Survival skills encompass essential techniques and knowledge that enable individuals to endure challenging environments and unforeseen situations. Mastering these skills ensures you can secure food, water, shelter, and safety in both wilderness and urban scenarios. Explore the rest of this article to discover key survival strategies that could make all the difference in an emergency.
Table of Comparison
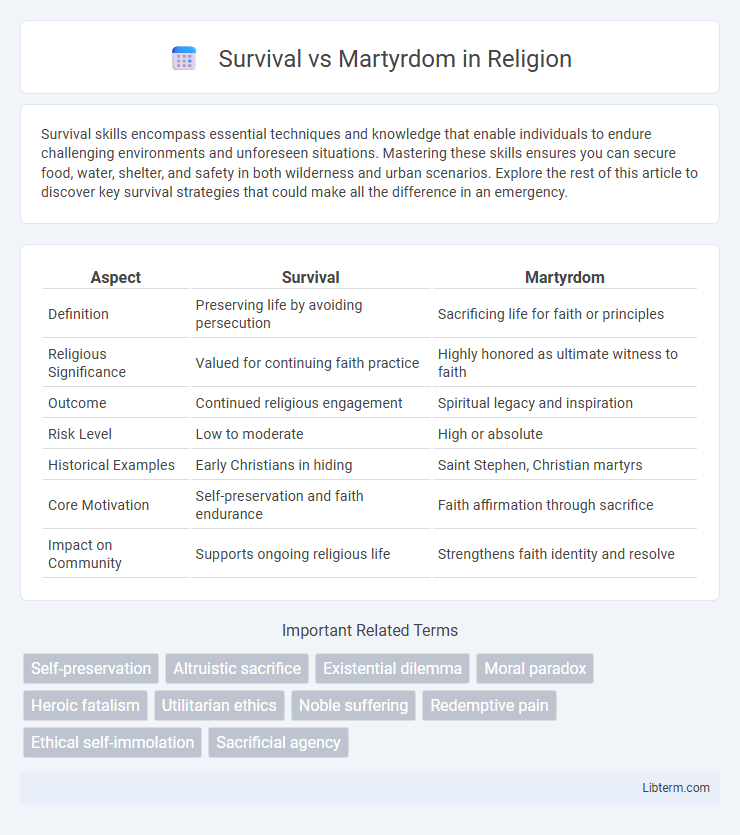
| Aspect | Survival | Martyrdom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preserving life by avoiding persecution | Sacrificing life for faith or principles |
| Religious Significance | Valued for continuing faith practice | Highly honored as ultimate witness to faith |
| Outcome | Continued religious engagement | Spiritual legacy and inspiration |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate | High or absolute |
| Historical Examples | Early Christians in hiding | Saint Stephen, Christian martyrs |
| Core Motivation | Self-preservation and faith endurance | Faith affirmation through sacrifice |
| Impact on Community | Supports ongoing religious life | Strengthens faith identity and resolve |
Defining Survival and Martyrdom
Survival refers to the act of enduring life-threatening situations by preserving one's existence through adaptive strategies and resilience. Martyrdom involves willingly sacrificing one's life or well-being for a cause or belief, often elevating moral or ideological commitment above personal survival. Both concepts represent distinct responses to extreme adversity, highlighting contrasting values of preservation versus principled sacrifice.
Historical Perspectives on Survival
Historical perspectives on survival reveal that communities often adapted cultural practices and social structures to endure existential threats, emphasizing resilience over sacrifice. In contrast to martyrdom, which valorizes death for a cause, survival strategies prioritized pragmatic decision-making, resource management, and alliances to secure continuity. Ancient civilizations such as the Romans and indigenous societies illustrate how survival underscored long-term persistence amid warfare, famine, and colonization.
The Legacy of Martyrs in Society
The legacy of martyrs in society often serves as a powerful symbol of sacrifice and unwavering commitment to a cause, inspiring collective memory and social movements across generations. Martyrs' stories reinforce cultural values and contribute to a shared identity, often catalyzing political or religious change. Their enduring influence shapes national narratives and motivates perseverance in the face of adversity.
Psychological Motivations Behind Survival
Psychological motivations behind survival often stem from a fundamental human drive to preserve life, influenced by innate fear responses and the need for self-preservation. Cognitive processes, such as hope, resilience, and the search for meaning, play critical roles in sustaining individuals through threatening situations. Neurobiological factors, like the activation of the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, regulate adaptive responses that enhance survival chances in life-threatening circumstances.
The Role of Belief in Embracing Martyrdom
Belief systems deeply influence the choice between survival and martyrdom, framing martyrdom as a transcendental act that affirms faith or ideology. Psychological studies reveal that strong spiritual conviction can reduce the fear of death and enhance the willingness to embrace martyrdom for a perceived greater cause. Historical and sociological data demonstrate that martyrdom often solidifies group identity and inspires collective resilience within communities bound by shared beliefs.
Societal Impact: Survivors vs. Martyrs
Survivors often catalyze societal resilience by embodying hope and facilitating recovery, enabling communities to rebuild and adapt after trauma. Martyrs, through their sacrifice, inspire collective identity and mobilize social movements, often accelerating change by highlighting injustice or oppression. The societal impact of survivors centers on continuity and healing, while martyrs drive symbolic transformation and galvanize activism.
Ethical Dilemmas: Choosing Life or Sacrifice
Survival and martyrdom present profound ethical dilemmas where the value of preserving life clashes with the moral weight of sacrifice for a greater cause. Decisions hinge on contextual factors such as the potential impact on community welfare, individual rights, and long-term consequences. Philosophical frameworks like utilitarianism and deontological ethics provide contrasting perspectives on whether survival or self-sacrifice holds greater ethical justification.
Cultural Narratives Shaping Survival and Martyrdom
Cultural narratives profoundly shape the concepts of survival and martyrdom by defining the values and meanings attributed to each within societies. Survival is often framed through stories emphasizing resilience, adaptability, and the preservation of life as a paramount goal, while martyrdom is portrayed as a self-sacrificial act imbued with honor, spiritual transcendence, or political significance. These narratives influence individual and collective behavior by reinforcing cultural identities and guiding responses to conflict, persecution, and existential threats.
Case Studies: Survival at the Cost of Values
Case studies of survival at the cost of values reveal individuals who compromised their ethical beliefs under extreme conditions, highlighting complex human responses to life-threatening situations. Historical examples such as prisoners of war or survivors of totalitarian regimes illustrate how survival instincts can override moral convictions, leading to actions that may be viewed as betrayal or collaboration. These cases underscore the psychological and sociological dynamics where preserving life sometimes necessitates difficult choices that conflict with deeply held principles.
Modern Interpretations and Relevance Today
Modern interpretations of survival versus martyrdom emphasize the complex ethical decisions faced in contemporary conflicts, where preserving life often intersects with standing for deeply held values. Psychologists and sociologists analyze how survival strategies can embody resilience without sacrificing moral integrity, while martyrdom is redefined beyond death to include acts of peaceful resistance and symbolic sacrifice. This nuanced understanding influences current debates on human rights, activism, and the psychological impact of trauma in war-torn societies.
Survival Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com