.
Historical Origins of Hyperdulia and Latria
Hyperdulia and Latria originated within the early Christian theological framework to distinguish levels of reverence given to saints and the divine. Latria, derived from the Greek word "latreia," signifies worship and adoration reserved exclusively for God, while Hyperdulia, a term developed in the medieval period, designates a special veneration accorded uniquely to the Virgin Mary, surpassing that given to other saints but subordinate to Latria. These distinctions emerged to safeguard monotheistic worship practices amidst evolving devotional customs in the history of Catholicism.
Theological Foundations in Catholic Doctrine
Hyperdulia and Latria represent distinct levels of veneration within Catholic doctrine, with Latria reserved exclusively for the worship of the Holy Trinity, emphasizing divine adoration as the highest form of reverence. Hyperdulia pertains specifically to the honor given to the Virgin Mary, acknowledging her unique role and sanctity without equating her to divine status. The theological foundation differentiates adoration from veneration, safeguarding monotheistic worship while honoring saints and Mary in a manner consistent with Church tradition and Scripture.
Scriptural Basis for Veneration and Worship
Hyperdulia refers to the veneration given specifically to the Virgin Mary, distinguished from Latria, the worship reserved for God alone. Scriptural basis for Latria is found in passages like Exodus 20:3-5, emphasizing exclusive worship of Yahweh, while Hyperdulia draws from texts highlighting Mary's unique role, such as Luke 1:28 and Revelation 12:1. The distinction safeguards monotheistic worship by honoring Mary's holiness and intercessory role without attributing divine status, aligning with biblical teachings on worship and veneration.
Hyperdulia: The Unique Honor Given to Mary
Hyperdulia represents a special category of veneration reserved exclusively for the Virgin Mary, distinguishing her from other saints through a higher degree of reverence. Unlike latria, which is adoration appropriate only for God, hyperdulia acknowledges Mary's unique role as the Mother of God and her exceptional holiness. This form of honor emphasizes Mary's intercessory power and singular place within Catholic devotional practice, balancing deep respect without equating her to divine worship.
Latria: Worship Reserved for God Alone
Latria is the highest form of worship in Christian theology, reserved exclusively for God, encompassing adoration and profound reverence toward the Divine Trinity. Unlike hyperdulia, which denotes veneration given to the Virgin Mary as the greatest of saints, latria involves absolute worship acknowledging God's supreme authority and divinity. This sacred worship emphasizes God's unique holiness, omnipotence, and role as the Creator, making latria fundamentally distinct from any form of honor or respect accorded to saints or angels.
Dulia: Veneration of Saints Explained
Dulia refers to the veneration given to saints, recognizing their exemplary holiness and closeness to God without equating it to worship. Unlike Latria, which is the adoration reserved for God alone, dulia expresses honor and reverence through gestures like prayers and feast days. This distinction safeguards the unique divine worship while fostering spiritual support through the intercession of saints.
Misconceptions and Common Confusions
Misconceptions about Hyperdulia and Latria often arise from misunderstanding their distinct theological significance in Catholic worship. Hyperdulia is the veneration reserved specifically for the Virgin Mary, acknowledging her unique role while Latria denotes the worship and adoration due to God alone, addressing the fundamental difference in reverence levels. Common confusions occur when both terms are mistakenly used interchangeably or when Hyperdulia is perceived as a form of worship rather than a special honor, obscuring the nuanced hierarchy of reverence established by Church doctrine.
Hyperdulia vs Latria: Practical Implications in Liturgy
Hyperdulia and Latria represent distinct levels of veneration in Catholic liturgy, with Hyperdulia reserved for honoring the Virgin Mary and Latria exclusively directed to God. Understanding this differentiation shapes practical liturgical practices, as Hyperdulia involves specific Marian feasts, prayers, and devotions that emphasize her unique role without equating her to the divine worship expressed in Latria. This hierarchy ensures clear theological boundaries in worship, maintaining the focus on God's ultimate sovereignty while honoring Mary's elevated intercessory position.
Importance of Distinctions in Catholic Spirituality
Hyperdulia refers to the veneration given specifically to the Virgin Mary, recognizing her unique role and holiness as the Mother of God, whereas Latria denotes the worship and adoration reserved solely for God. Distinguishing between Hyperdulia and Latria is crucial in Catholic spirituality to maintain proper reverence and avoid idolatry by clearly differentiating the honor due to saints from the worship owed to the divine. This clarification safeguards the theological integrity of Catholic worship practices and deepens the faithful's understanding of the hierarchy of divine and saintly honor.
Hyperdulia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com