Theology explores the nature of the divine, religious beliefs, and the relationship between humanity and higher powers through critical study and interpretation of sacred texts. It provides insights into ethical frameworks, spiritual practices, and the cultural impact of faith traditions. Dive deeper into this article to enrich your understanding of theology's profound influence on faith and life.
Table of Comparison
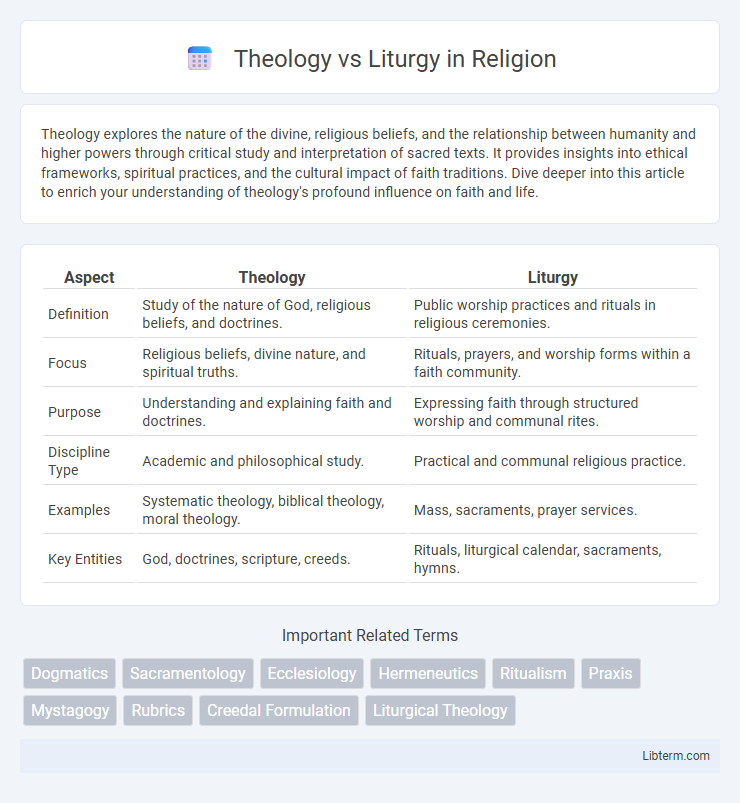
| Aspect | Theology | Liturgy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of the nature of God, religious beliefs, and doctrines. | Public worship practices and rituals in religious ceremonies. |
| Focus | Religious beliefs, divine nature, and spiritual truths. | Rituals, prayers, and worship forms within a faith community. |
| Purpose | Understanding and explaining faith and doctrines. | Expressing faith through structured worship and communal rites. |
| Discipline Type | Academic and philosophical study. | Practical and communal religious practice. |
| Examples | Systematic theology, biblical theology, moral theology. | Mass, sacraments, prayer services. |
| Key Entities | God, doctrines, scripture, creeds. | Rituals, liturgical calendar, sacraments, hymns. |
Understanding Theology: Foundations and Principles
Theology explores the study of divine nature, religious beliefs, and the foundational principles that shape faith systems, providing a critical framework for interpreting sacred texts and spiritual experiences. It delves into core concepts such as the existence of God, the nature of salvation, and ethical teachings, forming the intellectual basis for religious doctrine. Understanding theology requires analyzing historical context, philosophical arguments, and scriptural exegesis to grasp how these elements influence religious thought and practice.
Defining Liturgy: Rituals and Practices
Liturgy encompasses the structured rituals and practices used in public worship, shaping how theological beliefs are expressed and experienced within a faith community. These rituals include prayers, readings, sacraments, and ceremonies that collectively embody doctrinal teachings through symbolic actions. By defining worship patterns, liturgy serves as a tangible manifestation of theology, bridging abstract beliefs with communal religious expression.
Historical Evolution of Theology and Liturgy
The historical evolution of theology traces its origins to early philosophical inquiries and scriptural interpretations, progressively formalized through ecumenical councils and scholasticism. Liturgy developed concurrently as the structured practice of worship, reflecting theological doctrines in ritual forms shaped by cultural and ecclesiastical contexts. Both fields have influenced each other, with theological developments informing liturgical reforms and liturgical practices reinforcing doctrinal teachings throughout church history.
Major Differences Between Theology and Liturgy
Theology centers on the study and interpretation of religious beliefs, doctrines, and the nature of the divine, emphasizing intellectual understanding and systematic reflection. Liturgy involves the prescribed forms of public worship, including rituals, ceremonies, and prayers that express and enact theological principles in communal settings. Major differences lie in theology's abstract, theoretical focus versus liturgy's practical, ritualistic practice that facilitates spiritual experience and communal participation.
The Role of Theology in Shaping Belief
Theology critically shapes belief by providing a systematic framework that explores the nature of the divine, moral principles, and sacred texts, influencing individual and communal understanding of faith. It interprets religious doctrines, guiding adherents in forming coherent worldviews and ethical behaviors rooted in spiritual truths. This intellectual foundation informs liturgical practices, ensuring that rituals authentically express and reinforce core theological convictions.
Liturgy as Expression of Communal Faith
Liturgy serves as the embodied expression of communal faith, transforming theological beliefs into shared rituals that foster spiritual unity and collective worship. It functions as a living dialogue between doctrine and practice, shaping religious identity through symbolic actions and sacred texts. This communal participation reinforces the transmission of faith traditions across generations, anchoring theological concepts in tangible, experiential forms.
Interplay Between Doctrine and Worship
Theology shapes the doctrinal framework that informs liturgical practices, ensuring worship reflects core beliefs about God, salvation, and the Church. Liturgy, as the embodied expression of theology, enacts and reinforces these doctrines through ritual, symbol, and communal participation. This dynamic interplay deepens faith understanding and cultivates spiritual formation within religious communities.
Controversies: When Theology and Liturgy Clash
Conflicts arise when theology's doctrinal interpretations challenge liturgical practices, sparking debates over orthodoxy and ritual authenticity. Disputes often center on the balance between preserving traditional liturgical forms and adapting worship to contemporary theological insights. These controversies highlight tensions between institutional authority and evolving spiritual expression within religious communities.
Contemporary Perspectives on Theology vs Liturgy
Contemporary perspectives on theology versus liturgy emphasize the dynamic interplay between doctrinal beliefs and worship practices, highlighting how theology informs liturgical expression while liturgy simultaneously shapes theological understanding. Modern theologians explore this relationship through contextual and cultural lenses, integrating diverse traditions and addressing contemporary spiritual needs. This approach fosters a holistic view where theology and liturgy co-construct communal identity and religious experience in today's faith communities.
Integrating Theology and Liturgy for Holistic Faith
Integrating theology and liturgy fosters a holistic faith experience by aligning doctrinal beliefs with worship practices, deepening spiritual understanding and communal participation. Theology provides the foundational truths and doctrinal framework that guide the meaning behind liturgical actions and rituals, while liturgy actualizes these beliefs in tangible, embodied worship experiences. This synergy enhances both personal devotion and corporate worship, promoting a faith that is intellectually grounded and experientially rich.
Theology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com