Mujtahid refers to an Islamic scholar who is qualified to interpret Sharia law through ijtihad, or independent reasoning. This role requires deep knowledge of the Quran, Hadith, and Fiqh, enabling them to provide guidance on complex religious issues. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Mujtahid influences Islamic jurisprudence and your spiritual journey.
Table of Comparison
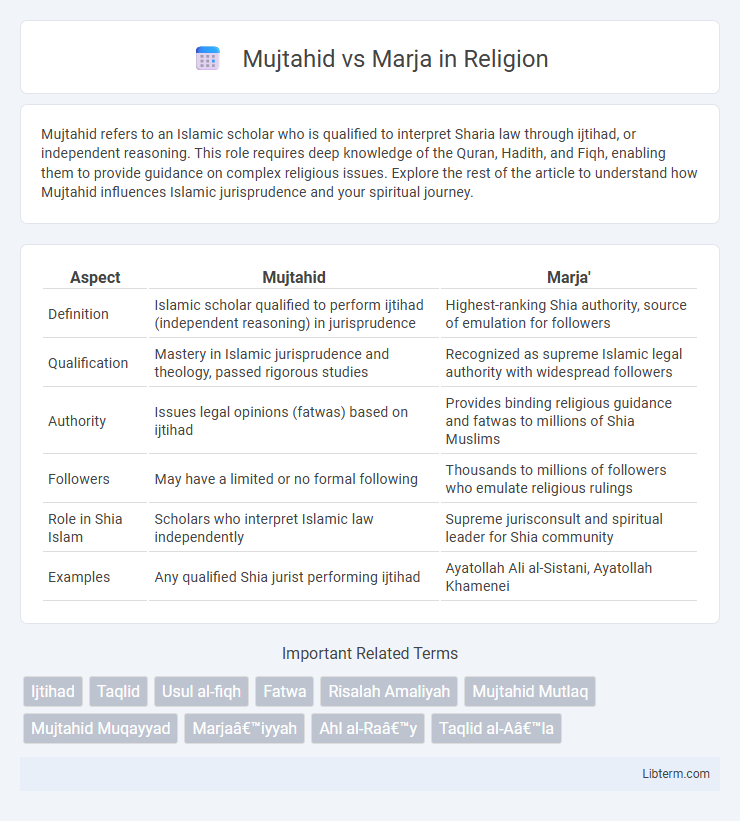
| Aspect | Mujtahid | Marja' |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic scholar qualified to perform ijtihad (independent reasoning) in jurisprudence | Highest-ranking Shia authority, source of emulation for followers |
| Qualification | Mastery in Islamic jurisprudence and theology, passed rigorous studies | Recognized as supreme Islamic legal authority with widespread followers |
| Authority | Issues legal opinions (fatwas) based on ijtihad | Provides binding religious guidance and fatwas to millions of Shia Muslims |
| Followers | May have a limited or no formal following | Thousands to millions of followers who emulate religious rulings |
| Role in Shia Islam | Scholars who interpret Islamic law independently | Supreme jurisconsult and spiritual leader for Shia community |
| Examples | Any qualified Shia jurist performing ijtihad | Ayatollah Ali al-Sistani, Ayatollah Khamenei |
Definition of Mujtahid
A Mujtahid is an Islamic scholar qualified to perform Ijtihad, the process of independent reasoning to interpret Sharia law based on the Quran and Hadith. This role requires extensive knowledge of Islamic jurisprudence, linguistics, and principles of jurisprudence (Usul al-Fiqh). Unlike a Marja, who serves as a high-ranking authority providing legal rulings and guidance for followers, a Mujtahid may not necessarily hold widespread religious authority or be recognized as a source of emulation.
Definition of Marja
A Marja is a supreme religious authority in Twelver Shia Islam, recognized for their deep knowledge of Islamic jurisprudence and ability to provide legal rulings and guidance to followers. Unlike a Mujtahid, who is a qualified jurist capable of independent reasoning (Ijtihad) in Islamic law, the Marja holds the highest rank and serves as a source of emulation (Taqlid) for Shia Muslims worldwide. The authority of a Marja includes issuing fatwas, interpreting Shariah, and guiding the community on religious, social, and legal matters.
