Mysticism explores the profound connection between the human soul and the divine, revealing hidden truths beyond ordinary perception. This spiritual path emphasizes direct experience and inner transformation, offering insight into the mysteries of existence. Discover how mysticism can deepen your understanding of reality by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
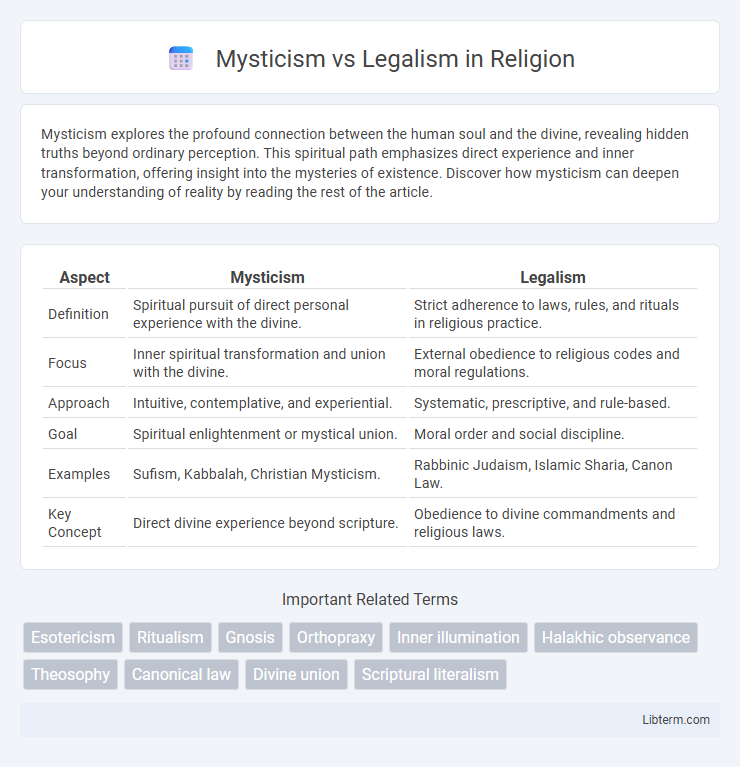
| Aspect | Mysticism | Legalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual pursuit of direct personal experience with the divine. | Strict adherence to laws, rules, and rituals in religious practice. |
| Focus | Inner spiritual transformation and union with the divine. | External obedience to religious codes and moral regulations. |
| Approach | Intuitive, contemplative, and experiential. | Systematic, prescriptive, and rule-based. |
| Goal | Spiritual enlightenment or mystical union. | Moral order and social discipline. |
| Examples | Sufism, Kabbalah, Christian Mysticism. | Rabbinic Judaism, Islamic Sharia, Canon Law. |
| Key Concept | Direct divine experience beyond scripture. | Obedience to divine commandments and religious laws. |
Understanding Mysticism: A Brief Overview
Mysticism emphasizes direct, personal experiences of the divine or ultimate reality beyond intellectual reasoning or ritualistic practices. It prioritizes inner spiritual transformation and insight, often through meditation, contemplation, or ecstatic states, distinguishing itself from legalism's strict adherence to external religious laws and formalities. Mystical traditions appear across various religions, including Sufism in Islam, Kabbalah in Judaism, and Christian mysticism, highlighting universal quests for deeper connection with the sacred.
Defining Legalism: Origins and Principles
Legalism originated in ancient China during the Warring States period, advocating for strict laws and centralized authority to maintain social order. Its principles emphasize clear, codified rules, harsh punishments, and the belief that human nature is inherently selfish and requires control through legal constraints. This philosophy contrasts with mysticism by prioritizing external regulation over spiritual or intuitive understanding.
Historical Roots of Mysticism and Legalism
Mysticism traces its historical roots to ancient spiritual traditions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and early Christian contemplative practices, emphasizing direct personal experience of the divine. Legalism originates from the Warring States period in China, particularly under the influence of Han Feizi, advocating strict adherence to laws and centralized control as essential for social order. The contrasting foundations highlight mysticism's focus on individual inner transformation versus legalism's emphasis on external regulation and political authority.
Core Beliefs: Experiential Faith vs. Rule-Based Living
Mysticism emphasizes experiential faith, prioritizing direct, personal encounters with the divine as the foundation of spiritual truth. Legalism centers on strict adherence to established rules and laws as the primary means to achieve righteousness and maintain order. The core belief in mysticism values inner transformation and spiritual experience, whereas legalism depends on external compliance and ritualistic observance.
Mysticism and the Pursuit of Inner Experience
Mysticism centers on the pursuit of inner experience, emphasizing direct, personal encounters with the divine or ultimate reality beyond external rituals. Practitioners seek transformative states of consciousness through meditation, contemplation, and spiritual insight, which foster profound connections to the transcendent. This inward focus contrasts sharply with legalism's emphasis on adherence to formal codes and external religious laws.
Legalism’s Emphasis on Law, Order, and Tradition
Legalism emphasizes strict adherence to law, order, and tradition as foundational to maintaining societal stability and authority. It prioritizes codified rules and hierarchical governance over personal beliefs or spiritual interpretations. This framework ensures predictable social conduct through rigorous enforcement and institutional control.
Contrasts in Spiritual Practices and Daily Living
Mysticism emphasizes direct, personal experiences of the divine through meditation and inner contemplation, fostering a fluid approach to spirituality that encourages intuition and transcendence. Legalism centers on strict adherence to established laws, rituals, and ethical codes, promoting order and discipline in daily living as the pathway to spiritual fulfillment. These contrasting practices reflect divergent priorities: mysticism values subjective spiritual insight and flexibility, while legalism upholds objective rules and consistent observance in everyday conduct.
The Psychological Impact: Freedom vs. Conformity
Mysticism fosters psychological freedom through personal spiritual experiences and inner exploration, promoting autonomy and emotional well-being. Legalism emphasizes strict adherence to rules, generating psychological conformity that can lead to stress, anxiety, and diminished self-expression. The contrast between these approaches highlights the impact of belief systems on mental health and individual identity formation.
Modern Relevance: Mysticism and Legalism in Contemporary Society
Mysticism emphasizes personal spiritual experiences and inner transformation, offering modern individuals a path to self-discovery and mental well-being amid rapid societal changes. Legalism, rooted in strict adherence to laws and rules, provides structure and social order crucial for governance and community stability in complex contemporary societies. Both frameworks address human needs for meaning and regulation, influencing current debates on individual freedom versus societal control.
Bridging the Divide: Is Reconciliation Possible?
Bridging the divide between mysticism and legalism requires recognizing their complementary roles in spiritual development: mysticism emphasizes personal, experiential union with the divine, while legalism focuses on adherence to established rules and ethical conduct. Successful reconciliation involves fostering a balanced approach that values inner transformation without discarding external discipline, enabling a holistic practice that nurtures faith through both experience and structure. Integrating these perspectives cultivates a dynamic spirituality where mystical insight deepens moral commitment, and legal frameworks provide a foundation for sustainable spiritual growth.
Mysticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com