Ijma, the consensus of Islamic scholars, serves as a fundamental source of Islamic law alongside the Quran and Sunnah. Its role in unifying diverse interpretations provides authoritative guidance on new issues not explicitly addressed in foundational texts. Discover how Ijma shapes Islamic jurisprudence and influences contemporary legal decisions in this article.
Table of Comparison
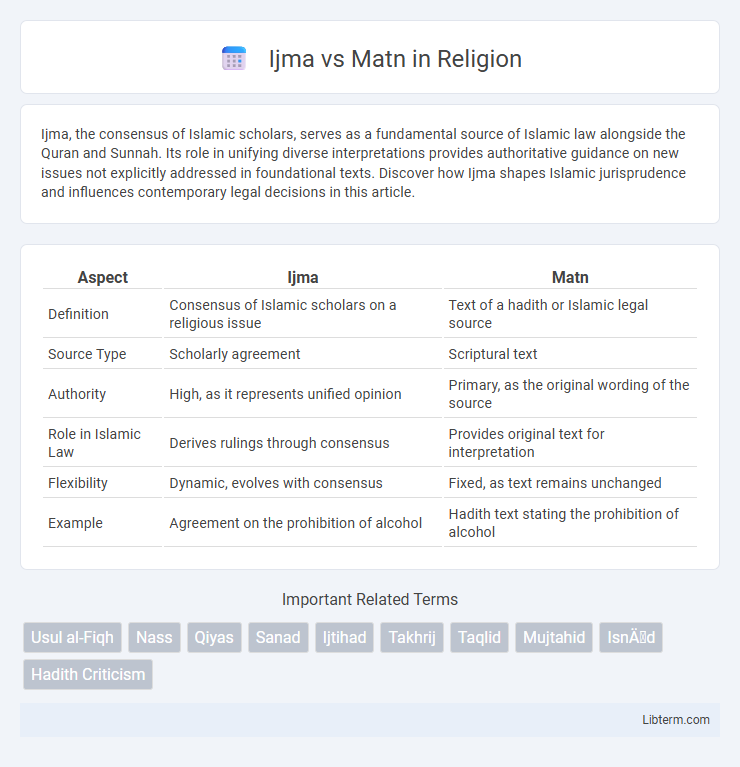
| Aspect | Ijma | Matn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consensus of Islamic scholars on a religious issue | Text of a hadith or Islamic legal source |
| Source Type | Scholarly agreement | Scriptural text |
| Authority | High, as it represents unified opinion | Primary, as the original wording of the source |
| Role in Islamic Law | Derives rulings through consensus | Provides original text for interpretation |
| Flexibility | Dynamic, evolves with consensus | Fixed, as text remains unchanged |
| Example | Agreement on the prohibition of alcohol | Hadith text stating the prohibition of alcohol |
Introduction to Ijma and Matn
Ijma refers to the consensus of Islamic scholars on a particular legal or theological issue, serving as a key source of Islamic jurisprudence after the Quran and Sunnah. Matn denotes the actual text or content of a hadith, which provides direct insights into the sayings and actions of Prophet Muhammad. Understanding the distinction between Ijma and Matn is essential for interpreting Islamic law, where Ijma validates collective scholarly agreement and Matn offers the foundational textual evidence.
Defining Ijma: Concept and Origins
Ijma, a foundational concept in Islamic jurisprudence, refers to the unanimous consensus of Islamic scholars on a legal or theological issue. Originating from the Quran and Hadith, Ijma serves as a secondary source of Sharia law when primary texts yield ambiguous rulings. This consensus mechanism reinforces the community's collective interpretation and application of divine guidance, distinguishing it from Matn, which denotes the actual text or content of prophetic traditions (Hadith).
Understanding Matn: Meaning and Role
Matn refers to the core text or main content of an Islamic legal source, typically the exact wording of a hadith or Quranic verse, which serves as the foundation for interpretation and jurisprudence. Understanding Matn involves analyzing its language, context, and meaning to ensure accurate derivation of rulings, distinguishing it from external commentary or consensus such as Ijma. The precise examination of Matn is crucial for verifying authenticity and applicability in Islamic legal principles.
Historical Development of Ijma
Ijma, the consensus of Islamic scholars, historically developed as a critical source of Islamic jurisprudence alongside the Qur'an and Sunnah, solidifying its authority through early scholarly agreements and community practices. This collective agreement served as a dynamic mechanism to address legal and theological issues, especially when clear guidance from the primary texts was absent. The evolution of Ijma emphasized its role in validating the authenticity and applicability of Matn, the textual content of hadiths, ensuring consistency and orthodoxy in Islamic law and doctrine.
Evolution and Significance of Matn
Matn, the core textual content of Hadith literature, evolved as a critical element for preserving prophetic traditions with accuracy and clarity, establishing a direct foundation for Islamic jurisprudence. Its precise wording and structure hold substantial significance in ensuring the authenticity and interpretative consistency across various Islamic legal schools. Unlike Ijma, which represents consensus and plays a collective role in shaping legal rulings, Matn serves as the primary source material whose textual integrity directly influences legal and theological discourse.
Key Differences between Ijma and Matn
Ijma refers to the unanimous consensus of Islamic scholars on a particular legal ruling, serving as a secondary source of Sharia after the Quran and Sunnah, while Matn is the actual text or content of a hadith, detailing the Prophet Muhammad's sayings or actions. The key difference lies in their nature: Ijma is a process and collective agreement, whereas Matn is a specific textual component essential for verifying hadith authenticity. Understanding Ijma emphasizes scholarly consensus in Islamic jurisprudence, whereas Matn analysis focuses on the reliability and meaning of hadith texts.
Role of Ijma in Islamic Jurisprudence
Ijma, the consensus of Islamic scholars, holds a pivotal role in shaping Islamic jurisprudence by providing authoritative interpretations when the Quran and Hadith offer ambiguity or lack explicit directives. Unlike Matn, which refers to the textual content of the Hadith, Ijma functions as a dynamic and collective mechanism to address new legal issues, ensuring adaptability and unity within Sharia law. This jurisprudential tool reinforces communal agreement, preserving doctrinal consistency and guiding legislative decisions across diverse Islamic communities.
Importance of Matn in Hadith Studies
Matn, the core text of a Hadith, is vital in Hadith studies as it conveys the actual sayings or actions of the Prophet Muhammad, providing the primary source for Islamic jurisprudence and theology. While Ijma represents scholarly consensus, Matn analysis ensures authenticity and context, allowing scholars to verify and interpret the Hadith accurately. Careful examination of Matn helps distinguish true prophetic guidance from fabricated or weak narrations, maintaining the integrity of Islamic teachings.
Contemporary Debates on Ijma and Matn
Contemporary debates on Ijma (consensus) and Matn (text) focus on the dynamic interpretation of Islamic law, highlighting tensions between traditional authority and modern contextual realities. Scholars argue over the scope of Ijma, questioning whether it must be unanimous or can reflect a qualified majority, while the Matn's literal versus thematic readings influence legal adaptability. This discourse impacts fiqh development, balancing textual fidelity with evolving societal needs in jurisprudential consensus.
Conclusion: Impact on Islamic Scholarship
Ijma, as the consensus of Islamic scholars, and Matn, the textual content of hadith, both critically shape Islamic jurisprudence by providing foundational sources for interpreting Sharia law. The integration of Ijma ensures communal validation and unity in legal rulings, while Matn analysis maintains the authenticity and reliability of prophetic traditions. Together, they have cemented a balanced framework that upholds doctrinal consistency and dynamic jurisprudential development in Islamic scholarship.
Ijma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com