Historical Development of Ijtihad and Marja’iyya
The historical development of Ijtihad and Marja'iyya traces back to early Islamic jurisprudence, where Mujtahids emerged as scholars qualified to perform independent reasoning in fiqh to address new issues. Over centuries, the role of Marja' evolved as supreme religious authorities recognized for their comprehensive knowledge and legal verdicts guiding Shia communities in compliance and religious practice. This institutionalization of Marja'iyya solidified during the Safavid dynasty, marking a distinctive phase in Shia clerical authority and Ijtihad's practical application.
Criteria to Become a Mujtahid
Becoming a Mujtahid requires extensive knowledge of Islamic jurisprudence, proficiency in Arabic, and the ability to perform ijtihad, or independent reasoning, based on the Quran, Hadith, consensus (ijma), and reasoning (qiyas). A Mujtahid must master principles of fiqh, usul al-fiqh, and demonstrate deep understanding of legal proofs to derive rulings accurately. Unlike a Marja, who is a senior Mujtahid providing guidance to followers, the primary criterion for becoming a Mujtahid lies in scholarly competence and recognized authority in Islamic legal interpretation.
Qualifications Required for Marja
A Marja, or Marja' Taqlid, must possess advanced expertise in Islamic jurisprudence, demonstrated through years of rigorous study in Usul al-Fiqh (principles of Islamic law) and Fiqh (jurisprudence). Unlike a Mujtahid, who is qualified to perform independent reasoning (Ijtihad) in legal matters, a Marja holds the highest religious authority, issuing binding legal opinions (fatwas) that followers must adhere to. Recognition by peers, publication of scholarly works, and ethical integrity are critical qualifications for attaining the status of Marja within Shia Islam.
Roles and Responsibilities of Mujtahid
A Mujtahid holds the crucial role of interpreting and deriving Islamic law through independent reasoning (ijtihad) based on primary sources like the Quran and Sunnah, serving as a jurist who addresses new legal questions. This position demands deep scholarly expertise in jurisprudence, principles of Islamic law (Usul al-fiqh), and the ability to adapt rulings to contemporary issues while maintaining doctrinal authenticity. Unlike a Marja, who functions as a source of emulation with authority to issue binding religious rulings and followers, the Mujtahid primarily provides scholarly interpretations and legal reasoning that can inform or influence Maraji' (plural of Marja) and the broader Muslim community.
Authority and Influence of Marja
A Marja holds the highest religious authority in Shia Islam, recognized for their extensive knowledge and ability to issue binding legal rulings (fatwas) on Islamic law, whereas a Mujtahid is qualified to interpret the Quran and Hadith but may not have the widespread recognition or follower base to assert such influence. The Marja's influence extends beyond jurisprudence, shaping social, political, and cultural aspects of Shia communities worldwide due to their authoritative religious guidance. Their decrees are followed by millions of adherents who seek practical and spiritual leadership, underscoring the Marja's unparalleled status as the ultimate source of emulation (Taqlid).
Key Differences Between Mujtahid and Marja
A Mujtahid is an Islamic scholar qualified to perform ijtihad, meaning they can independently interpret Sharia law through deep understanding of Quran, Hadith, and Islamic jurisprudence. A Marja, or Marja' Taqlid, holds a higher status as a Grand Ayatollah whose legal opinions and religious rulings are followed by ordinary Shia Muslims who engage in Taqlid (emulation). The key difference lies in authority and followers: while all Maraji are Mujtahids, not all Mujtahids achieve the recognition and large following required to be a Marja.
Impact on Shia Islamic Jurisprudence
Mujtahid and Marja play pivotal roles in shaping Shia Islamic jurisprudence by interpreting and implementing Islamic law through ijtihad, with Marja holding higher authority as a source of emulation for followers. The Marja's rulings directly influence religious practices, legal decisions, and community norms within Shia communities worldwide. This hierarchical structure ensures dynamic jurisprudential development while maintaining doctrinal consistency and adaptability to contemporary issues.
Choosing a Marja: Guidance for Followers
Choosing a Marja involves evaluating their religious expertise, piety, and recognition among Shia scholars to ensure credible spiritual guidance. Followers prioritize Marjas with strong jurisprudential knowledge, adherence to Quranic principles, and consistent issuance of fatwas aligning with contemporary issues. Trust in a Marja's moral integrity and scholarly reputation plays a crucial role in establishing reliable religious leadership.
Mujtahid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com