Patrilineal descent traces lineage through the male line, connecting individuals to their paternal ancestors and inheritance. This system influences family structures, cultural identity, and property rights in many societies around the world. Explore the rest of the article to understand how patrilineal descent shapes social dynamics and your heritage.
Table of Comparison
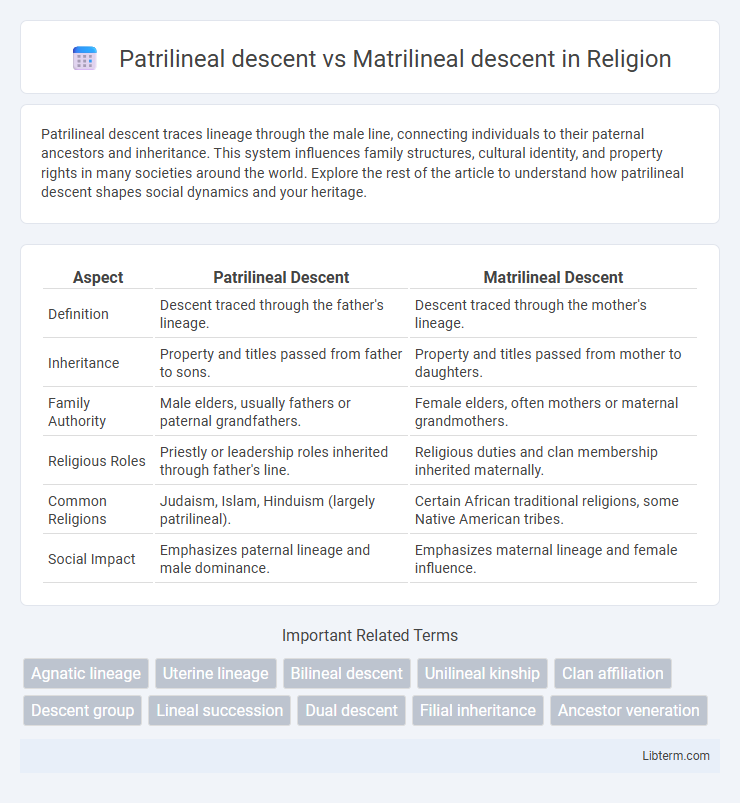
| Aspect | Patrilineal Descent | Matrilineal Descent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through the father's lineage. | Descent traced through the mother's lineage. |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed from father to sons. | Property and titles passed from mother to daughters. |
| Family Authority | Male elders, usually fathers or paternal grandfathers. | Female elders, often mothers or maternal grandmothers. |
| Religious Roles | Priestly or leadership roles inherited through father's line. | Religious duties and clan membership inherited maternally. |
| Common Religions | Judaism, Islam, Hinduism (largely patrilineal). | Certain African traditional religions, some Native American tribes. |
| Social Impact | Emphasizes paternal lineage and male dominance. | Emphasizes maternal lineage and female influence. |
Introduction to Lineal Descent Systems
Patrilineal descent traces lineage through the father's side, emphasizing inheritance, family name, and social status passed from father to offspring, which is prevalent in many societies worldwide. Matrilineal descent, by contrast, follows the mother's line, often granting inheritance and clan membership through maternal relatives, influencing kinship and social organization differently. Lineal descent systems shape cultural identity, property rights, and familial roles by defining how ancestry and heritage are socially recognized within communities.
Defining Patrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent is a kinship system where lineage, inheritance, and family ties are traced through the male line, primarily from father to son. This form of descent shapes social organization, property rights, and cultural identity in many societies, emphasizing paternal ancestry. Compared to matrilineal descent, which follows the mother's lineage, patrilineal descent places greater importance on male relatives for succession and clan membership.
Defining Matrilineal Descent
Matrilineal descent traces lineage, inheritance, and family ties through the mother's line, emphasizing maternal ancestry in social, legal, and cultural contexts. This system contrasts with patrilineal descent, which prioritizes the father's lineage for determining heritage and succession. In matrilineal societies, property, clan membership, and social status are commonly passed down from mothers to their offspring, reinforcing the central role of women in kinship structures.
Historical Origins of Patrilineal and Matrilineal Descent
Patrilineal descent, historically rooted in agricultural and pastoral societies of the ancient Near East, emphasizes lineage traced through the male line to secure property and inheritance rights. Matrilineal descent, prominent among indigenous communities in Africa, Oceania, and parts of Asia, traces descent through the female line, often linked to social organization and kinship roles revolving around maternal ancestry. Archaeological and ethnographic studies reveal that these systems evolved to address distinct socio-economic needs and cultural practices in early human settlements.
Social Structure and Family Roles
Patrilineal descent traces lineage through the father's line, often assigning inheritance and family name to male descendants, reinforcing male authority in social structure and family roles. Matrilineal descent follows the mother's lineage, emphasizing maternal relatives for inheritance and social ties, which can elevate the status and influence of women within the family and community. These systems fundamentally shape kinship, resource distribution, and leadership roles, influencing societal organization and gender dynamics.
Inheritance Patterns and Property Rights
Patrilineal descent assigns inheritance and property rights through the male lineage, often granting sons primary ownership and control over family assets. Matrilineal descent transfers inheritance along the female line, where daughters or maternal relatives typically receive property and authority, ensuring wealth remains within the maternal family group. These contrasting systems influence social organization, with patrilineal societies emphasizing paternal ancestry for succession, while matrilineal societies prioritize maternal kinship ties for distributing property and legal rights.
Influence on Gender Roles and Authority
Patrilineal descent systems assign inheritance and family lineage through the male line, often reinforcing male authority and traditional gender roles where men hold leadership and decision-making power. Matrilineal descent traces lineage through the female line, frequently empowering women with significant social and economic influence, shaping gender roles that emphasize maternal authority and community cohesion. These contrasting descent systems fundamentally impact the distribution of power and gender dynamics within societies.
Cultural Examples Worldwide
Patrilineal descent, common in many societies such as the Maasai of East Africa and traditional Chinese families, emphasizes lineage and inheritance through the male line, influencing social structure and property rights. Matrilineal descent, found among the Akan of Ghana and the Navajo of North America, traces ancestry and inheritance through the female line, often granting women significant authority in kinship and clan affairs. These systems shape cultural identity, familial roles, and inheritance patterns, reflecting diverse social values and historical contexts globally.
Modern Trends and Changes in Lineal Descent
Modern trends in lineal descent reveal a shift towards more inclusive family structures, reducing the strict adherence to traditional patrilineal or matrilineal systems. Technological advancements such as DNA testing and changes in legal frameworks increasingly recognize diverse forms of inheritance and kinship beyond gender lines. Urbanization and globalization contribute to blended descent practices, reflecting evolving social norms and values in lineage determination.
Comparative Analysis: Patrilineal vs Matrilineal Systems
Patrilineal descent traces lineage through the male line, emphasizing inheritance and family name continuity via fathers, whereas matrilineal descent follows the female line, focusing on maternal relatives for inheritance and social identity. Patrilineal societies often prioritize male authority and lineage, while matrilineal systems elevate women's roles in kinship and property rights. These contrasting structures significantly influence social organization, inheritance laws, and gender roles across cultures globally.
Patrilineal descent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com